Crystal Systems Activity
advertisement
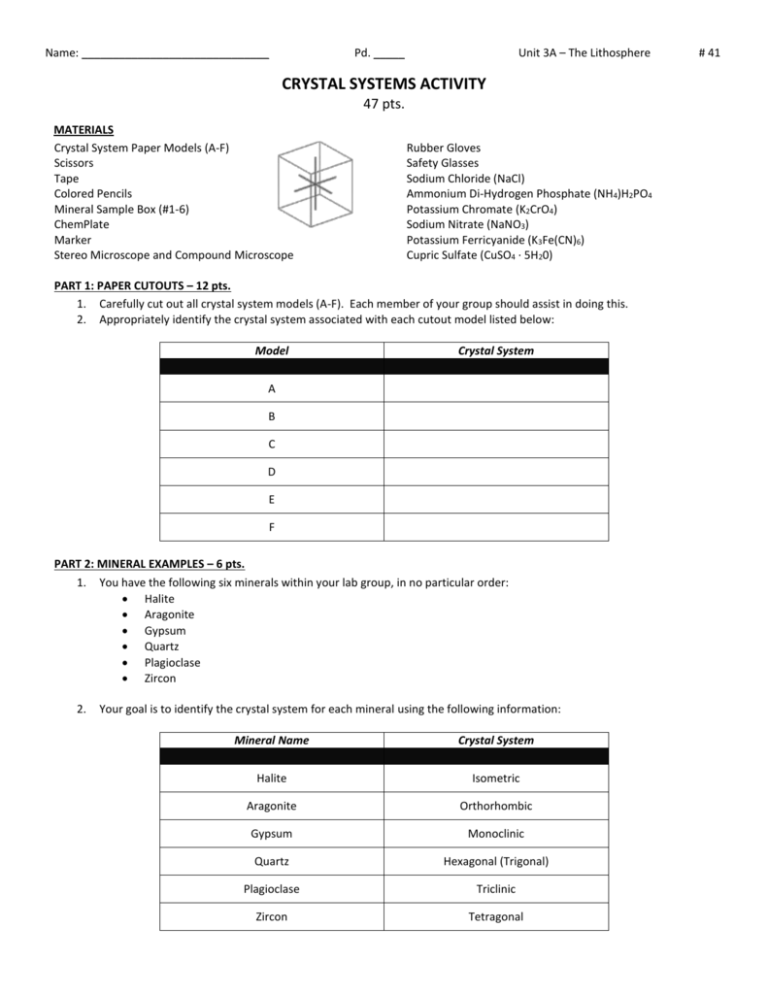
Name: ______________________________ Pd. _____ Unit 3A – The Lithosphere CRYSTAL SYSTEMS ACTIVITY 47 pts. MATERIALS Crystal System Paper Models (A-F) Scissors Tape Colored Pencils Mineral Sample Box (#1-6) ChemPlate Marker Stereo Microscope and Compound Microscope Rubber Gloves Safety Glasses Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Ammonium Di-Hydrogen Phosphate (NH4)H2PO4 Potassium Chromate (K2CrO4) Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3) Potassium Ferricyanide (K3Fe(CN)6) Cupric Sulfate (CuSO4 · 5H20) PART 1: PAPER CUTOUTS – 12 pts. 1. Carefully cut out all crystal system models (A-F). Each member of your group should assist in doing this. 2. Appropriately identify the crystal system associated with each cutout model listed below: Model Crystal System A B C D E F PART 2: MINERAL EXAMPLES – 6 pts. 1. You have the following six minerals within your lab group, in no particular order: Halite Aragonite Gypsum Quartz Plagioclase Zircon 2. Your goal is to identify the crystal system for each mineral using the following information: Mineral Name Crystal System Halite Isometric Aragonite Orthorhombic Gypsum Monoclinic Quartz Hexagonal (Trigonal) Plagioclase Triclinic Zircon Tetragonal # 41 3. Appropriately identify each mineral by completing the following table using your new knowledge of crystal systems: Mineral # Mineral Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 PART 3: MICROSCOPIC CRYSTAL SLIDES – 6 pts. 1. At the compound microscope set-up in the back of the lab, study the various slides containing the six different types of crystal systems. Make sure each member of your group gets a chance to view the crystal slides. Draw what you see in the appropriate spaces below: ISOMETRIC HEXAGONAL MONOCLINIC TETRAGONAL ORTHORHOMBIC TRICLINIC PART 4: MICROCRYSTAL GROWTH – 18 pts. 1. Everyone must wear safety glasses during this part of the activity and the person handling the solutions must also wear rubber gloves. 2. Use the following information to label your ChemPlate with numbers 1 to 6 and the names of member of your group: #1 – NaCl #2 – (NH4)H2PO4 #3 – K2CrO4 #4 – NaNO3 #5 – K3Fe(CN)6 #6 – CuSO4 · 5H20 3. Drop four drops of each chemical solution, located at the center lab table, into the correct spot plate well. Be certain to match the number with the correct chemical as listed above. 4. Allow the solutions to slowly evaporate overnight, placing them on the storage table. 5. During the second day of the activity, retrieve your ChemPlate and study each crystalline spot under the Stereo Microscope. Describe and draw the crystals in the appropriate space. Use the crystal systems worksheet to help in determining the crystal system each salt belongs to. Try to find crystals that stand up on the ChemPlate so you can check for angles between crystal faces that are not 90°. Think of crystal axes as unit cells or building blocks of crystals. Spot # Chemical Salt 1 NaCl 2 (NH4)H2PO4 3 K2CrO4 4 NaNO3 5 K3Fe(CN)6 6 CuSO4 · 5H20 Description Drawing Crystal System ANALYSIS QUESTIONS – 5 pts. 1. What are the five (5) characteristics defining a mineral? ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 2. What is the basic building block of all silicate minerals? _______________________________________________________ 3. The hardest known mineral, according to Moh’s Hardness Scale is what? _________________________________________ 4. Describe rhombohedral cleavage. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Why is color not the best property to use when identifying minerals? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________


![ULEXITE [NaCaB5O6.8H2O]: An Extreme](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006902682_2-6ec8a0d1193ce61c1182d5c91126ae5a-300x300.png)