Introduction to Multisim
advertisement

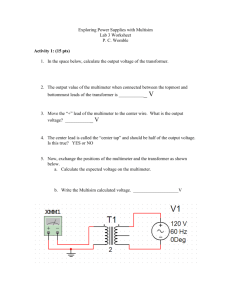
Introduction to Multisim ECE 1020 Professor Ahmadi What is Multisim? • A virtual circuit simulator for both analog and digital design • Allows you to test circuits without having to physically build them Starting the Program • Start Menu All Programs National Instruments Circuit Design Suite Multisim Program Interface You start off with an empty workspace. Placing Components Placing Components onto the Workspace • • Filter the components you want to see by using the Group dropdown, selecting a Family, and searching for the Component name Select your component, click OK, and click on the workspace to place it Component list Libraries Let’s Build This Circuit Finding the Voltage Source and Ground Finding the Resistor Type 1k into the search box to find the 1kOhm resistor Placing Wires • A circuit is not complete if the components are not connected • Click Place Wire • Click on the workspace to designate the start point and click again to place the stop point Taking Measurements • We need to tell the software where we want to measure and what to measure with • Let’s use the multimeter to measure the voltage across the resistor and the current through it Measuring with the Multimeter • On the right hand side, click the Multimeter (1st icon) • Place onto the workspace Measuring the voltage across R1 Use wires the connect the positive and negative terminals of the multimeter to the circuit. Simulating • To simulate the circuit, go to Simulate Run, Hit F5, or click the Play button start pause stop Reading the Voltage • Double-click the multimeter icon on your workspace and click the V button • It says 12V which is what we expect Reading the Current • • • • • To measure the current at a location within a circuit, we must place the measuring device in series with the circuit at that location Close the multimeter window and Stop the simulation Connect the multimeter as shown and Start the simulation Double-click the multimeter and click the A button It says 12mA which is what we expect (12V/1kOhm=12mA) Diodes and AC Circuits • Diodes are essentially electrical switches • The switch is CLOSED when the voltage across the diode exceeds some threshold (~0.6V) • Otherwise, it is OPEN (OFF) Let’s Build This Circuit (2) Finding the Diode Finding the AC Source Changing the AC Source Values Double-click the AC source and change the fields to match the ones below. 2.12 Vrms is 3Vpeak Measuring the Voltage Across R1 • Because we are using an AC source, we need to use an oscilloscope to the see the AC voltage • From the right-hand column, select the Oscilloscope (4th icon down) and place it onto the workspace Connect as follows… • Change the color of the wire in Terminal A by right-clicking it and selecting Color Segment • This configuration will measure the input voltage (Terminal A) and the voltage after the diode and across R1 (Terminal B) • The negative terminals are left open because the ground reference is the same for both measurements • However, if they were not the same, they must be connected appropriately Simulation • Start the simulation and double-click the oscilloscope • Hit Single on the bottom right • Drag the triangle markers across the traces to read their values Analysis • The peak voltage for Channel A is 3V which is expected • The peak voltage for Channel B is 3V0.6V=2.4V which is correct • But the red trace has no negative portion!!! • This is because the diode is ON only when the voltage across it is 0.6V, therefore, no current will pass through when the AC source dips below 0.6V Oscilloscopes • Try measuring the circuit with the other oscilloscope components (e.g. Agilent Oscilloscope or Tektronix Oscilloscope) • They look like the actual scopes seen on your lab benches • Play around with the knobs to get familiar with their functions