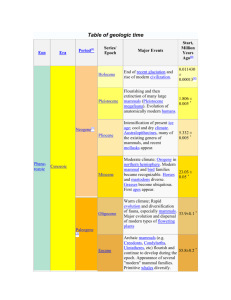
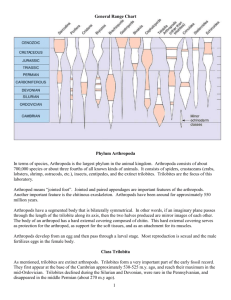
Geological Time Scale & Evolution Worksheet
advertisement
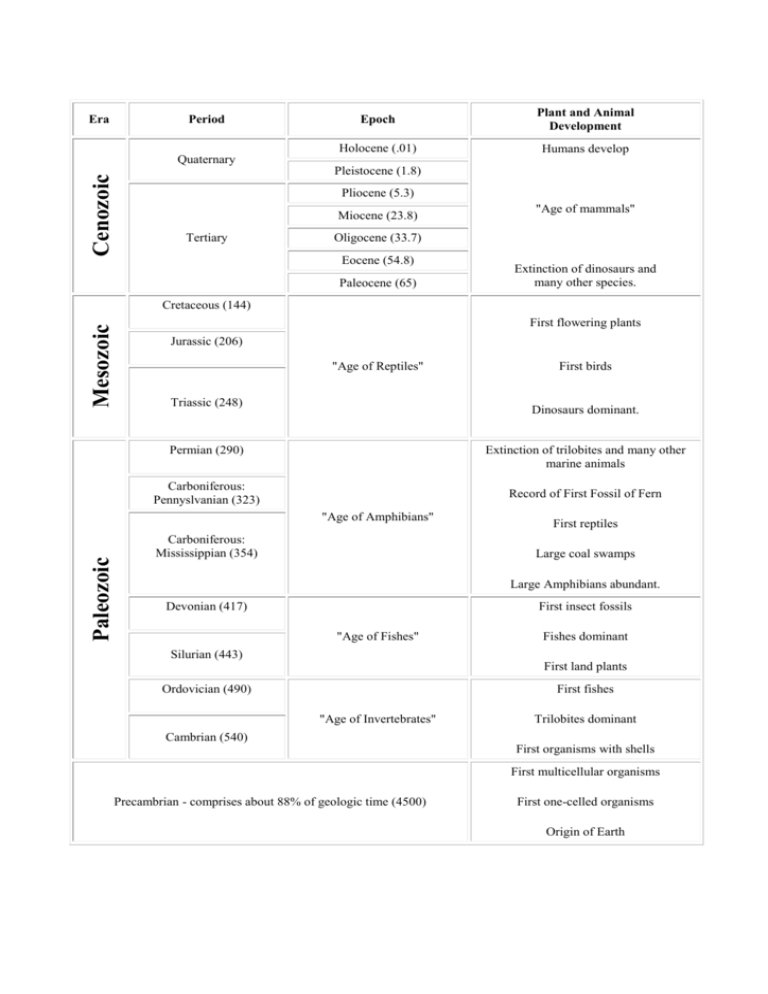
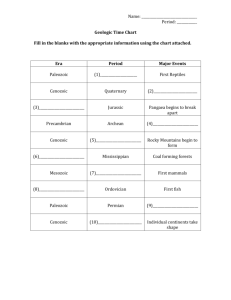
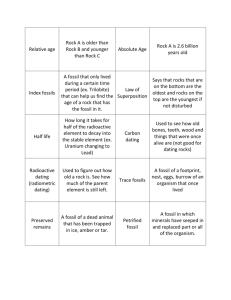
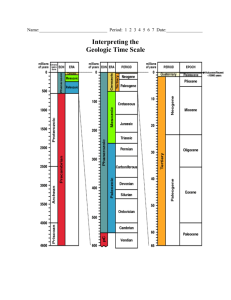
Era Period Cenozoic Quaternary Epoch Plant and Animal Development Holocene (.01) Humans develop Pleistocene (1.8) Pliocene (5.3) Miocene (23.8) Tertiary "Age of mammals" Oligocene (33.7) Eocene (54.8) Paleocene (65) Extinction of dinosaurs and many other species. Mesozoic Cretaceous (144) First flowering plants Jurassic (206) "Age of Reptiles" Triassic (248) Dinosaurs dominant. Permian (290) Extinction of trilobites and many other marine animals Carboniferous: Pennyslvanian (323) Record of First Fossil of Fern "Age of Amphibians" Paleozoic First birds Carboniferous: Mississippian (354) First reptiles Large coal swamps Large Amphibians abundant. Devonian (417) First insect fossils "Age of Fishes" Silurian (443) Fishes dominant First land plants Ordovician (490) First fishes "Age of Invertebrates" Cambrian (540) Trilobites dominant First organisms with shells First multicellular organisms Precambrian - comprises about 88% of geologic time (4500) First one-celled organisms Origin of Earth What are trilobites? Trilobites are an extinct group of arthropods (jointed-legged animals) known from more than 10,000 fossil species. The group Trilobita existed from early in the Cambrian Period (520 million years ago) until the end of the Permian Period (250 million years ago). The name Trilobita is derived from the three (tri-) lobed structure of the exoskeleton, which has a raised central lobe (or axis) and a pair of side lobes, called Pleurae. Ferns first appear in the fossil record in the early-Carboniferous period. By the Triassic, the first evidence of ferns related to several modern families appeared. Year 10 Evolution Name: _________________________________ Answer the questions based on the Geological Time Scale 1. What does the geologic time scale represent? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Scientists have devised the Geologic Time Chart so that Time can be understood from the largest and most general intervals, or units, to the smallest, most specific intervals. Arrange these geological time intervals from largest to smallest: periods eons epochs eras 3. How old is our Earth? ____________________________________ 4. What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Give examples. