year 9 gothic mid year assessment
advertisement

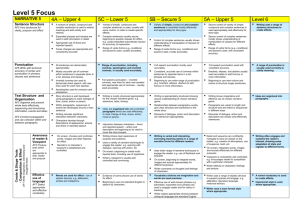
English Mid-Year Assessments – Year 9 What to expect You will have an exam which is in two parts: Section A: Reading Section B: Writing You will have 1 hour and 45 minutes to complete the task, so time your responses carefully! Section A: Reading: Timing: 15 minutes reading time, 45 minutes answering time. You will be given an extract from a novel, and four extended questions to answer. Top Tips Read the extract carefully. Take your time to read the question carefully and make sure you answer the question properly. If bullet points are given – use them to structure your answer. If it helps, highlight the text as you read it. Only use bullet points or a list in your answer if you are told to, otherwise write in sentences and paragraphs. Remember to use small quotations – write a little about a lot. Make sure that you explain your point using quotations or structural features. An explanation may include why the writer chose it, how it makes us think or feel, what ideas or themes it relates to. Remember to use SPEED paragraphs where applicable. Here are some useful sentence starters to remind you how to use it: Signpost: Firstly, secondly, later on, we also discover… Point: The character feels/thinks… The writer reveals… The atmosphere is Evidence: Use a short relevant quotation from the text Explanation: This implies/suggests/reveals/highlights/emphasises… Development: This could also infer/suggest…. This links to the idea later in the text……. Connective Firstly Secondly Thirdly As well as this Furthermore Moreover Finally Lastly Likewise Similarly The author / language in the text… Builds Connotes Contrasts Conveys Creates Demonstrates Describes Depicts Emphasises Evokes Exaggerates Expresses Gives the impression Gives a sense Highlights Informs Implies Indicates Narrates Realises Recognises Refers to Reflects Reveals Signifies Suggests Shows Tells The reader… (or ‘we’…) Is made aware Is informed Is told Learns Discovers Realises Read below for guidance about the types of questions you will be asked: Question 1 will ask you to locate and retrieve information. It will ask you to list information you have found from the text. Question 2: The effect of language features. You need to look out for: - Words and phrases: look for ones which show strong emotion or atmosphere. Remember, you will need to explain the effect using examples and quotations from the text. Language features: for example; similes, metaphors, personification, onomatopoeia, alliteration, assonance, pathetic fallacy, juxtaposition, etc. Look over your skills lists and exercise books remind you about what they mean. Question 3: - The effect of structure: for example; order of sentences and paragraphs, ellipsis, colons, hyphen, change in perspective, length of paragraphs, focus on specific or general detail, narrative voice, tenses, change of place and time, pattern repetition, chronological, cause and effect, problem and solution. Remember, the writer uses structure to focus the reader’s attention on certain things or emphasise similarities and/or differences between subjects. Question 4: - Impressions of characters or places. Choose a range of vocabulary to describe your impressions of characters. Explain why you have these impressions using quotations. Evaluate how these impressions are created using appropriate examples from the text. Remember to comment on the writer’s choices and their effects. Try to list a range of vocabulary you can use to describe emotions and/or impressions of character. Section B Writing You will be able to choose from two pieces of writing based on the theme of gothic horror. Both will ask you to use descriptive language. You only need to answer one. Top Tips - Descriptive writing Paragraphs are very important. Aim for three to six paragraphs Try to link some paragraphs using connectives Use descriptive language – use your senses, figurative language and powerful verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Check you are opening sentences in a variety of ways Do not use first person. E.g. Do not use ‘I’ Imagine you are a CCTV camera – zooming in and out and focus on a scene Include some gothic features such as contrasts of beauty and horror, fog, secrecy, luxury and wealth, androgyny, entrapment, colour, etc. Use a range of sentence types. Short, simple sentences can be very powerful Describe where things are in relation to each other. E.g. The chair is next to…above…under. You must try to be as accurate as possible with your spelling, punctuation and sentence structures. Include a range of punctuation – use commas and full stops and try to incorporate an exclamation mark and/or question mark. Use a varied and interesting vocabulary e.g. Do not use ‘Nice’ ‘Good’ ‘Bad’ ‘Boring’ ‘Weird’ Punctuation: You must be able to use punctuation correctly. Make sure you use at least 3 types of punctuation in any piece of writing. Practise writing a description or narrative in timed conditions. Focus on using correct punctuation. Full Stops: Use a full stop to end a sentence. A sentence is one idea. Read through your writing. Full stops should help it make sense. Commas: Commas are used to separate items on a list. Example: He was tall, thin and had piercing blue eyes. Commas are also used to separate clauses in a sentence. Example: As he walked into the room, all heads turned towards him. Exclamation marks: Use the exclamation mark when you are referring to a very strong emotion. Use it when something is being expressed and you’re very angry, very excited or very scared. Example: Dial 999 now! Question marks: Use a question mark when you are looking for an answer. A question mark is always used when asking a question. It is always used at the end of a sentence that asks a direct question. Example: Will you please pass me the butter? Apostrophe: The apostrophe has 2 functions. One is to show ownership. Example: John’s new shoes are red. An apostrophe is also used to show a word or letter(s) is missing: Example: Don’t go outside. (Do not) I’ll finish my homework later. (I will – I’ll) Paragraphs: Paragraphs are used to show a change of: Time, place, topic, person In order to make your writing flow, you need to link them. They can be linked by: • Using connectives (time, opposition, adding information, cause) • Repeat a key word or phrase • Re-word a key word or phrase • Use a pronoun like ‘these’ or that which refers to something or someone in the previous paragraph. Tenses: You must make sure you write in the correct tense. For example: I am revising for my exam = present tense I was revising for my exam = past tense. The following phrases are often written incorrectly. Remember: I/he/she/it was We/they/you were Vocabulary: You must make sure you use a range of vocabulary for effect. Use a thesaurus to find alternative words for the following: Good Bad Say Go Happy Sad Look at these different types of sentences. Try to identify them when you’re reading. Try to include them in your own writing. 1. A BOYS sentence has two parts. The first start ends with a comma, and the second part starts with one of the words: but, or, yet, so Examples: He was a friendly man most of the time, but he could become nasty. He could be really friendly, or he could be miserable. It was a warn day, yet the storm clouds gathered over the distant mountains. It was a beautiful morning for a walk, so he set off quite happily. 2. A 3 ED sentence begins with three related adjectives, each of which ends in ed. The words must be followed by commas. Most ed words are used to describe emotions. They are very good for telling your reader about the character and how they are feeling. Examples: Frightened, terrified, exhausted, they ran from the creature. Amused, amazed, excited, he left the circus reluctantly. 3. The emotion word, (comma) sentence starts with an adjective describing an emotion. It then describes some actions Examples: Desperate, she screamed for help. Terrified, he froze instantly on the spot where he stood. Anxious, they began to realise they were lost in the maze. 4. A many questions sentence usually starts with one of these words: WHO, WHAT, WHERE, WHEN, WHY, HOW, WHAT IF. Examples: Where is the treasure? The diamonds? The gold? The rubies? What if it rained? It poured? It thundered? It became story? 5. A De:de sentence is created by having two separate parts, which are separated by a colon. The first part of the sentence is description: the second part is detail. Examples: I was shattered: I hadn’t slept for more than three days. Hamsters are nocturnal: they sleep during the daytime. 6. A burger sentence is created by including a subordinate clause in the middle of a sentence. Examples: The grasshopper, who had been jumping all day, went to sleep. The children, quickly and quietly, returned to their seats. Now work through the literacy pack. Pay attention to those areas you know you need help with.