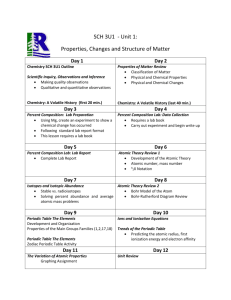
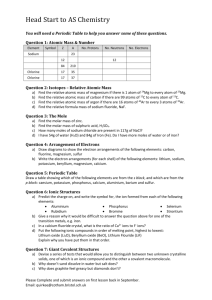
Unit 2 - Periodic Table
advertisement

Unit 2 - Periodic Table Name___________________________ Period______ 1. Which of the following are elements, and which are compounds? (a) sulfur trioxide; (b) gold; (c) table salt (sodium chloride); (d) phosphorus pentabromide; (e) chlorine; (f) titanium. 2. Classify the following as compounds or elements: (a) potassium chloride (salt substitute); (b) calcium oxide (lime); (c) ammonium nitrate (used in fertilizers); (d) tungsten; (e) zinc. 3. From the symbols and formulas given, classify the following substances as elements or compounds: (a) Cu; (b) Mg(NO3)2; (c) CO2; (d) NaF; (e) Sg. 4. Which of the following are elements, and which are compounds? (a) KCN; (b) CaCl2; (b) Ne; (d) Ni; (e) CuO 5. How can you tell if a substance is an element or a compound on the macroscopic level? How can you tell on the particulate level? 6. Can a compound be decomposed into two other compounds? 7. Classify each substance in the illustration bellow as an element or a compound: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 8. (a) Which of the following substances would you expect to be elements and which would you expect to be compounds? (1) aluminum sulfate; (2) osmium; (3) radon; (4) lithium carbonate; (5) dimethylhydrazine. (b) On what general rule do you base your answers to part (a)? Can you name any exceptions to this general rule, for both elements and compounds? 9. A white, crystalline material that looks like table salt gives off a gas when heated under certain conditions. There is no change in the appearance of the solid that remains, but it does not taste the same as it did originally. Was the beginning material an element or a compound? Explain your answer. 10. Complete the table: Solid/Liquid/Gas Pure/Mixture Hom/Het Element/Compound Pure/Mixture Hom/Het Element/Compound Limestone (CaCO3) Lead Fresh squeezed OJ Oxygen Cold Butter 11. Complete the table: Solid/Liquid/Gas Factory Smoke Concrete Helium Hummingbird Food Table salt 12. Before electronic flashes were commonly used in photography, a darkened area was lighted by a device known as a flash bulb. This one-use device was essentially a glass bulb filled with oxygen that encased a metal wire. An electrical discharge from the camera ignited the wire causing a brief flash of light as the wire quickly burned. How would you expect the mass of a flash bulb before use compare with its mass after use? Explain. 13. The rock that remains after solid limestone is heated weighs less than the original limestone. What do you conclude has happened? 14. Identify several energy conversions that occur regularly in your home. State whether each is useful, wasteful, or sometimes useful and sometimes wasteful. 15. Consider the sample below: Answer each questions independently and explain your answers. (a) Is the sample homogeneous or heterogeneous? (b) Is the sample a pure substance of a mixture? (c) Are the particles elements or compounds? 16. Write the symbols of the elements in Group 2A (a) of the periodic table. Write the atomic numbers of the elements in Period 3. 17. How many elements are in Period 5 of the periodic table? Write the atomic numbers of the element sin Group 3B (3). 18. Locate in their periodic able each pair of elements whose atomic numbers are given below. Does each pair belong to the same period or the same chemical family? (a) 12 / 16; (b) 7 / 33; (c) 2 / 10; (d) 42 / 51. 19. Locate in the periodic table each element whose atomic number is given, and identify first the number of the period it is in and then the number of the group: (a) 20; (b) 14; (c) 43. 20. Referring only to the periodic table, list the atomic masses of the elements having atomic numbers 24, 50, and 77. 21. Using only a periodic table for reference, list the atomic masses of the elements whose atomic numbers are 29, 55, and 82. 22. What are the atomic masses of potassium and sulfur? 23. Write the atomic masses of helium and aluminum. 24. Complete the table: Name of Element Sodium Atomic Number Elemental Symbol Pb Aluminum 26 F Boron 18 Silver 6 Copper Be Krypton Chlorine 1 Mn 24 Cobalt 80 25. Complete the table: Name of Element Atomic Number Elemental Symbol Mg 8 Phosphorous Ca Zinc Li Nitrogen 16 53 Barium K 10 Helium Br Ni Tin 14 26. The stable form of seven elements is the diatomic molecule. Write the names and formulas of those elements. 27. The elements of Group 8A (18) are stable as monatomic atoms. Write their formulas. Questions 28-33: Given the name, write the formula; given the formula, write the name. 28. Carbon, iodine, zinc, argon 29. Fluorine, boron, nickel, sulfur 30. Cr, Cl2, Be, Fe 31. Hydrogen, lead, silicon, sodium 32. Krypton, copper, manganese, nitrogen 33. O2, Ca, Ba, Ag 34. Determine whether each statement that follows is true or false: a. Periods are arranged vertically in the periodic table. b. The atomic mass of the second element in the right column of the periodic table is 10 amu. c. Nb is the symbol of the element for which Z=41. d. Elements in the same column of the periodic table have similar properties. e. The element for which Z=38 is in both Group 2A (2) and the fifth period. 35. Explain the meaning of ionization energy. 36. What is the general trend in ionization energies of elements in the same chemical family? 37. List the following in order of increasing first ionization energy: Chlorine, Phosphorus, and Magnesium. 38. List the following in order of decreasing ionization energy: Lithium, Potassium and Sodium. 39. List the following in order of increasing electron affinity: Oxygen, Fluorine, and Boron. 40. What does it mean when two elements are in the same chemical family. 41. Identify the chemical families to which (a) Iodine and (b) Rubidium (Z=37) belong. 42. Identify the chemical families to which (a) Krypton (Z=36) and (b) Beryllium are found. 43. Where in the periodic table do you find transition elements? Are they metals or non metals? 44. Identify an atom in group 15 that is (a) larger than an atom of Arsenic (Z=33) and (b) smaller than an atom of Arsenic. 45. Identify an atom in period 4 that is (a) larger than an atom of Arsenic (Z=33) and (b) smaller than an atom of Arsenic. 46. Why does atomic radius increase as you go down a column in the periodic table? 47. List the following in order of increasing atomic radius: Selenium, Chlorine, and Sulfur. 48. List the following in order of decreasing atomic size: Magnesium, Calcium, and Potassium. 49. What property of atoms of an element determines that the element is a metal rather than a non metal? 50. What are metalloids or semi metals? 51. List the following in order of increasing metallic character: Magnesium, Silicon, and Sodium. 52. List the following in order of decreasing metallic character: Krypton, Argon, and Xenon. Use the periodic table below to answer questions 19-24 with letters from that table. 53. Give the letters that are in the positions of (a) Halogens and (b) alkali metals. 54. Give the letters that are in the positions of (a) alkaline earth metals and (b) noble gases. 55. Give the letters that correspond to transition elements. 56. List the letters that correspond to non metals. 57. List the elements K, B, Al in order of decreasing atomic size (largest atom first). 58. List the elements Ca, F, Cl in order of increasing atomic size (smallest atom first). 59. The first ionization energy for an atom is always less than the second ionization energy. Why is this so? 60. The text describes the formation of a sodium ion as the removal of one electron from a Sodium atom. Predict the size of a Sodium ion compared to the size of a Sodium atom. Explain your prediction.