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Fill in the table with information about Era’s (using the information below) 1. Precambrian Era (earliest forms of life, such as bacteria and blue-green algae; later in the period, invertebrates such as jellyfish). 2. Paleozoic Era (Pangaea; invertebrate life, such as trilobites, later in the era, followed by development of vertebrates, including fish; development of vertebrates, amphibians, and the beginnings of reptiles; development of simple plants, such as mosses and ferns) 3. Mesozoic Era (Pangaea separates into continents; "Age of Reptiles"; dinosaurs, flowering plants, small mammals and birds) 4. Cenozoic (Present Era) Ice Age; mammoths; gradual development of mammals, birds and other animals recognizable today; humans; flowering plants, forests, grasslands.) More: http://naturesblog.blogspot.com.au/2007/04/four-geologic-eras.html http://evolution.about.com/od/LifeOrigins/tp/The-Geologic-Time-Scale.htm Era Meaning Duration Examples of life 6. Which periods did Dinosaurs live on Earth? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Arrange the animals in terms of evolution from the oldest to the youngest. reptiles, invertebrates, bacteria, fish, mammals, amphibians, birds ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Give 2 differences between amphibians and reptiles in terms of their evolution and living habitats. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Which type of plant was the first land plant? Conifers, Angiosperms, Mosses and Ferns ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Arrange these 4 types of plants in order of primitive to most recently evolved. Conifers, Angiosperms, Mosses and Ferns ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. How could plants like Conifers, Ferns and Conifers grow bigger in size compared to mosses? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Explain why insects have evolved most successfully to colonise the Earth? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ http://intl-icb.oxfordjournals.org/content/49/5/590.full http://www.brisbaneinsects.com/brisbane_insects/InsectSuccess.htm 13. In Ordovician Period, trilobites became dominant. What type of animal did trilobites belong to? How long did they live on Earth? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 14. When did first human evolve on Earth? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ http://www.livescience.com/4406-humans-time-origin-pinned.html http://news.nationalgeographic.com.au/news/2009/10/091001-oldest-human-skeletonardi-missing-link-chimps-ardipithecus-ramidus.html 15. When did mammal start to evolve? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ http://www.earthlife.net/mammals/evolution.html