Lecture 18 Basics: Genes and Alleles Basic vocabulary Gene: Allele
advertisement
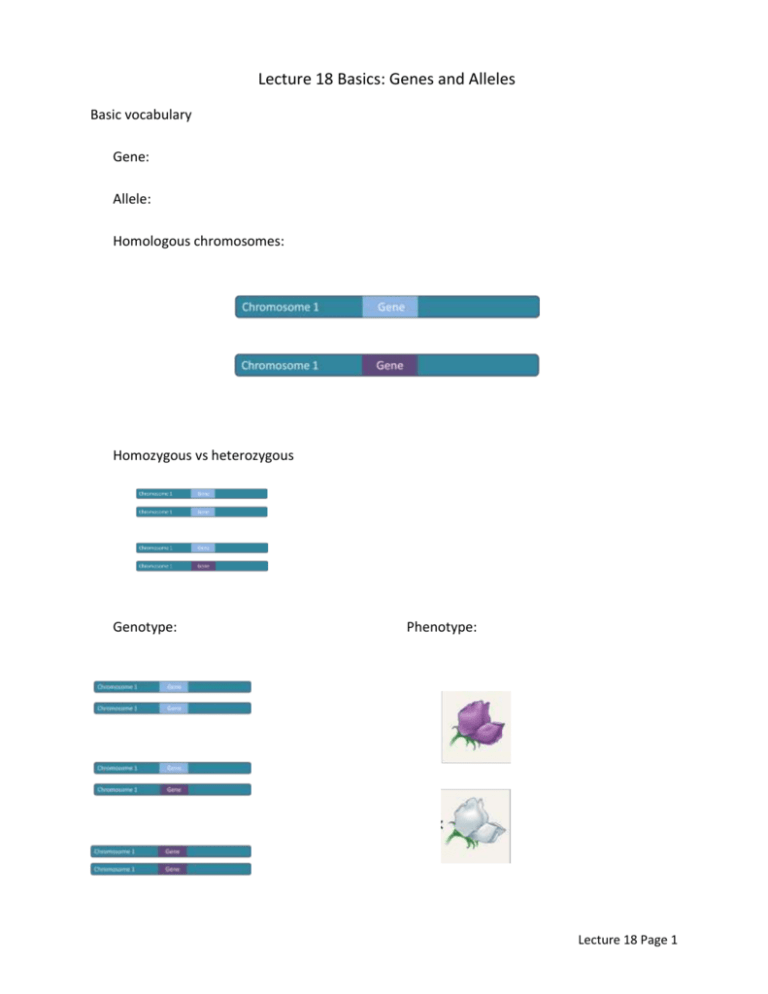
Lecture 18 Basics: Genes and Alleles Basic vocabulary Gene: Allele: Homologous chromosomes: Homozygous vs heterozygous Genotype: Phenotype: Lecture 18 Page 1 More vocabulary: P (Parental) generation: Gamete: F1 generation: F2 generation: True-breeding: Dominance As Mendel understood it: Offspring are purple Therefore, the “big P” purple allele is dominant to the “little p” white allele. Dominance Explained: Pigment that causes purple color: anthocyanin 2 Genes: transcription factor on one chromosome, enzyme gene on another chromosome The “Big P” allele Lecture 18 Page 2 The “Little p” allele Homozygous PP Homozygous pp Heterozygous Pp Dominant allele: Recessive allele: Lecture 18 Page 3 Punnett Squares Calculating Probabilities: Multiplication rule: Q: What is the probability that two pea parents that are heterozygous for flower color will have a homozygous recessive offspring? Addition rule: Q: What is the probability that two pea parents that are heterozygous for flower color will have a homozygous recessive offspring? Lecture 18 Page 4 18.5 The Test cross: determines genotype in an organism showing the dominant trait Given an unknown: Solution: Offspring if PP: Offspring if Pp: Lecture 18 Page 5 Practice problems: 1. In pea plants, spherical seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? ________________ 2. In guinea pigs, short hair is dominant to long hair (S,s). Use a Punnett square to determine the following. a. One guinea pig has long hair, the other is a heterozygote. What proportion of the offspring will have short hair? ________________ b. A litter of guinea pigs all have short hair. One parent has short hair, the other long hair. What is the genotype of the short haired guinea pig? ________________ 3. In humans, being a tongue-roller is dominant over non-roller (R, r). A man who is a non-roller marries a woman who is a heterozygous for tongue-rolling. a. What is the father’s phenotype? ________________ b. What is the father’s genotype? ________________ c. What are the possible gametes the father can give his offspring? ________________ d. What are the possible gametes the mother can give her offspring? ________________ e. What is the probability their child will be a tongue-roller? ________________ f. What is the probability that their first two children will be tongue-rollers? ______________ A decent set of more questions can be found here: http://www.iusd.org/uhs/apbiology/Unit%20Resources/Unit%205/Genetics%20Problems.pdf Lecture 18 Page 6 Class Notes: Learning Goal: Explain Mendelian genetics using modern cell biology explanations. Use your new understanding to create “new” definitions that explain using mutation, gene products, and pigment. Why are white pea flowers white? Old: They are homozygous for the recessive allele New: The recessive allele produces a nonfunctioning gene product What is true-breeding? Old: Parental phenotype remains the same after multiple generations New: In purple flowers, why does the F1 generation all look like the dominant parent? Old: Purple is dominant to white New: Learning Goal: Solve difficult monohybrid cross and probability problems quickly and correctly. In (oversimplified) humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue (b). A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of which are brown-eyed and one is blue-eyed. What is the genotype of the man? A. bb B. BB C. Bb Melanistic jaguars are black versions of the regular, spotted jaguar. The black trait is dominant. In 2006, a black jaguar named Diablo was inadvertently mated to a female lion named Lola at a wildlife sanctuary. The offspring were a black female and a spotted male jaglion. What was the genotype of Diablo? A. Homozygous dominant B. Homozygous recessive C. Heterozygous Lecture 18 Page 7 The following problem is an example of a dihybrid cross. Parental genotypes: GGww x ggWW What are the genotypes of the F1 generation? _______________ What is the probability that the F2 generation will have at least one dominant allele for each trait? Answer (broken into steps) a. What are the genotypes of the two parents? ________________________ _________________________ b. What is the probability of the offspring having at least one G allele? c. What is the probability of the offspring having at least one W allele? d. Do you add or multiply these probabilities? Explain why. What is the probability that the F2 generation will have at least one dominant allele for each trait? ________________ Apply what you’ve learned. For the parents below: AaBBCcdd x aaBbccDd What is the probability that the offspring will have at least one dominant allele for each trait? ________________ For the same parents, what is the probability that the offspring will be a aaBBccdd? ________________ Lecture 18 Page 8