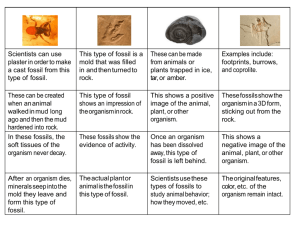
Evidence For Evolution V2 Biological evolution is defined as . There
advertisement
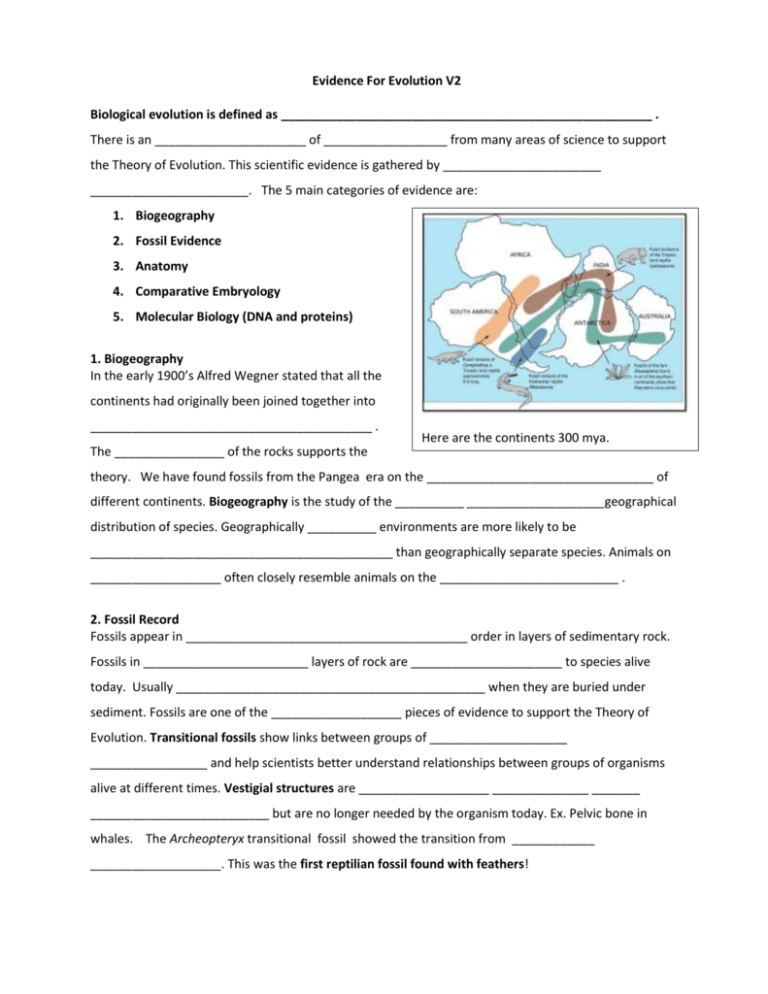
Evidence For Evolution V2 Biological evolution is defined as ______________________________________________________ . There is an ______________________ of __________________ from many areas of science to support the Theory of Evolution. This scientific evidence is gathered by _______________________ _______________________. The 5 main categories of evidence are: 1. Biogeography 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Anatomy 4. Comparative Embryology 5. Molecular Biology (DNA and proteins) 1. Biogeography In the early 1900’s Alfred Wegner stated that all the continents had originally been joined together into _________________________________________ . The ________________ of the rocks supports the Here are the continents 300 mya. theory. We have found fossils from the Pangea era on the _________________________________ of different continents. Biogeography is the study of the __________ ____________________geographical distribution of species. Geographically __________ environments are more likely to be ____________________________________________ than geographically separate species. Animals on ___________________ often closely resemble animals on the __________________________ . 2. Fossil Record Fossils appear in _________________________________________ order in layers of sedimentary rock. Fossils in ________________________ layers of rock are ______________________ to species alive today. Usually _____________________________________________ when they are buried under sediment. Fossils are one of the ___________________ pieces of evidence to support the Theory of Evolution. Transitional fossils show links between groups of ____________________ _________________ and help scientists better understand relationships between groups of organisms alive at different times. Vestigial structures are ___________________ ______________ _______ __________________________ but are no longer needed by the organism today. Ex. Pelvic bone in whales. The Archeopteryx transitional fossil showed the transition from ____________ ___________________. This was the first reptilian fossil found with feathers! 3. Anatomy Homologous structures are structures that have _______________________ _________ but have different functions now. Ex. Bat ________________ ___________________ . Analogous structures are structures that perform a similar function now but ____________________ _________________ Ex. _____________ wings and ______________ wings 4. Comparative Embryology This is the study of ______________________ during embryonic development. Similarities in development are indicative of ___________ ____________________. Historical note: “Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny.” For example, all vertebrate embryos have structures called pharyngeal pouches in their throat at some stage in their development. These embryonic structures develop into very different, but still homologous, adult structures, such as __________________________________. 