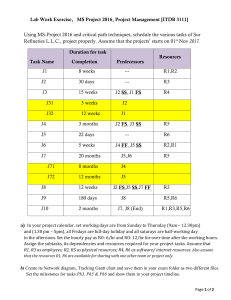
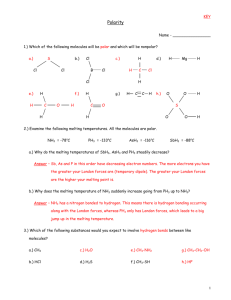
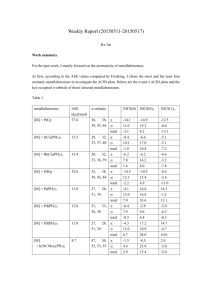
a.Calculate the molality of a 20.0% by mass aqueous solution of NH
advertisement

a.Calculate the molality of a 20.0% by mass aqueous solution of NH4Cl. (4.67m) b. Calculate the freezing point of this solution. (Kf=1.86⁰C/m) (-17.37⁰C/m) c. Calculate the vapor pressure of this solution at 29.0⁰C(vapor pressure of water at 29.0⁰C is 29.8torr) (25.5Torr) d. If the density of the solution is 1.10g/mL, determine the osmotic pressure of the solution. (203.8atm) Place in order of decreasing solubility in ammonia: CH2Cl2, CH4, H2O H2O---CH2Cl2---CH4 Which solvent(water or hexane) would you choose to dissolve: a. Ethanol water b. CCl4 hexane c. H 2S water d. Benzene hexane Rank in increasing boiling point: Br2, He, Cl2, I2, Ne He, Ne, Cl2, Br2, I2 A solution containing 3.23grams of unknown compound dissolved in 100.0g water freezes at -0.97⁰C. Solution does not conduct electricity. Calc. molar mass of compound. (Kf=1.86⁰C/m) (61.9g/mol) Rank in increasing boiling point: SbH3, AsH3, NH3, PH3 (PH3, AsH3, SbH3, NH3) 0.3m Ca(NO3)2 0.3m CH3(CH2)4CH3 0.3m MgSO4 0.3m K3PO4 a. smallest b.p.e? (CH3(CH2)4CH3) b. largest f.p.d? (K3PO4) c. highest v.p? (CH3(CH2)4CH3) d. same f.p. as 0.2m Na2SO4 (MgSO4) Add KCl to water What happens to the b.p? f.p? v.p? o.p? b.p.↑ f.p.↓ v.p.↓ o.p↑ What is b.p. of a 2m solution of NaCl in water? (102.08⁰C) CO2, PH3, CH4, C2H4 Largest dipole? Lowest v.p? Highest b.p? Highest solubility in H2O? (PH3) (PH3) (PH3) (PH3) Solution of H2O2 is 26.2% by mass with a density of 1.11g/mL. Molarity? (8.56M) Calculate the concentration of oxygen gas in water at 25.0⁰C under a partial pressure of oxygen at 0.22atm. (The Henry’s law constant is 3.5 x10-4M/atm) (7.7x10-5M) What is vapor pressure of water at 52.0⁰C (ΔHvap for H2O=40.7kJ/mol) (0.144atm or 109Torr) What is osmotic pressure of a NaCl aqueous solution that is 14.0% by mass at 25.0⁰C and has a density of 1.02g/mL? (119.4atm) How many grams of dissolved CO2 are in 1.00L under a pressure of 2.4atm at 20.0⁰C? (k=1.38x10-3M/atm) (0.146grams) A solution is prepared by dissolving 35.0 g of hemoglobin in enough water to make up 1.00 L in volume. The osmotic pressure of the solution is found to be 10.0 mmHg at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of hemoglobin. (64,871g/mol)