notes for power point
advertisement

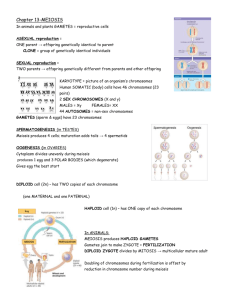
Meiosis (Gametogenesis) ___________________ have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. You have body cells and gametes. Body cells are also called ______________________________. __________________________________ cells develop into gametes. Germ cells are located in the ________________________ and _________________. __________________________ are sex cells: egg and sperm. Gametes have DNA that can be passed to offspring. Your cells have _______________________ and _____________________________. Your body cells have _______________________ of chromosomes. ____________________________ pairs of chromosomes have the same structure. For each homologous pair, one chromosome comes from each parent. Chromosome pairs 1-22 are _________________________. Sex chromosomes, _________ and ___________, determine gender in mammals Chromosomes You have 23 different pairs of chromosomes, for a total of________ chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair came from your mother and one from your father. Each chromosome in a pair is said to be ___________________, meaning that the chromosome from the father has a corresponding chromosome from the mother. Body cells are _________________; gametes are ______________________ Fertilization between egg and sperm occurs in sexual reproduction. Diploid (2n) cells have two copies of every chromosome. ___________________ are diploid. Half the chromosomes come from each parent. _________________ (n) cells have one copy of every chromosome ______________________ are haploid. Gametes have ____________ autosomes and____________ sex chromosome. Cells that contain both sets of homologous chromosomes are called_____________________ (2N). All of your cells except the _____________________ are diploid (2N). ________________ are haploid (N), meaning they contain only one copy of each chromosome. When one sperm and one egg combine their DNA, there are two versions of each chromosome. We use “N” to represent the haploid number of chromosomes and “2N” to represent the diploid number of chromosomes. For humans, the haploid number is ______________. We write this as N = 23. The diploid number is ____________, which we write as 2N = 46. In fruit flies, N = 4 and 2N = 8. Meiosis makes ______________ cells from ____________ cells Meiosis occurs in ____________________. Meiosis produces ____________________. 6-2 Meiosis Meiosis is the process that divides ______________ (2N) cell to form ________________ (N) cells. This process is a __________________________division because the number of chromosomes per cell are cut in half. _________________ is how gametes are formed. Cells go through two rounds of division in meiosis. Meiosis reduces chromosome number and creates _________________________ Meiosis I and meiosis II each have four phases, similar to those in mitosis. Pairs of __________________________________ separate in meiosis I. Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. _________________________________ divide in meiosis II. Sister chromatids are copies of the same chromosome. There are two divisions that occur in meiosis: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. 1. Before meiosis I begins, cells go through ____________________. 2. This involves DNA replication, forming a duplicate copy of each chromosome. 3. Each chromosome is made of two ____________________________. Meiosis I occurs after DNA has been ______________________ Meiosis I divides homologous chromosomes in four phases a. Prophase I: i. Centrioles are visible on opposite sides of the nucleus ii. Nucleolus disappears iii. Nuclear envelope breaks down iv. _____________________________________________________ pair 1. When a pair of chromosomes aligns a ______________________ is formed. 2. When chromosomes form a tetrad, they exchange portions of their chromatids in a process called _________________________________________ 3. Crossing-over produces _______________________________________ of DNA. b. Metaphase I: i. Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes at the centromere c. Anaphase I: i. Spindle fibers pull _____________________________________ toward opposite ends of the cell. ii. Chromosomes move and separate into two groups near the spindle iii. Anaphase ends when the chromosomes stop moving d. Telophase I i. Nuclear membranes form around chromosomes ii. Daughter nuclei form e. Cytokinesis Meiosis I produces ______________________ (2N) daughter cells. Each chromosome is made of two _________________________________. Meiosis II After Meiosis I, cells enter Meiosis II. No DNA replication occurs between Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Meiosis II separates the ______________________________________________. a. Prophase II: I. Centrioles are visible on opposite sides of the nucleus ii. Nucleolus disappears iii. Nuclear envelope breaks down b Metaphase II: I. Chromosomes align like they do in mitosis ii. Chromosomes are attached to the spindle at the centromere. c. Anaphase II: i________________________________ separate and move towards opposite ends of the cell. d. Telophase II: i. Nuclear membranes form around chromosomes ii. Daughter nuclei form e. Cytokinesis: f. Meiosis II - produces ________________________________ (N) daughter cells Gamete formation In male animals, the haploid gametes are called _____________________ In female animals, the haploid gametes are called ____________________ Meiosis differs from mitosis in significant ways. Meiosis has ___________________ cell divisions while mitosis has _____________________. In mitosis, ______________________________________________ never pair up. Meiosis results in ____________________________ cells; mitosis results in________________________________ cells. When the male and female gametes join, this is called ____________________________ and a _____________________________ is formed. Haploid cells develop into mature gametes. _______________________________________is the production of gametes. Gametogenesis differs between females and males. Sperm become streamlined and _______________________. Sperm primarily contribute ________________________to an embryo. Eggs contribute DNA, cytoplasm, and organelles to an embryo. During meiosis, the _________________ gets most of the contents; the other cells form ___________________________.