Electronic-Measure-and-Test-Task-Book-IV-20123
advertisement

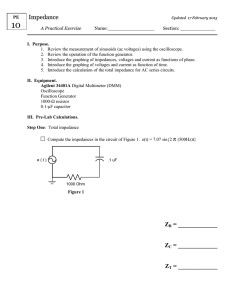
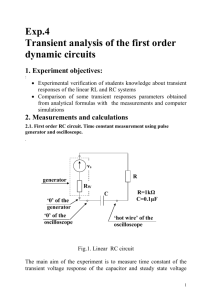
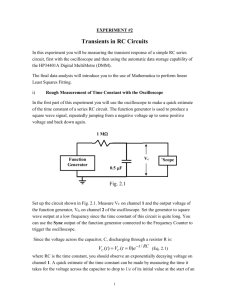
BTEC National Diploma in Engineering Unit 53 Electronic Measurement and Testing Qualification BTEC National Diploma in Engineering Unit Unit 53 Electronic Measure and Test Number Assessor Name Learner Name Paul Lewis Achievement at a glance, deadlines given in module weeks, for example P1 should be completed by the 3rd week of the module. P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 M1 M2 M3 D1 D2 Year 2 Year 2 Year 2 Year 2 Year 2 Tutor sign and date for each achieved outcome MW 3 MW 3 MW 9 MW 10 MW 11 MW 12 MW 6 MW 6 Learner sign and date for each submitted outcome Learner Declaration I confirm that the work submitted to complete the given tasks is my own. I have indicated where research and other resources have been used to confirm the conclusions reached within the submission and listed those resources in a bibliography. Sign………………………………………………… Date…………………………………………. Task 1 (P1) Describe the function, features and characteristics of a measurement instrument Check the following Yes No Have you included documentary evidence such as a drawing, illustration or photograph which you can label and indicate the function of the various buttons and dials? Have you fully described the features of an oscilloscope e.g. its input and output connectors? Have you described the importance of the characteristics of an oscilloscope such as its input and output impedance, bandwidth and accuracy? Task 1. Describe the function, features and characteristics of an oscilloscope. Task 2 (P2) Describe the function, features and characteristics of three different pieces of electronic test equipment Check the following Yes No Have you included documentary evidence such as a drawing, illustration or photograph which you can label and indicate the function of the various buttons and dials? Have you fully described the features of test equipment such as function generators e.g. such as its portability or in built calibration facilities Have you described the importance of the characteristics of test equipment such as its input and output impedance, bandwidth and accuracy? Tasks Describe the function, features and characteristics of the following three pieces of electronic test equipment. 1. A function generator 2. A power supply 3. A logic probe Task 3 P3 Use test equipment and measuring techniques to take measurements from three different pieces of electronic equipment This is a complex task that is split into 3 parts. P3 Part 1 Practical Task and written report Construct the circuit below 1. Connect the function generator and oscilloscope as shown 2. Set the function generator to give a sine wave output with a frequency of 1 kHz and an amplitude of 10 volts peak to peak 3. Set up the oscilloscope to measure and compare the input and output 4. Measure and record the input and output for this circuit (screen dump, photo) 5. Using the equation FrequencyCUTOFF = 1/(2πcr) find the cut-off frequency for this circuit 6. Adjust the function generator to give the output frequency and use the oscilloscope to measure and record it (screen dump, photo) 7. Write a brief report on your findings including the differences between both amplitude and phase of the input and output waveforms at the cut-off frequency P3 Task 2 Choose a resistor and capacitor combination that gives a time constant between 1 – 5 seconds and construct the circuit shown below. Please note that the component shown do not give the correct time constant. Tasks 1. Use the following equation Vinst =Vsupply(1 – e-t/CR) to predict the time at which the voltage across the capacitor will be at 10% and 90% of its maximum value 2. Connect the power supply (12 volts) and use an oscilloscope to measure the change in voltage across the capacitor over a period of 5 time constants. Freeze the display 3. Measure the rise time of this voltage (rise time is measured between 10% and 90% of the minimum and maximum voltages) you will need to use the cursor controls to get an accurate reading 4. Relate your measured results to the values predicted by the given equation 5. Write a brief report on this experiment including a circuit diagram, relevant screen dumps, calculated and measured results and an evaluation P3 Task 3 The purpose of this task is to find the unknown internal resistance of a battery using 2 multi-meters and applying Ohm’s law. 1. Use a multi-meter to measure the off load voltage of a given battery. A 9 volt battery is used for this example. Note the voltage 2. Now set up the circuit shown below to measure the voltage drop across the electrical load (called the on load voltage) and the current drawn by the circuit. This is the resistance you are trying to find 3. Use the following equation to calculate the approximate internal resistance of the battery 4. Include your findings in a brief report including a photo of the circuit set up and a short evaluation. The evaluation should include the reasons why a voltmeter always measures voltage in parallel and an ammeter always measure current in series Task 4 (P4) Explain the importance of test specifications as an aid to ensuring the validity and consistency of measurements Scenario Imagine you are an Electronics company manager; you have just designed and built a prototype circuit that meets your client’s specifications. They request an order of 1,000 circuits to be made. To deal with this demand you enlist a team of test engineers. You need some way of ensuring that the tests to be carried out will get the results that meet the specification. How can you ensure they get valid and consistent measurements every time? Aims and objectives Define Validity and consistency. Explain why both are important parameters when taking measurements. Explain what a test specification is Why is a test specification important in measurement taking? Use one of the Tasks in P3 as an example to showcase this. Task 5 (P5) Describe the principles