Atmospheric Circulation: Wind & Pressure Worksheet
advertisement
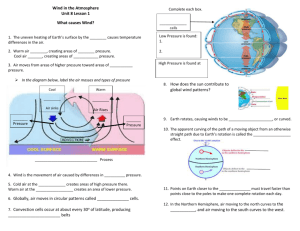
Atmospheric Circulation Wind & Pressure 1. The atmosphere is a ____________________of gases 2. Wind is the ____________________ of these gases 3. Named for the direction they come _________________ 4. Gases move from areas of _________________pressure to areas of ________________ pressure 5. Low pressure centers are also called C_______________ (_______________clockwise*) 6. High pressure centers are also called _______________________(clockwise*) 7. _____________ Pressure causes air to ______________ & generally takes water vapor up = • Clouds and __________________ 8. _____________Pressure causes air to sink & generally keeps moisture _________ of the atmosphere= • Clear skies & ______________ weather 9. Winds ________________ move from ___________ pressure areas to ___________ pressure areas!!!!!!! Convection 10. Air is __________________at the _________________. Warm air ______________. 11. Air is _______________ higher in the __________________. Cold air ________________. Local Winds 12. Local winds are caused either by ______________________effects (mountains and land) or variations in ____________________composition (near _________________) Land and Sea Breezes 13. Coastal Areas During the day, land heats up quicker than the water The heated air above the land expands and rises=LOW pressure Colder air over the water is denser= HIGH pressure Pushes into land= ______________ ___________________ 14. Coastal Areas • Land cools faster than water • The air above the water is warmer = LOW pressure • Air above the land is cooler= HIGH pressure. • Making a _________________ _______________________ Mountain and Valley Breezes 15. Valley Breeze: During the ___________, the valley floor heats up and air above it does too. Warm air __________ up the mountain. Air _____________ as it goes up in elevation & _____________ may form. 16. Mountain Breeze: After sunset the pattern _________________. As slopes cool, nearby air cools and _______________down the mountain. Global Winds 17. _____________________ heating and cooling of the atmosphere from continents and _________________ creates high and low air pressures. Add in the ____________________of the Earth and global wind patterns emerge. 18. On a hypothetical ________-_______________ planet with a __________________surface of either _______ land or all _________________, two large thermally produced ____________ would form. 19. Air would warm and_____________ at the equator and cool and _____________ at the poles. Coriolis Effect 20. The Coriolis Effect describes the ____________________ __________________ of an object based on the _________________________ of the _____________ below it. 21. Objects appear to deflect to the ________________ in the northern hemisphere and to the ____________in the southern hemisphere 22. When the effect of _______________ is added to the global circulation model, the ________-cell convection system breaks down into ___________smaller cells. 23. These cells lead to the formation of the global ______________ _________________. Wind Belts 24. _______________ Winds are two belts of winds that blow from __________________ directions at latitudes from ______ to ________ north and south. They contain ______________ moist, rising air that result in _________ pressure. 25. _____________________ are the prevailing winds that blow ____________ to __________ in the middle latitudes from ________ to ________ north and south. 26. The ____________________ wind is the wind that blows more often from one direction than from any other. In the United States, the ______________________consistently move weather from west to east across the continent. 27. Polar __________________ are the winds that blow from polar _________ to sub-polar ________. From _________ to _________ north and south. They are _______ and ________ air masses Windless Belts 28. ____________________ occur where ____________________ trade winds meet at the equator (O latititude) create _________________ areas. 29. ________________ latitudes __________________ westerlies and trade winds (easterlies) create _______________ areas at approximately 30o latitude. Jet Stream 30. Jet streams form at boundaries between ______________________ cells; they are _____________ speed winds that blow in upper ____________________and lower ________________________.