LAB Ionic and Covalent Compounds SOLUTIONS
advertisement

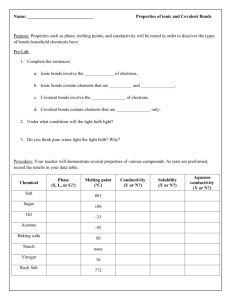
IONIC & COVALENT COMPOUND LAB Name: PURPOSE To compare the physical properties of ionic and molecular (covalent) solids HYPOTHESIS Based on your knowledge, which solid do you think is ionic and which is covalent? Explain Substance Ionic/Covalent? Why? ionic metal and a non-metal Covalent Soft, so it must have weaker attraction between molecules Ionic Metal and a non-metal Covalent Has a prefix in the name, therefore covalent. It is also a liquid at room temperature, therefore it must have a low melting point sodium chloride (s) paraffin wax (s) potassium carbonate (s) cyclohexane (l) unknown substance (s) MATERIALS Scoopula Conductivity tester Well plate Hot plate 4 test tubes small beaker Test tube rack Distilled water Sodium chloride (s) Paraffin wax (s) Potassium carbonate (s) Cyclohexane (l) (located in the fume hood) Unknown Substance (s) PROCEDURE ****No chemicals are to be placed down the drain as they will clog the drain. Use the disposal beaker at the front of the room. For the waxy substances, allow to cool and scrape contents into the garbage**** 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Create an observation table in which to record data about the odour, hardness, crystalline structure, melting point, solubility in water and conductivity in water for the 5 substances. Using the scoopulas, obtain a small amount of each substance into a small beaker to take back to your station. Use the wafting technique to make an observation about the odour for each solid. Use your scoopula to crush to compare for hardness. Determine if the solid has a crystalline structure by viewing it. Place a small amount of each solid side by side in a large beaker and put it on the hot plate. Turn on the hot plate. Observe and record what happens. Place a small amount of each solid in separate test tubes. Use a pipette and small beaker to take the distilled water to your lab bench. Add some distilled water. Shake or stir. Record your observations under “solubility” in water. Pour some solution from the test tube from step 6 into a separate well on the well plate. Use the conductivity tester. Record your observations. Clean your workstation and return all materials neatly (remember not to pour anything down the drain). Observations: Substance sodium chloride (s) paraffin wax (s) potassium carbonate (s) no odour Hard crystalline structure? Yes slight odour Soft No no odour Hard Yes strong odour N/A liquid Yes strong odour Hard no odour hardness cyclohexane (l) unknown substance (s) melting point High Does not melt Low Melts easily High Does not melt Very low liquid at room temp Low Melts easily solubility Soluble conductivity Conductive Not soluble Not Floats on top conductive Soluble Conductive Not soluble Forms bubbles on top like oil and water Not soluble Not conductive Not conductive ANALYSIS 1 2 3 4 What does a strong odour indicate about the ease with which the particles in the solid leave its surface? Which type of solid had the strong odour? A strong odour indicates that particles of a substance can easily leave the surface and float into the air where they can enter our nose. This suggests that there is a very weak attraction between particles of the substance with the strong odour. Covalent molecules have weak attractions between molecules, meaning covalent substances may have stronger odours. The cyclohexane and the unknown substance had very strong odours indicating that both of these substances are covalent. What does a low melting point indicate about the bonds between particles in a solid? Which type of solid had the low melting point? A low melting point indicates that there are weak attractions between particles in a solid. Covalent substances have weak attractions between molecules which mean they would have low melting points. In other words it would take little heat to cause molecules in a covalent substance to separate further apart to form a liquid. Cyclohexane has the lowest melting point because it was already a liquid at room temperature. The unknown substance and the wax also had low melting points as they both melted when heated on the hotplate. Based on your observations, which type of solid was harder? Explain. makes sense in that the sodium chloride and potassium carbonate were hard as they are both ionic compounds because of their make-up of a metal and non-metal. Ionic compounds are harder substances because of their crystalline structure that is made up of the positive and negative ions tightly packed together. The attraction between each ionic compound is strong because of the positive and negative charges that exist due to the exchange in electrons. The hardness of the unknown substance does not make that much sense as it shows more properties of a covalent bond as opposed to the ionic bond. From your observations to the above questions, which of the two types of solid (ionic/covalent) seems to have stronger forces of attraction between the particles? The ionic solids have stronger forces of attraction between particles because they are the harder solids, have very high melting points and do not release an odour. Covalent seem to have the weaker forces of attraction between particles because they are softer, have low melting points and release strong odours. CONCLUSION Briefly summarize your observations Substance Ionic/Covalent? sodium chloride (s) Ionic paraffin wax (s) Covalent potassium carbonate (s) Ionic cyclohexane (l) Covalent unknown substance (s) covalent Why? Because it is a metal and a non-metal, but also because it had no smell, was hard and had a crystalline structure. It also had a high melting point, was soluble and conducted electricity Because it was soft, had a slight smell, had a low melting point, was not soluble and did not conduct electricity Because it is a metal and a non-metal, but also because it had no smell, was hard and had a crystalline structure. It also had a high melting point, was soluble and conducted electricity Because it had a very strong smell, had a very low boiling point as it was a liquid at room temperature, also, it was not soluble and did not conduct electricity Because it had a very strong smell, had a low boiling point was not soluble and did not conduct electricity What did you learn? I learned how to distinguish between ionic and covalent substances. I learned that ionic substances have a stronger bond due to the fact that the elements give or take electrons, leaving charged ions to make up the hard crystalline structure that is hard to break up. These ionic substances are soluble and can conduct electricity due to the charged particles left after the electrons are exchanged. I learned that covalent substances have weak bonds because they share electrons and therefore the particles are easy to separate which allows for strong smells, lower melting points and softer substances.