and need for the calibration of an item of electronic test equipment Produce a report highlighting the reasons why electronic test and measurement equipment needs to be calibrated on a regular basis. Your report should include references to: Primary, secondary, working standards and SI units Metrology, calibration, accuracy, precision, sensitivity and resolution A reasonable calibration interval for equipment in regular use (4+ hours per day) 3 reasons why an instrument might need to be calibrated within the calibration interval 3 reasons why calibration is normally carried out by specialist companies The effect that temperature and relative humidity can have on measurements The impact of calibration on quality, productivity and safety Task 6 (P6) Describe the health, safety and configuration issues that need to be considered when connecting test equipment to an item of electronic equipment that needs testing Scenario You have been employed as a junior electrical/electronic technician for a small local firm specializing in the repair, installation and commissioning of direct online starting equipment for small to medium power electrical motors. One of your best customers has a motor starter which has developed a fault. You have been tasked with finding the fault and testing the equipment before handing it back to the client. The motor will need to be tested using a 440 volt 3 phase supply. Describe the procedures you would take to ensure that this equipment can be tested safely. You description could include illustrations, diagrams and examples from industry. Here are some of the areas you should include: Precautions to be taken when working with live electrical equipment Procedures which ensure that electrical/electronic test equipment is suitable and safe for use with live electrical equipment (use of manuals and manufacturer’s procedures) The importance of checking that electrical equipment is properly bonded to earth Safe isolation techniques for electrical/electronic equipment Hidden dangers of working with electronic equipment which has been safely isolated The importance of electrical safety cut-outs such as RCD’s Removing and replacing inspection covers Task 7 P7 Use a virtual measurement and test system to carry out a test on piece of electronic equipment You have a choice of using either P3 part 1 or 2, or the LM386 amplifier build and test as a basis for this outcome. Your report should include: A description of the test carried out A circuit diagram showing the test points A brief description of the test and measurement equipment used A detailed oscilloscope screen dump, properly labelled showing the outcome of the test P8 Describe the measurement techniques, instrument connection, hardware and software used Check the following Have you described the type of virtual oscilloscope used to carry out this task? Have you listed the system requirements needed to run this virtual measurement and test system (processor speed, bandwidth, ram, operating system, bus capability) Have you provided screen dumps showing how you set up the virtual scope to capture data from the test? Have you described or demonstrated how data can be stored from the test? Yes No 1. You can reproduce either task 1 or 2 from P3 to complete this outcome using a virtual oscilloscope. Make sure you have covered the points in the table. Task 8 (M1) Explain the importance of resolution, accuracy, sensitivity bandwidth and input impedance on the performance of a piece of test equipment Assessor Feedback Achieved? Explain the importance of resolution, accuracy, sensitivity bandwidth and input impedance on the performance of an oscilloscope. You can use any of the tests in the pass section (which required an oscilloscope) as a basis for your submission, especially the tasks carried out for P3 Task 9 (M2) Use a manufacturer’s recommended procedure together with laboratory instruments and standards to calibrate and configure an item of electronic test equipment Assessor Feedback Achieved? 1. Use the manufacturer’s recommended procedure to calibrate and configure a laboratory oscilloscope. 2. Use the calibrated scope to check the accuracy of a laboratory function generator with respect to frequency and amplitude. 3. Check the accuracy of your measurements against that given by the manufacturer of the function generator. 4. Based on your findings, would you recommend that the function generator needs to be sent back to the manufacturer for calibration? You need to justify this recommendation. Task 10 (M3) Use appropriate software to display and analyse voltage/time data captured from a virtual oscilloscope Assessor Feedback Achieved? 1. This is a natural extension of the task given for P7. In this case you are required to analyse a waveform. The best way to accomplish this is to use either task 1 or 2 for P3 as a basis for comparing the captured data with the results predicted by theory Task 11 (D1) Evaluate the accuracy of your own test measurements and relate them to limitations of the test equipment, test procedures or possible emergent fault conditions Assessor Feedback Achieved? 1. You can use any of the tests carried out in the various exercises or practical projects as a basis for this evaluation. The submission needs to be an ‘in-depth’ investigation of the effects of connecting test/measurement equipment to a circuit under test and how the results are limited by the characteristics of the test equipment and test procedures. 2. As an example, an oscilloscope is incapable of accurately displaying a transient pulse due to its finite bandwidth. This could be the basis of an investigation carried out by you to explain why? Task 12 (D2) Devise and demonstrate a calibration procedure for an item of electronic test equipment Assessor Feedback Achieved? 1. Devise and demonstrate a calibration procedure for a x10 oscilloscope probe to be used with the laboratory oscilloscopes. Explain why the probe needs to be calibrated and under what circumstances such a probe might be required in preference to a standard x1 probe.