5. Molecular Biology By comparing the DNA of different organisms, scientists can determine their _________________ ________. Each DNA gene controls the _____________________________________. Proteins control the _______________________________ of an organism. Here scientists compare the amino acid sequences that make up the hemoglobin protein in different organisms. The ___________ ______________________ of a protein depends on the ______________________________________ in the DNA (GCAT). In conclusion the major areas of evolutionary evidence are ___________________ to make the best theory for evolution of a specific organism or to decide on a family tree. Evidence For Evolution V2 Biological evolution is defined as the genetic change in a population of an organism over time. Scientific evidence is gathered by observing the world around us. There is an abundance of evidence from many areas of science to support the Theory of Evolution. The five main categories of evidence are: 1. Biogeography 2. Fossil Evidence 3. Anatomy 4. Comparative Embryology 5. Molecular Biology (DNA and proteins) 1. Biogeography In the early 1900’s Alfred Wegner stated that all the continents had originally been joined into one super continent called Pangea. We have found fossils from this era on the corresponding locations of different continents. The geology of the rocks also supports the theory. Biogeography is the study of the past and present geographical distribution of species. Geographically close environments are more likely to be populated by related species than geographically separate species. Animals on islands often closely resemble animals on the closest continent 2. Fossil Record Fossils appear in chronological (time) order in layers of sedimentary rock. Fossils in young layers of rock are more similar to species alive today. Usually only bones form fossils when they are buried under sediment. Fossils are one of the strongest pieces of evidence to support the Theory of Evolution. Transitional fossils show links between groups of prehistoric organisms and help scientists better understand relationships between group of organisms alive at different times. Vestigial structures are reduced forms of structures that once were useful in ancestors but are no longer needed by the organism today. Ex. Pelvic bone in whales The Archeopteryx transitional fossil showed the transition from reptile to bird. This was the first reptilian fossil found with feathers! 3. Anatomy Homologous structures are structures that have similar parts and a common ancestry or origin but have different functions now. Ex. Bat wings and human hands Analogous structures are structures that perform a similar function now but do not have a common evolutionary origin. Ex. Insect wings and bat wings 4. Comparative Embryology This is the study of structures that appear during embryonic development. Similarities in development are indicative of common ancestry. Historical note: “Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny.” For example, all vertebrate embryos have structures called pharyngeal pouches in their throat at some stage in their development. These embryonic structures develop into very different, but still homologous, adult structures, such as the gills of fish or the Eustachian tubes in mammals. 5. Molecular Biology By comparing the DNA of different organisms, scientists can determine their degree of relatedness. Each gene controls the production of a protein from amino acids. Proteins control the structure and function of an organism. Scientists compare the amino acid sequences that make up the hemoglobin protein in different organisms. The amino acid sequence of a protein depends on the nitrogen base sequence in the DNA (ex. GCATTGA).