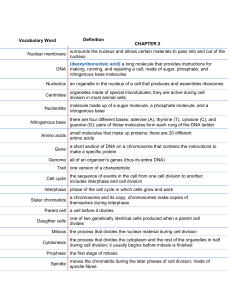
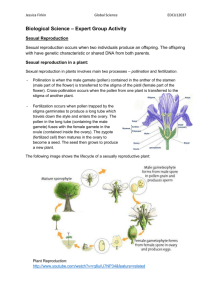
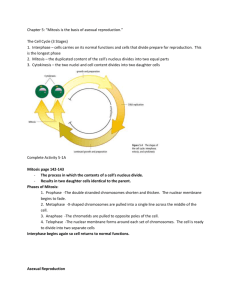
LO: Describe the difference between Asexual and Sexual
advertisement
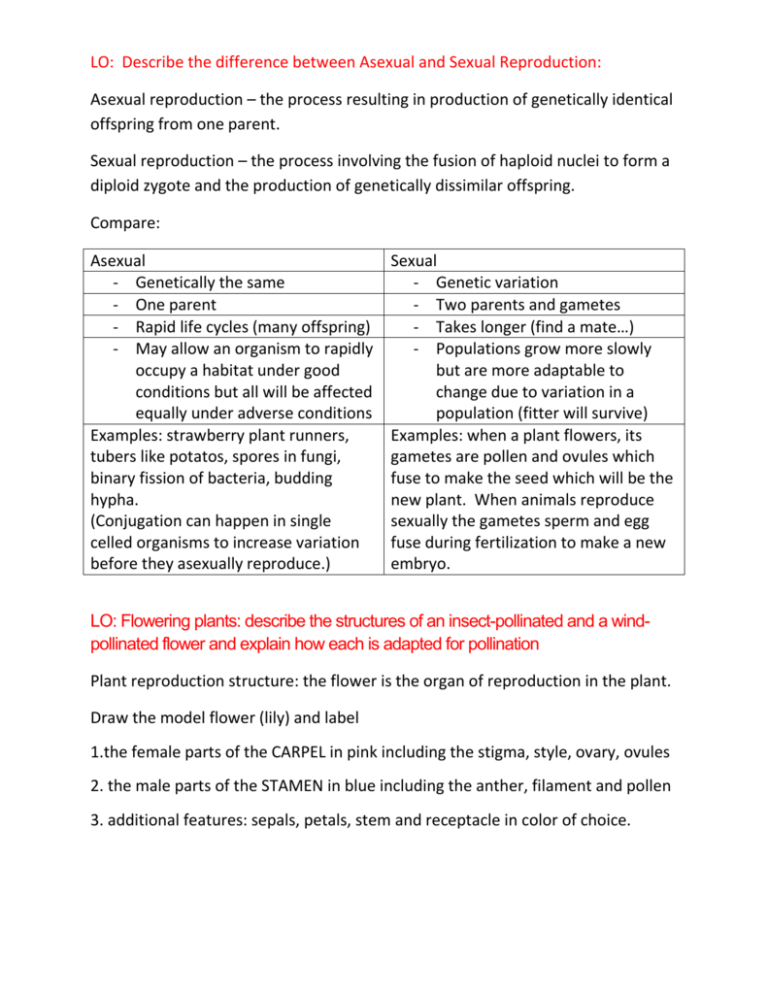
LO: Describe the difference between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction – the process resulting in production of genetically identical offspring from one parent. Sexual reproduction – the process involving the fusion of haploid nuclei to form a diploid zygote and the production of genetically dissimilar offspring. Compare: Asexual - Genetically the same - One parent - Rapid life cycles (many offspring) - May allow an organism to rapidly occupy a habitat under good conditions but all will be affected equally under adverse conditions Examples: strawberry plant runners, tubers like potatos, spores in fungi, binary fission of bacteria, budding hypha. (Conjugation can happen in single celled organisms to increase variation before they asexually reproduce.) Sexual - Genetic variation - Two parents and gametes - Takes longer (find a mate…) - Populations grow more slowly but are more adaptable to change due to variation in a population (fitter will survive) Examples: when a plant flowers, its gametes are pollen and ovules which fuse to make the seed which will be the new plant. When animals reproduce sexually the gametes sperm and egg fuse during fertilization to make a new embryo. LO: Flowering plants: describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and a windpollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination Plant reproduction structure: the flower is the organ of reproduction in the plant. Draw the model flower (lily) and label 1.the female parts of the CARPEL in pink including the stigma, style, ovary, ovules 2. the male parts of the STAMEN in blue including the anther, filament and pollen 3. additional features: sepals, petals, stem and receptacle in color of choice. LO: Describe the difference between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction – the process resulting in production of genetically identical offspring from one parent. Sexual reproduction – the process involving the fusion of haploid nuclei to form a diploid zygote and the production of genetically dissimilar offspring. Compare: Asexual - Genetically the same - One parent - Rapid life cycles (many offspring) - May allow an organism to rapidly occupy a habitat under good conditions but all will be affected equally under adverse conditions Examples: strawberry plant runners, tubers like potatos, spores in fungi, binary fission of bacteria, budding hypha. (Conjugation can happen in single celled organisms to increase variation before they asexually reproduce.) Sexual - Genetic variation - Two parents and gametes - Takes longer (find a mate…) - Populations grow more slowly but are more adaptable to change due to variation in a population (fitter will survive) Examples: when a plant flowers, its gametes are pollen and ovules which fuse to make the seed which will be the new plant. When animals reproduce sexually the gametes sperm and egg fuse during fertilization to make a new embryo. LO: Flowering plants: describe the structures of an insect-pollinated and a windpollinated flower and explain how each is adapted for pollination Plant reproduction structure: the flower is the organ of reproduction in the plant. Draw the model flower (lily) and label 1.the female parts of the CARPEL in pink including the stigma, style, ovary, ovules 2. the male parts of the STAMEN in blue including the anther, filament and pollen 3. additional features: sepals, petals, stem and receptacle in color of choice.