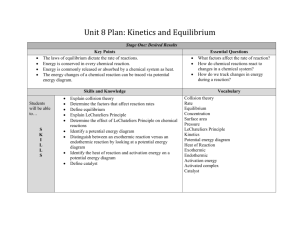
Extra Kinetics and Equilibrium Review
advertisement
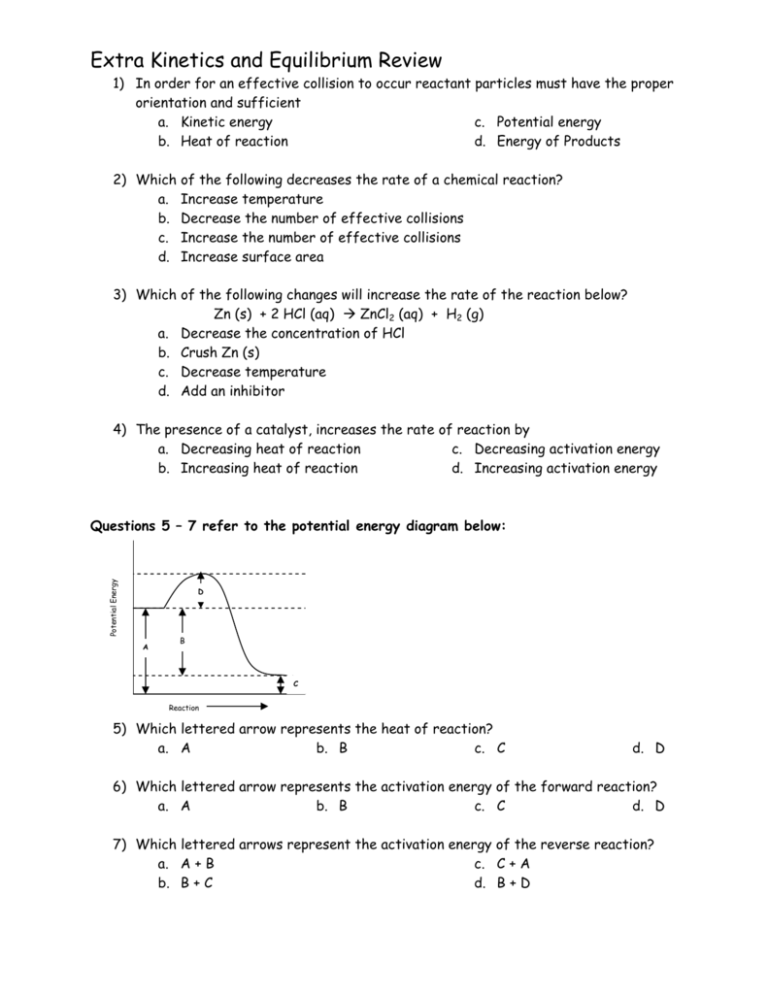
Extra Kinetics and Equilibrium Review 1) In order for an effective collision to occur reactant particles must have the proper orientation and sufficient a. Kinetic energy c. Potential energy b. Heat of reaction d. Energy of Products 2) Which of the following decreases the rate of a chemical reaction? a. Increase temperature b. Decrease the number of effective collisions c. Increase the number of effective collisions d. Increase surface area 3) Which of the following changes will increase the rate of the reaction below? Zn (s) + 2 HCl (aq) Æ ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) a. Decrease the concentration of HCl b. Crush Zn (s) c. Decrease temperature d. Add an inhibitor 4) The presence of a catalyst, increases the rate of reaction by a. Decreasing heat of reaction c. Decreasing activation energy b. Increasing heat of reaction d. Increasing activation energy Potential Energy Questions 5 – 7 refer to the potential energy diagram below: D A B C Reaction 5) Which lettered arrow represents the heat of reaction? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6) Which lettered arrow represents the activation energy of the forward reaction? a. A b. B c. C d. D 7) Which lettered arrows represent the activation energy of the reverse reaction? a. A + B c. C + A b. B + C d. B + D Extra Kinetics and Equilibrium Review 8) When a system is at equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is ____________ the rate of the reverse reaction. a. Greater than b. Equal to c. Less than 9) When a system is at equilibrium, the concentration of products are a. Increasing c. Decreasing b. Constant d. Less than the reactants 10) Given the following equation: 2 NO (g) Æ N2 (g) + O2 (g) + 183.6 kJ The reaction is a. At equilibrium b. Endothermic 11) Given the following reaction: 2 C (s) + 2 H2 (g) + 53.0 kJ Æ C2H4 (s) The reaction is a. Endothermic, & ∆H is positive b. Exothermic, & ∆H is positive c. Exothermic d. Nonspontaneous c. Endothermic, &∆H is negative d. Exothermic, & ∆H is negative 12) According to the reaction at equilibrium: 2 CO + O2 ÅÆ 2 CO2 + 566 kJ How will the equilibrium shift with an increase in temperature? a. Left b. No change c. Right 13) Which of the following changes will shift the equilibrium to the right? N2 + 3 H2 ÅÆ 2 NH3 + 91.8 kJ a. Increase temperature c. Decrease [N2] b. Increase [NH3] d. Increase [H2] ANSWERS: 1) A 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) B 6) D 7) D 8) B 9) B 10) C 11) A 12) A 13) D