Prokaryotes: Bacteria & Archaea Name: Bacteria, which outnumber
advertisement

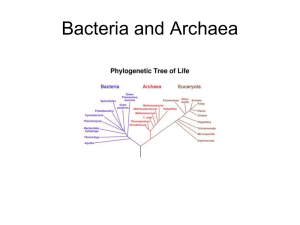
Prokaryotes: Bacteria & Archaea Name: Bacteria, which outnumber all eukaryotes combined, differ from eukaryotes in at least seven ways. Membrane-Bound Organelles: Bacteria are prokaryotes. Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes lack a cell nucleus and all other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotes do contain ribosomes, granules of stored nutrients, enzymes, and certain internal structures, however. Cell Size: Most bacterial cells are about 1 µm in diameter; most eukaryotic cells are more than 10 times that size. Multicellularity: All bacteria are single cells. Some eukaryotes are single-celled, but most are multicellular. Chromosomes: Bacterial chromosomes consist of a single circular piece of DNA. Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear pieces of DNA that are associated with proteins. Prokaryotes also have plasmids, small extra loops of DNA. Reproduction: Bacteria reproduce by binary fission, a process in which one cell pinches into two identical cells. In eukaryotes, however, microtubules pull chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis. Afterward, the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell divides in half, forming two cells. Flagella and Pili: Bacterial flagella are simple structures that spin like a corkscrew to move the cell. Eukaryotic flagella are more-complex structures made of microtubules that whip back and forth rather than spin. Some bacteria also have short, thin, protein tubes called pili that attach to surfaces or to other cells. Metabolic Diversity: Bacteria have diverse metabolic abilities. For example, some bacteria get their energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. Others get energy from inorganic molecules that contain sulfur or nitrogen. Most bacteria get nutrients and energy by feeding on other organisms. In the space provided, write the letter of the phrase that best completes the statement. 1. Write 3 things that describe the characteristics of prokaryotes. To the left of the number, write E if the characteristic describes only eukaryotes, B if the characteristic describes only bacteria, or EB if the characteristic describes both eukaryotes and bacteria. 2. reproduce by binary fission 3. lack a cell nucleus 4. chromosomes are linear pieces of DNA 5. have pili for attaching to surfaces and other cells 6. have plasmids 7. divide by mitosis 8. most cells are about 1 µm in diameter 9. single cells 10. cytoplasm contains membrane-bound organelles 11. simple flagella spin like a corkscrew 12. are about 10 µm in diameter 13. flagella are complex structures made of microtubules 14. most are multicellular 15. during cell division, microtubules pull chromosomes to opposite poles 16. cytoplasm lacks organelles 17. lack plasmids 18. some get energy from inorganic molecules that contain sulfur or nitrogen 19. two identical cells form when cytoplasm pinches in half 20. chromosomes consist of a single circular piece of DNA 21. have ribosomes 22. have a single chromosome called a nucleoid 23. have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan 24. have enzymes for performing metabolic activities 25. How do the sizes compare between virus, bacteria, and eukaryotic cells? 26. (Underline)Escherichia coli are [Gram-negative / Gram-positive] eubacteria. 27. (Underline) [Conjugation / Transduction] is a process in which two bacteria exchange genetic material. 28. (Underline)Escherichia coli have [pili and flagella / only flagella]. 29. (Underline)Many bacteria move with [flagella / pili]. 30. Complete the chart. Define Photoautotrophic Eukaryotic, prokaryotic, or both Chemoautotrophic Heterotrophic In the space provided, write the name of the metabolic group—photoautotrophic, chemoautotrophic, or heterotrophic—to which each of the following types of bacteria belongs. _____________________ 31. Cyanobacteria _____________________ 32. purple sulfur bacteria _____________________ 33. bacteria that form their own proteins from hydrogen-rich chemicals like H2S _____________________ 34. Anabaena _____________________ 35. Rhizobium 36. The two domains of prokaryotes are called ______________________ and ______________________. 37. Bacteria often have small extra loops of DNA called ______________________. 38. The cell wall of bacteria contains a protein-carbohydrate compound called _______________________. 39. Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to medicines because they have a(n) ______________________ ______________________. 40. Some bacteria can survive harsh conditions by forming thick-walled _______________________. 41. List and describe 1 beneficial bacteria. 42. List and describe 1 harmful bacteria (not anthrax). 43. Describe anthrax and explain the concern with it.