Explanation Of Construction
advertisement

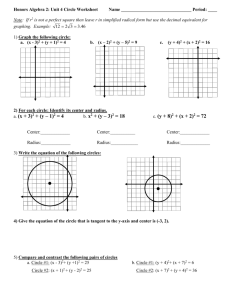
Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 CHAPTER WITH EXPLAINATION CONSTRUCTION 1. To construct a tangent to a circle at any point on it. Case - I : The centre of the circle is given Steps of construction : Let the point on the circle be P and centre of the circle be O. 1. OP is joined. 2. A line PT perpendicular to OP is drawn at P. 3. TP is produced to R. The line TR is the tangent to the circle at P. Case - II : When the centre of the circle is not known. Steps of construction : Let the point on the circle be P. 1. Any two points A and B is taken on the circle. 2. PA, PB and AB are joined. 3. On PA, is constructed equal to . 4. TP is produced to R. The line TR is the required tangent. 2. To construct tangents to a circle from a point outside it. Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 1 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 Case - I : The centre of the circle is known. Steps of construction: Let the given point be P outside the circle with centre O. i. OP is joined. ii. AB, the perpendicular bisector of OP is drawn intersecting OP at C. iii. Taking C as centre and CP as radius, a circle is drawn intersecting the given circle at Q and R. iv. PQ and PR are joined PQ and PR are the required tangents. Case - II : The centre of circle is not given. Steps of construction : Let the given point be P outside the circle. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A line through P is drawn into secting the circle at B and A. PA is bisected at C. Taking C as a centre and CP as a radius a semi- circle is drawn. At B, a line BD is drawn perpendicular to PA meeting the semi-circle at D. With P as centre and PD as radius two arcs are drawn cutting the given circles at Q and R. 6. PQ and PR are drawn. PQ and PR are the required tangents. 3. Two construct a direct common tangent to two circles. Steps of construction : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 2 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 i. ii. Two circles with centres A and B with given radius are drawn at a given distance. In the larger circle with centre B, a new concentric circle with radius equal to the difference of the radii of the given circles is drawn. iii. AB is bisected at C. iv. A semi-circle is drawn with C as the centre and AC as a radius, cutting new circle at D. v. BD is joined and produced to meet larger circle at Q. vi. A line AP parallel to BQ is drawn to meet smaller circle at P. vii. PQ is joined. PQ is the required direct common tangent to the circles. 4. To construct a transverse common tangent to two circles Steps of construction : i. Two circles with centres A and B with given radius are drawn at a given distance. ii. iii. iv. v. Outside the smaller circle with centre A, a new concentric circles is drawn with radius equal to the sum of the radius of two given circles. AB is bisected as C. With C as centre and AC as radius a semi-circle is drawn meeting the new circle at D. AD is joined which intersect smaller circle at P. Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 3 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 vi. vii. BQ is drawn parallel to AP to intersect bigger circle at Q. PQ is joined PQ is the required transversal common tangent to the circles. 5. To construct incircle of a triangle. Steps of construction : Let given triangle be ABC. i. Angle bisector of are drawn which inter set at I ii. I M is drawn perpendicular to AB. iii. Taking I as centre and I M as radius circle is drawn. This is the required incircle of . 6. To construct circumcircle of a given triangle. Steps of construction: Let given triangle be ABC. 1. Perpendicular bisectors of sides AB and BC are drawn which intersect at O. 2. Taking O as centre and OA as radius, a circle is drawn. This is the required circum circle of the triangle ABC which passes through A, B and C. 7. Construction of Regular Polygon in and about a circle i. Constructing of equilateral triangle in a circle Steps of Construction: Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 4 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. ii. iii. 2. Three radii OA, OB and OC are drawn such that angle between them is 1200 3. AB, BC and CA are joined. ABC is the required triangle in the circle. Construction of equilateral triangle about a circle. Steps of construction : 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. 2. Three radii OA, OB and OC are drawn such that angle between them is 1200 . 3. At A, B and C perpendiculars on OA, OB and OC are drawn respectively and they are produced to intersect at P, Q and R. Thus PQR is the required triangle To construct a square in a circle. Steps of constructions : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 5 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 1. A circle of given radius is drawn iv. v. 2. Two diameters AOC and BOD perpendicular to each other are drawn. 3. AB, BC, CD and DA are joined ABCD is the required square in the given circle. To construct a square about a circle. Steps of construction : 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. 2. Two diameters AOC and BOD are drawn perpendicular to each other. 3. At A, B, C and D, perpendiculars to OA, OB, OC and OD are drawn and produced to form a square PQRS. PQRS is the required square about the circle.. To construct a regular pentagon in a circle. Steps of construction : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 6 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. vi. vii. 2. Radii OA and OB are drawn such that . 3. Arcs BC, CD, and DE are cut off each equal to arc AB. 4. AB, BC, CD, DE and EA are joined. ABCDE is a required pentagon in a circle To construct a regular pentagon about a circle. Steps of construction : 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. 2. Radii OA and OB are drawn such that 3. Arcs BC, CD, DE and EA are cut off each equal to arc AB. 4. OC, OD and OE are joined 5. At A, B, C, D and E, perpendiculars on OA , OB, OC, OD and OE respectively are drawn and produced to form a pentagon PQRST. PQRST is the required pentagon. To construct a regular hexagon in a circle. Step of construction : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 7 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. 2. Radii OA and OB are drawn such that 3. Arcs BC, CD, DE, EF are cut off each equal to arc AB. 4. AB, BC, CD, DE, EF and FA are joined ABCDEF is the required hexagon in the given circle. viii. To construct a regular hexagon about a circle. Step of construction : 1. A circle of given radius is drawn. 2. OA and OB are drawn such that 3. Arcs BC, CD, DE and EF are cut off equal to arc AB. 4. OC, OD, OE and OF are joined 5. At A, B, C, D, E and F, perpendiculars are drawn on OA, OB, OC, OD, OE and OF respectively and produced to form hexagon PQRSTU. PQRSTU is the required hexagon. 8. TO construct a circle of given radius passing through two given points Steps of construction : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 8 Mathematics Class-X i. 2015-2016 Line segment AB of given length is drawn. ii. iii. iv. Perpendiculars bisector PQ of AB is drawn. With A as centre and given radius an arc is drawn to PQ at O. With O as centre and OA as radius circle is drawn. This is the required circle of given radius passing through A and B. 9. To construct a circle of given radius and touching two given intersecting lines Steps of construction : i. of given measurement is constructed. ii. BD is drawn bisector of . iii. A line EF parallel to BC is drawn at a given distance from BC. EF and BD intersect at O. iv. With O as centre and given radius circle is drawn touching AB and BC. 10. To construct a circle of given radius touching a given circle and a given line. Steps of construction : Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 9 Mathematics Class-X 2015-2016 1. EF is drawn parallel to AB at a given distance R from AB. 2. With C as centre and radius equal to (r + R) an arc is drawn to cut EF at O. 3. With O as centre and radius R a circle is drawn touching AB at P and circle with radius r at Q. Hence the circle drawn is the required circle. Sudheer Gupta . Be positive and constructive. Page 10