Nutrition Homework answer key
advertisement

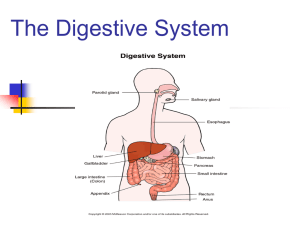
Unit: Digestion HW 1 Read Concepts Pages 106 (Protozoa) - 112 Answer the following: 1. Define the terms intracellular and extracellular digestion. Intracellular digestion occurs inside a cell while extracellular digestion occurs outside of a cell 2. How does mechanical digestion aid chemical digestion Mechanical digestion physically breaks down food thus increasing the surface area of the food and allowing chemical digestion performed by enzymes to occur faster 3. Why is a one-way digestive tract evolutionarily more efficient than a two way tract? One way is more efficient for two reasons: (1) specialized structures allow for more efficient digestion of materials and (2) Food can be stored for later use where in a two way tract food may be lost before digestion is completed Unit: Nutrition HW 2 Read Miller/Levine pages 978-984 Answer the following: 1. Discuss the importance of teeth in human nutrition Teeth perform mechanical digestion thus increasing the surface area of food for salivary amylase to work and for the enzymes of the stomach and small intestine to work more efficiently 2. Describe how food passes through the esophagus Food is pushed down the esophagus to the stomach through the process of peristalsis. Wave-like contractions alternate between contraction and relaxation to push the food through the entire digestive tract from the esophagus through the stomach, small intestine and large intestine. 3. Why would the enzymes in your mouth not work in your stomach and the enzymes in your stomach not work in your mouth? Mouth enzymes, salivary amylase, would be denatured in the stomach due to the pH of 2 in the stomach. Pepsin, stomach enzyme, would be denatured because its optimum pH is 2 and the mouth has a pH of 7. Unit: Nutrition HW 3 1. Using Concepts create a table of the Malfunctions of the Digestive System (pages 209 - 211) Malfunction Description Ulcer Erosion of the surface of a portion of the digestive tract, normally in the stomach due to action of irritants Constipation Too much water absorption in the large intestine causing fecal matter to be too dry Diarrhea Not enough water reabsorption in the large intestine causing fecal matter to be watery (loose stool) Gall stones Salt crystals form in the gall bladder and clog the tube connecting the gall baldder to the small intestine. This reduces bile release, reduces lipase activity, reduces fat digestion and causes pain 2. create a chart including mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder. Identify the secretions of enzymes (give specific enzyme names and substrates), if any, and the role of each structure listed. Site also mechanical, chemical and extracellular digestion Structure Mouth Secretion Salivary amylase (enzyme); substrate: starch Stomach Pepsin (enzyme); substrate: polypeptides Small intestine Enzymes originate from the pancreas Large intestine Pancreas Liver Proteases (trypsin and chymotrypsin) Lipase Carbohydrases (maltase, sucrase, lactase) Nucleases (digest DNA and RNA) Synthesizes bile (emulsifies lipids) Gall bladder Function Chemical digestion of carbohydrates Mechanical digestion Both extracellular Storage of food Extracellular chemical digestion of proteins Kill pathogens Site of chemical digestion Site of nutrient absorption Site of water absorption Home of mutualistic bacteria Synthesize and secrete enzymes into the small intestine Synthesizes and secretes biocarbonate ions into the small intestine Store Bile Release bile into the small intestine when fats are present Unit: Nutrition HW 4 Read: Concepts page 208-209 (Absorption in the small intestine) Miller/Levine page 983 Answer the following: 1. State the functions of the small intestine. Describe how it is structured to carry out its functions. Site of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption. Lined with villi (finger-like projections into the lumen) that have microvilli on them. Villi and microvilli increase the surface area of the small intestine to increase the ability to absorb nutrients. Villi absorb materials using active transport How would the introduction of cyanide, a chemical that inhibits ATP (chemical energy) production affect the functioning of the small intestine? Cyanide would prevent mitochondria from producing ATP (energy) thus active transport in the small intestine would stop and no nutrients would be absorbed Graph the data on page 994 (Miller/Levine). Identify the independent and dependent variables. 9 8 Protein Digestion 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Temperature (Celcius) Copy and answer question 23 on page 993 (Miller/Levine) The experiment was repeated a third time, using apple instead of gelatin. There was no evidence of any digestion after 48 hours at any temperature. Explain why no digestion occurred. The enzyme used to digest the gelatin has a specific shaped active site for the substrate gelatin. The apple is a carbohydrate thus does not fit into the active site of the protein (gelatin) digesting enzyme. Copy and answer question 25 on page 994 (Miller/Levine) Individuals who have had part, or even all, of their stomachs removed can survive if fed predigested food. Could individuals with a stomach survive without a small intestine if they were fed predigested food? Support your answer with an explanation. The person will not survive because the small intestine is involved in nutrient absorption as well as digestion. No small intestine means no nutrient absorption leading to death.