Name: Date: Section: Body systems study guide Systems to know
advertisement

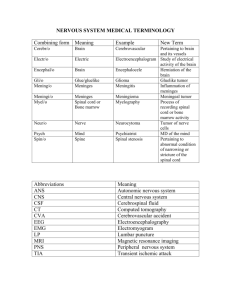
Name: Date: Section: Body systems study guide Systems to know: Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, nervous system, excretory system Concepts to know: How do cells impact body systems? Cells that work together to perform a certain function form a tissue. tissues that work together to perform a specific function form organs organs that work together to perform a specific function form systems Organs perform a specific job Examples include: brain, stomach, heart, lungs Each organ in the body is part of an organ system or a group of organs that work together Know and explain the function and parts of each system: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: FUNCTION:To transport oxygen, nutrients and wastes through the blood and to the cells. PARTS: HEART, capillaries, arteries, veins, plasma, Platelets, red blood cells, white blood cells Heart: the main organ of the system, pumps blood throughout the body Plasma- liquid part of blood that carries nutrients from the digestive system and moves chemicals throughout the body Red blood cells- shaped like a disc, carry oxygen White blood cells-different sizes, protect the body from germs Platelets- form irregular shapes, form blood clots Arteries: carry blood Away from the heart Veins: carry blood to the heart Capillaries: Connect arteries and veins RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: FUNCTION: To bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide (CO2) PARTS: LUNGS, trachea, bronchi, alveoli Trachea- or windpipe Alveoli- where the gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Found at the end of the smallest bronchi tubes, they are tiny, thin walled sacs of lung tissue where gases can move between air and blood. Bronchi- air moves from the trachea into the left and right bronchi, which takes air into the lungs. Lungs- main organs of the respiratory system. Inside the bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: FUNCTION:To break down food into nutrients and to get the nutrients into the blood. PARTS: Stomach, liver, esophagus, small intestines, villi, large intestines Mechanical and chemical digestion: Mechanical digestion- example: chewing food in your mouth. Teeth crushes the food into pieces. Chemical digestion- example: saliva breaks down food in your mouth, and acids break down food in your stomach Esophagus: peristalsis occurs here (muscles that help push the food down your esophagus), it’s a long tube that leads to the stomach Stomach- chyme (slushy milkshake of all the food you ate is broken down) -gastric juices: contain ac ids and chemicals that help break down food further once it gets to the stomach Small intestine- most digestion occurs here – molecules pass through villi into the bloodstream here (very long about 20 feet) Liver- produces bile which helps break down fats into smaller pieces to be digested more easily Large intestine- forms solid wastes, absorbs nutrients and water Gall bladder- stores bile Rectum- stores wastes Anus-area where waste exists Villi- part of the small intestines that absorb nutrients Pancreas- contains chemicals that help finish digestion EXCRETORY SYSTEM: FUNCTION: To remove wastes from the blood and body. PARTS: Bladder, kidneys, ureters, nephrons Urea- one of the wastes your body must eliminate. This is a chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins Urine- remaining water is eliminated in fluid called urine which includes urea and other wastes Nephrons- tiny filter in the kidneys that collect waste from the blood. The waste is called urea. Ureters- the urine slides down the ureters to the bladder where it is then released through another tube called the urethra Kidneys- regulate the amount of water in your body, filter blood, and help maintain internal stability NERVOUS SYSTEM: FUNCTION: To direct your movements -The nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It directs how y our body responds to this information, and helps the body maintain homeostasis. PARTS: brain, spinal cord, nerves Brain- control center Spinal cord- thick column of nervous tissue that links the brain to the peripheral nervous system, most impulses from the peripheral nerves travel through the spinal cord to get to the brain Nerve- a bundle of nerve fibers Synapse- the place where a neuron transfers an impulse to another structure Neurons- cells that carry information through the nervous system Central Nervous System: controls the functions of the body. The central nervous system includes your brain and spinal cord and acts like a traffic cop. Peripheral nervous system: a network of nerves that branches out from the central nervous system and connects it to the rest of the body. It is involved in both involuntary and voluntary actions.