X - Solon City Schools
advertisement

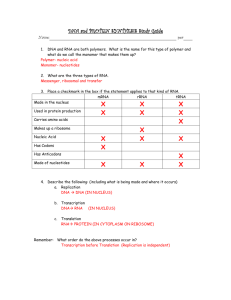
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Name:________________________________________________________ per____ 1. DNA and RNA are both polymers. What is the name for this type of polymer and what do we call the monomer that makes them up? Polymer- nucleic acid Monomer- nucleotides 2. What are the three types of RNA. Messenger, ribosomal and transfer 3. Place a checkmark in the box if the statement applies to that kind of RNA. mRNA rRNA tRNA Made in the nucleus Used in protein production X X X X Carries amino acids Makes up a ribosome X X Nucleic Acid Has Codons X X X X X X Has Anticodons Made of nucleotides X X X X 4. Describe the following: (including what is being made and where it occurs) a. Replication DNA DNA (IN NUCLEUS) b. Transcription DNA RNA (IN NUCLEUS) c. Translation RNA PROTEIN (IN CYTOPLASM ON RIBOSOME) 5. Be as specific and complete as possible. How does DNA code for a protein? Many possibilities- an example of how to start… Small pieces of DNA called genes hold the code for making individual proteins. When the cell needs to make that protein, an enzyme unzips the gene and makes a copy of the code in a piece of mRNA. (This copy must be made because DNA is not allowed to leave the nucleus but mRNA is) The mRNA then goes out to the cytoplasm to join up with a ribosome (made of rRNA) Here, the ribosome puts the amino acids together in the correct order etc… If any of these lines of code are known, the others can be determined: DNA mRNA tRNA protein DNA mRNA tRNA protein DNA mRNA tRNA protein TAC AUG UAC ATG UAC AUG CTA GGT ATC GCT CAC GGT GAU CCA UAG CGA GUG CCA CUA GGU AUC GCU CAC GGU Methionine Tyrosine Aspartate Proline ATG UAC AUG Tyrosine TAC AUG UAC TAC AUG UAC Fill in the blanks. STOP Arginine Valine Proline GAT CCA TAG CGA GTG CCA CUA GGU AUC GCU CAC GGU GAU CCA UAG CGA GUG CCA Methionine Leucine Glycine Isoleucine Alanine Histidine glycine ATG UAC AUG CTA GGT ATC GCT CAC GGT GAU CCA UAG CGA GUG CCA CUA GGU AUC GCU CAC GGU Methionine Tyrosine Aspartate Proline STOP Arginine Valine Proline 1. What are the 3 base sections of mRNA called?_______codons________ 2. What are the 3 base sections of tRNA called?________anticodons__________________ 3. What do you notice about DNA and tRNA? Why could you have predicted this? They are both complementary to the mRNA, so they are the same except for the U’s and T’s 4. In table one, you use the DNA blueprint of bases to make RNA. This is called ___transcription___________ 5. You then make a string of amino acids to form a __protein______________. 6. What is that process called (when you join amino acids using the RNA as a blueprint?)translation