NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
advertisement

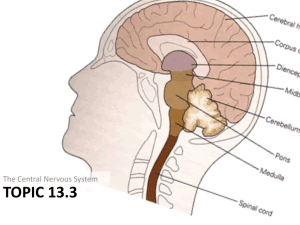
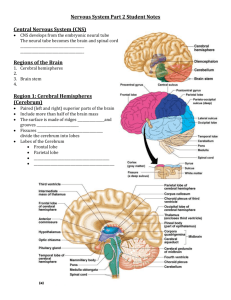
NERVOUS SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Combining form Meaning Example Cerebr/o Brain Cerebrovascular Electr/o Electric Encephal/o Brain Gli/o Mening/o Glue/gluelike Meninges Meningi/o Myel/o Meninges Spinal cord or Bone marrow Neur/o Nerve Psych Spin/o Mind Spine Abbreviations ANS CNS CSF CT CVA EEG EMG LP MRI PNS TIA New Term Pertaining to brain and its vessels Electroencephalogram Study of electrical activity of the brain Encephalocele Herniation of the brain Glioma Gluelike tumor Meningitis Inflammation of meninges Meningioma Meningeal tumor Myelography Process of recording spinal cord or bone marrow activity Neurocytoma Tumor of nerve cells Psychiatrist MD of the mind Spinal stenosis Pertaining to abnormal condition of narrowing or stricture of the spinal cord Meaning Autonomic nervous system Central nervous system Cerebrospinal fluid Computed tomography Cerebrovascular accident Electroencephalography Electromyogram Lumbar puncture Magnetic resonance imaging Peripheral nervous system Transient ischemic attack ASSOCIATED PREFIXES AND SUFFIXES A, AN, IN WITHOUT, ABSENCE OF DYS PAINFUL, DIFFICULT EU GOOD, NORMAL HEMI HALF INFRA POSITIONED BENEATH ISO SAME, EQUAL POLY MANY, MUCH PARA NEAR, SURROUNDING, TWO LIKE PARTS QUADRI FOUR AL, IC, OUS PERTAINING TO ALGIA PAIN CELE HERNIA CYTE CELL ECTOMY EXCISION OF GRAPHY PROCESS OF RECORDING IATRIST/OLOGIST SPECIALIST IT IS INFLAMMATION OMA TUMOR OSIS ABNORMAL CONDITION OTOMY INCISION INTO PARESIS SLIGHT/PARTIAL PARALYSIS PATHY DISEASE PHAGIA EATING, SWALLOWING PHASIA SPEECH PLEGIA PARALYSIS MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY NERVOUS SYSTEM RELATED NERVOUS SYSTEM TERMS Phobia Ment Mnes Algesia Praxia Di Sthenia Lexia Atel/o Fear Mind Memory Sense of pain Action Two Strength Diction Imperfect Lalia Thym Hypno Mania Phthisis Tripsy Noia Lemma Mimetic Pheo Polio Pyro Chrom/a/o Sympath Concuss To talk Mind, emotion Sleep Madness A wasting Crushing Mind Sheath, husk, rind Mimic, imitate Dusky Gray Fire Color Sympathy To shake or be shaken up ANATOMICAL NERVOUS SYSTEM “WORDBYTES” Arachn Astro Cyt/e Cerebell/o Cerebro Cordo Crani Disk Dur Ganglion Hydro Oligo Dendro Rachio Radico Radicul Spondylo Trephinat Vago Ventriculo Cisterno Spider Star-shaped Cell Little brain Cerebrum Cord Skull Disk Dura, hard Knot Water Little Tree Spine Root Root Vertebra A bore, a hole Vagus, wandering Little belly Reservoir, cavity PATHOLOGY OF THE HEAD, BRAIN, MENINGES CELPHALAGIA MIGRAINE HEADACHE ENCEPHALOCELE/CRANIOCELE MENINGIOCELE HYDROCEPHALUS MENINGITIS Headache Syndrome characterized by sudden, severe, sharp headache usually present only on one side Congenital gap in skull with herniation of brain substance Protrusion of the membranes of the brain or spinal cord through a defect in the skull or spinal column Abnormally increased amount of CSF within the brain Inflammation of meninges of brain/spinal cord DISORDERS OF THE BRAIN ALZHEIMER’S (AD) Group of disorders associated with degenerative changes in the brain COGNITION Mental activities – thinking, learning and memory ENCEPHALITIS Inflammation of the brain PARKINSON’S (PD) Chronic, slowly progressive, degenerative CNS disorder. Fine muscle tremors, masklike facial expression, shuffling gait (walking) TETANUS Tet – lockjaw – acute and potentially Immunization can prevent it. fatal bacterial infection of the CNS caused by tetanus bacillus. BRAIN INJURIES AMNESIA Memory disturbance – lack of recall CONCUSSION (concuss – shaken together) Shake/jar brain CEREBRAL CONTUSION Bruising of brain tissue CRANIAL HEMATOMA Collection of blood trapped in brain tissue. Named for location – epidural, subdural, intracerebral ALTERED STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS Conscious Alert, awake, aware and responding Syncope Lethargy Stupor Coma Comatose – one who is in coma appropriately Fainting, brief loss of consciousness caused by brief apnea in brain Lowered level of consciousness marked by listlessness, drowsiness and reduced level of activity State of impaired consciousness marked by a lack of responsiveness to environmental stimuli Deep state of unconsciousness marked by absence of spontaneous eye movements, no response to painful stimuli and no vocalization. DELIRIUM – Potentially reversible condition often associated with high fever that comes on suddenly in which the patient is confused, disoriented and unable to think clearly. DEMENTIA – Slow, progressive decline in mental abilities including memory, thinking, judgment and the ability to pay attention. STROKES STROKE – CVA TIA – transient ischemic attack ISCHEMIC STROKE –most common type In elderly persons – affects cerebrum and damages movement, language, senses control APHASIA = without speech “a” “phasia” HEMORRHAGIC STROKE – less common, but more deadly stroke. Damage or death of brain tissue caused by interrupted blood flow by clot or vessel rupture Temporay interruption in blood flow to brain. Sx – weakness, dizziness, balance off. Sx may pass or may be stroke warning Carotid artery narrowed blocking blood to brain or cerebral thrombosis in which a thrombus (clot) blocks the artery. Loss of ability to speak, write or comprehend the written or spoken word A “bleed” – brain vessel leaks or ruptures Affects brain areas damaged by leaking blood SLEEP DISORDERS – 1. Insomnia – prolonged or inability to sleep. 2. Narcolepsy – syndrome with recurrent, uncontrollable seizures of drowsiness or sleep. “narco”=stupor “lepsy” = seizure 3. Somnambulism – noctambulism – “sleepwalking” – condition of walking without awakening. “somn” = sleep “ambul” – to walk “ism” condition of 4. Somnolence – condition of unnatural sleepiness or semiconsciousness approaching coma. Person can usually be aroused by verbal stimuli. MEDICAL SPECIALTIES RELATED TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Anesthesiologist = MD Anesthetist = Nurse - Administers anesthetic agents before and during surgery. “an”-without “esthesi”-feeling “ologist” – specialist. 2. Neurologist – Specialist – diagnoses (dx) and treats (tx) nervous system disorders. Neurosurgeon – Specialist - surgery on the nervous system. 3. Psychiatrist – Specialist – MD who dx and tx emotional problems, chemical dependencies and mental illness. 4. Psychologist – Nonmedical degree – evaluates/tx emotional problems.