Implications for High School Implementation of the HCCC
advertisement
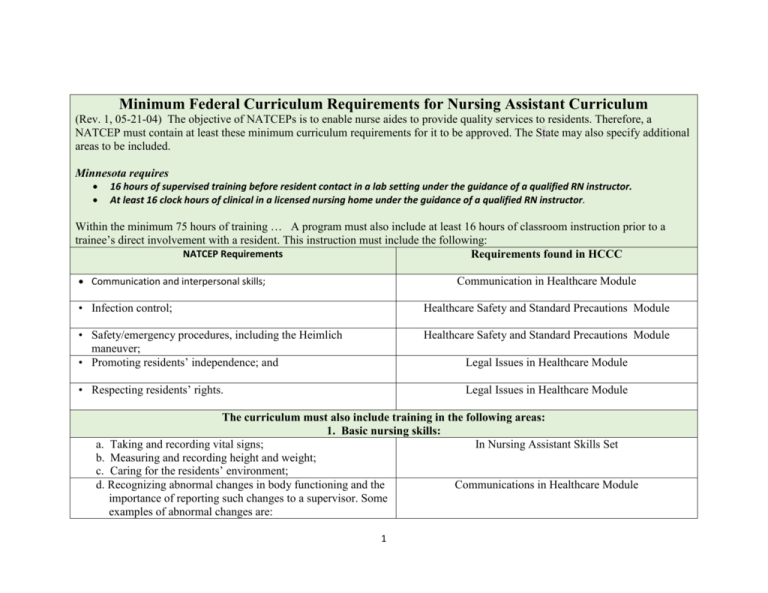
Minimum Federal Curriculum Requirements for Nursing Assistant Curriculum (Rev. 1, 05-21-04) The objective of NATCEPs is to enable nurse aides to provide quality services to residents. Therefore, a NATCEP must contain at least these minimum curriculum requirements for it to be approved. The State may also specify additional areas to be included. Minnesota requires 16 hours of supervised training before resident contact in a lab setting under the guidance of a qualified RN instructor. At least 16 clock hours of clinical in a licensed nursing home under the guidance of a qualified RN instructor. Within the minimum 75 hours of training … A program must also include at least 16 hours of classroom instruction prior to a trainee’s direct involvement with a resident. This instruction must include the following: NATCEP Requirements Requirements found in HCCC Communication and interpersonal skills; Communication in Healthcare Module • Infection control; Healthcare Safety and Standard Precautions Module • Safety/emergency procedures, including the Heimlich maneuver; • Promoting residents’ independence; and Healthcare Safety and Standard Precautions Module Legal Issues in Healthcare Module • Respecting residents’ rights. Legal Issues in Healthcare Module The curriculum must also include training in the following areas: 1. Basic nursing skills: a. Taking and recording vital signs; In Nursing Assistant Skills Set b. Measuring and recording height and weight; c. Caring for the residents’ environment; d. Recognizing abnormal changes in body functioning and the Communications in Healthcare Module importance of reporting such changes to a supervisor. Some examples of abnormal changes are: 1 • Shortness of breath; • Rapid respiration; • Fever; • Coughs; • Chills; • Pains in chest; • Blue color to lips; • Pain in abdomen; • Nausea; • Vomiting; • Drowsiness; • Excessive thirst; • Sweating; • Pus; • Blood or sediment in urine; • Difficulty urinating; • Frequent urination in small amounts; • Pain or burning on urination; and • Urine has` dark color or strong odor. e. Caring for residents when death is imminent. Awareness and Sensitivity to Client Needs Module 2. Personal care skills: 2 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Bathing; Grooming, including mouth care; Dressing; Toileting; Assisting with eating and hydration; Proper feeding techniques; Skin-care; and Transfers, positioning, and turning. Nursing Skills Set 3. Mental health and social service needs: a. Modifying aide’s behavior in response to resident’s Awareness and Sensitivity to Client Needs Module behavior; b. Awareness of developmental tasks associated with the aging process; c. How to respond to resident behavior; d. Allowing residents to make personal choices, providing and reinforcing other behavior consistent with the resident’s dignity; and e. Utilizing resident’s family as a source of emotional support. 4. Care of cognitively impaired residents: a. Techniques for addressing the unique needs and behaviors of individuals with dementia (Alzheimer’s and others); b. Communicating with cognitively impaired residents; c. Understanding the behavior of cognitively impaired residents; d. Appropriate responses to the behavior of cognitively impaired residents; and e. Methods of reducing the effects of cognitive impairments. 5. Basic Restorative Services - The nurse aide should be able to demonstrate skills which incorporate principles of restorative nursing, including: 3 a. Training the resident in self-care according to the resident’s Nursing Skills Set abilities; b. The use of assistive devices in transferring, ambulation, eating, and dressing; c. Maintenance of range of motion; d. Proper turning and positioning both in bed and chair; e. Bowel and bladder training; and f. Care and use of prosthetic and orthotic devices. 6. Residents’ Rights - The nurse aide should be able to demonstrate behavior that maintains residents’ rights, including but not limited to: a. Providing privacy and maintenance of confidentiality; Legal Issues in Healthcare Module b. Promoting the resident’s right to make personal choices to accommodate their needs; c. Giving assistance in resolving grievances and disputes; d. Providing needed assistance in getting to and participating in resident and family groups and other activities; e. Maintaining care and security of resident’s personal possessions; f. Providing care which maintains the resident free from abuse, mistreatment, and neglect, and reporting any instances of such treatment to appropriate facility staff; and g. Avoiding the need for restraints in accordance with current professional standards. 4 Awareness and Sensitivity to Client Needs Module Legal Issues in Healthcare Module