GTS 161 - PRACTICAL 2 – 2014 Additional questions NOT IN
advertisement

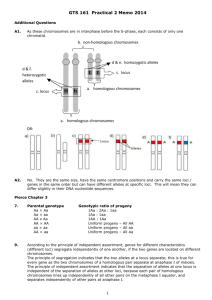
GTS 161 - PRACTICAL 2 – 2014 ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS NOT IN TEXTBOOK A1. Draw 2 pairs of chromosomes (in a non-dividing cell or G1 of interphase) and indicate the following on the diagram: a. homologous chromosomes b. non-homologous chromosomes c. locus d. alleles e. homozygotic alleles f. heterozygotic alleles A2. Are homologous chromosomes identical? If not, how do they differ? TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS CHAPTER 3 Comprehension Questions 7, 9, 10 (Not present in 4th Ed) 7. Give the genotypic ratios that may appear among the progeny of simple crosses (i.e. crosses for a single locus with only two different alleles), and the genotypes of the parents that may give rise to each ratio. 9. What is the principle of independent assortment? How is it related to the principle of segregation? 10. In which phases of mitosis and meiosis are the principles of segregation and independent assortment at work? Application Questions and Problems 15, 16, 18 a, b, c, 20, 25, 28, 31, 34 b, d, (4th Ed Q’s (no equiv of Q15) 4, 6 a, b, c, 7, 12, 15, 18, 20 b, d) 15. Figure 1.1 (page 2) shows three girls, one of whom has albinism (recessive disorder). Could the three girls shown in the photograph be sisters? Why or why not? 16. JW McKay crossed a stock melon plant that produced tan seeds with a plant that produced red seeds and obtained the following results. Cross F1 F2 tan ♀ x red ♂ 13 tan seeds 93 tan, 24 red seeds Explain the inheritance of tan and red seeds in this plant. Assign symbols for the alleles in this cross and give genotypes for all the individual plants. a. b. 18. a. b. c. 20. In cats, blood type A results from an allele (IA) that is dominant over an allele (iB) that produces blood type B. There is no O blood type. The blood types of male and female cats that were mated and the blood types of their kittens follow. Give the most likely genotypes for the parents of each litter. Male parent A B B Female parent B B A Kittens 4 with blood type A, 3 with blood type B 6 kittens with blood type B 8 kittens with blood type A Joe has a white cat named Sam. When Joe crosses Sam with a black cat, he obtains one-half white kittens and one-half black kittens. When the black kittens are interbred, they produce all black kittens. On the basis of these results, would you conclude that white or black coat colour in cats is a recessive trait? Explain your reasoning. 1 25. a. b. c. d. What is the probability of rolling one six-sided die and obtaining the following numbers? 2 1 or 2 An even number Any number but a 6 28. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disease that results from a recessive gene. Two normal parents produce a child with PKU. What is the probability that a sperm from the father will contain the PKU allele? What is the probability that an egg from the mother will contain the PKU allele? What is the probability that their next child will have PKU? What is the probability that their next child will be heterozygous for the PKU gene? a. b. c. d. 31. a. b. c. 34. b. d. In watermelons, bitter fruit (B) is dominant over sweet fruit (b), and yellow spots (S) are dominant over no spots (s). The genes for these two characteristics assort independently. A homozygous plant that has bitter fruit and yellow spots is crossed with a homozygous plant that has sweet fruit and no spots. The F1 are intercrossed to produce the F2. What will be the phenotypic ratios in the F2? If an F1 plant is backcrossed with the bitter, yellow-spotted parent, what phenotypes and proportions are expected in the offspring? If an F1 plant is backcrossed with the sweet, nonspotted parent, what phenotypes and proportions are expected in the offspring? The following two genotypes are crossed: AaBbCcddEe × AabbCcDdEe. What will the proportion of the following genotypes be among the progeny of this cross? Aa bb Cc dd ee AA BB CC DD EE ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS NOT IN TEXTBOOK A3. In humans there is a dominant gene (A) for the absence of moles. The allele (a) is recessive, and determines the presence of moles. A couple who are both heterozygous for this locus (Aa) plan to have five children. a. Expand the binomial (p + q)5. b. What is the probability that: (i) The first child that is born will have moles. (ii) All of the children will not have moles. (iii) The first two children will have moles and the last three will have no moles. (iv) Of the 5 children, 3 will have no moles and 2 will have moles c. Assume this couple now have two children, one with moles and one without moles. What is the probability that the child born without moles is a carrier of the a-allele (ie heterozygous)? A4. A sugarcane plant with wavy leaves and round pollen is crossed with a plant with wavy leaves and elongated pollen. Seed are collected and germinated. The following results are obtained in the progeny: 122 wavy leaves, round pollen 118 wavy leaves, elongated pollen 38 smooth leaves, round pollen 41 smooth leaves, elongated pollen (NB Hint: When two traits are involved, it is often easier to first consider the traits separately, convert the numbers to ratios for each locus on its own, and determine alleles, dominance and genotypes for each trait. Then combine these to give parental genotypes and work out the cross.) a. Assign symbols for the alleles of both these genes, indicate the dominance interaction between the two alleles, and give all possible genotypes and their associated phenotypes for each locus. b. Give the genotypes of the parents of this cross. c. Give the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the progeny of this cross. 2