Direct Heat Energy
advertisement

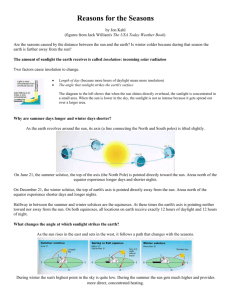
Objective Students will understand how Earth’s tilt on its axis changes the length of daylight and creates the seasons. Reason Why We Have Seasons 23.5o (Source: BBC - KS3 Bitesize Science) It’s the tilt, Baby! The Earth is tilted 23.5o. We have seasons because of the Earth’s tilt. Position of Sun in the Sky Throughout the Year Position of Sun – Summer Solstice (High in sky; direct sunlight) 1|Page Objective Students will understand how Earth’s tilt on its axis changes the length of daylight and creates the seasons. Position of Sun – Autumn Equinox (sunlight becoming indirect); Spring Equinox (sunlight becoming more direct); Half-way between solstices. Position of Sun – Winter Solstice (Low in sky; indirect sunlight) (All three picture source: University of Wisconsin Milwaukee pantherFILE) 2|Page Objective Students will understand how Earth’s tilt on its axis changes the length of daylight and creates the seasons. Seasons Are Reversed in the Hemispheres Date Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere June 21st – September 20th Summer Winter September 21st – December 20th Autumn Spring December 21st – March 20th Winter Summer March 21st – June 20th Spring Autumn Direct & Indirect Heat Energy From the Sun Direct Heat Energy The Sun is high in the sky. The heat energy covers a small area and is warmer. Indirect Heat Energy The Sun is low in the sky. The heat energy (we receive the same amount in summer and winter) covers a large area and is cooler. (Source: Morehead Planetarium UNC) Seasons Vocabulary Seasons - Due to the tilt of Earth as it travels around the Sun, we have spring, summer, fall, and winter. Earth’s Revolution - The circling of the Earth around the Sun. (The Moon also revolves around the Earth.) It takes 365 days (one year) for the Earth to revolve once around the Sun. 3|Page Objective Students will understand how Earth’s tilt on its axis changes the length of daylight and creates the seasons. Axis of Rotation - An imaginary line going from the North Pole to the South Pole. The Earth spins on this line. Earth’s Rotation – The Earth spinning on its axis. It takes the Earth 24 hours (one day) to revolve one time around its axis. Earth’s Tilt - The Earth’s axis is not straight up and down, instead it leans at a 23.5degree angle. Orbit - The path that a planet travels as it goes around the Sun or a moon takes as it goes around a planet. Autumn Summer Winter Spring Direct Sunlight (heat energy) - Covers a small surface area; heat is concentrated and warmer; Sun is high in the sky; summer heat energy is direct. Indirect Sunlight (heat energy) - Covers a large surface area; heat is spread out and colder; Sun is low in the sky; winter heat energy is indirect. Summer Direct Heat Energy Winter Indirect Heat Energy 4|Page