PP text
advertisement

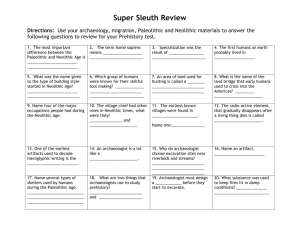
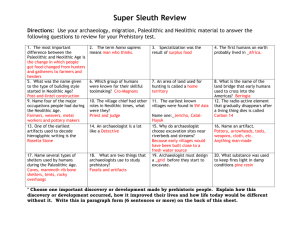
Civ IN- PowerPoint text from Lecture 1 Lecture 1B- Prehistory I) Evolution (?) II) Paleolithic Age III) Neolithic Age IDs: Epistemology Literalism Evolution fides et ratio hominids Ardi Paleolithic hunter/gatherer Tools Ancestor worship Neanderthal Cromagnon Great Ice Age Agricultural Revolution River plains societies Urban Revolution Debate over evolution Prof. Fitzgibbons Epistemology Debate: Literalist vs. Symbolic Catholic teaching? Humani Generis (1950) Humani Generis (1950) ...the Teaching Authority of the Church does not forbid that, in conformity with the present state of human sciences and sacred theology, research and discussions, on the part of men experienced in both fields, take place with regard to the doctrine of evolution, in as far as it inquires into the origin of the human body as coming from pre-existent and living matter—for the Catholic faith obliges us to hold that souls are immediately created by God. However this must be done in such a way that the reasons for both opinions, that is, those favorable and those unfavorable to evolution, be weighed and judged with the necessary seriousness, moderation and measure, and provided that all are prepared to submit to the judgment of the Church, to whom Christ has given the mission of interpreting authentically the Sacred Scriptures and of defending the dogmas of faithful. -Pius XII, Enc. Humani Generis, 36. Pope John Paul II on science and religion (speech to the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, 1979) “We cannot but deplore certain attitudes which have existed among Christians themselves, insufficiently attentive to the legitimate autonomy of science. Sources of tensions and conflicts, they have lead many minds to conclude that faith and science are mutually opposed.” (1979) Further statement (on science and religion in general): Fides et Ratio (1998) Pope John Paul II on evolution (1996) “Today, more than a half-century after the appearance of [Pius XII’s Humani Generis], some new findings lead us toward the recognition of evolution as more than an hypothesis.” Early hominids “Lucy” Approx. 3 million years ago Recent discovery Ethiopia- “Ardi” c. 4.4 million years ago Concurrent types of hominids II) Paleolithic Age Paleolithic Peoples 2.5m years BC- 10,000 BC “Old” + “stone” Discovery of fire- c. 500,000 BC Hunter/gatherer communities - followed herds - 20-30 individuals Moved from Africa to Europe and Asia Stressful life Paleolithic Shelters Paleolithic Era Inhabitants Homo sapiens- approx. 200,000 BC - 2 types #1- Neanderthals - 100,000 BC - 40,000 BC - similar practices - early language - hiactic bones - tools and graves? - “ancestor worship” Neanderthal burial Cave Paintings Paleolithic Era Inhabitants Homo sapiens- approx. 200,000 BC - 2 types #1- Neanderthals - 100,000 BC - 40,000 BC - similar settlement patterns,practices - early spoken language - early religion- “ancestor worship” #2 Cromagnon (homo sapiens sapiens)c. 250,000- 10,000 BC - one-armed skeleton (adult male) -meaning? III) Neolithic Age Neolithic Changes Began after the end of the Great Ice Age (40,000- 10,000 BC) Food moved north Mild and damp climates Revolution #1: Agricultural Revolution 1st Major change: Agricultural Revolution - 7,000 or 8,000 years BC - domestication - gamble - payoff Neolithic creations Neolithic burial Urban Revolution Earliest (?)- Satal Huyuk (Catal Hüyük)- c. 7000 BC Around 6,000 residents Agricultural Revolution: Locations 5 possible sites (concurrent) “Civilization” and the Urban Revolution: 4 basic components Political - irrigation→ organization Religious - elemental gods Economic/social - surplus - specialization Cultural - pictographs