EXAM REVIEW 2015
advertisement

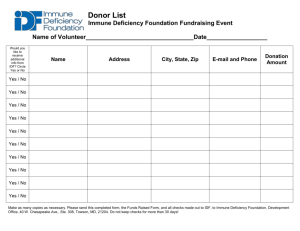
EXAM REVIEW 2015 – BIOLOGY 30S EXAM DATE: Tuesday June 16th 9:00am Red Gym The following is an outline of topics you should review for the exam. The exam will consist mostly of multiple choice and long answer questions. It would be VERY wise to review previous tests for the exam. This review is by no means ‘the exam’. Please refer back to the notes, assignments, labs, tests and quizzes to better prepare yourself! You will have 4-5 review periods. My suggestion to you is that you aim to cover one-two units per review period. We have covered the following units this year, please be prepared to answer questions pertaining to each of them! Good luck studying 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Homeostasis Respiratory system Circulatory system Immune system Digestive system Nervous system Urinary system Students who complete this review in its entirety by Tuesday June 9th may earn up to 3% BONUS on their final exam. The review must be hand written. Reviews that are copied in ANY WAY from another student will be given a mark of zero. Answers to all questions will be found in your notes, labs and assignments. I. HOMEOSTASIS *TEST: Wellness & Homeostasis *LAB: Osmosis & Diffusion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. II. Major Concepts Define Homeostasis Describe each of the following: Osmoregulation, thermoregulation, waste management and how they help maintain homeostasis. Explain and provide an example of the negative feedback cycle (Include: negative feedback loops for thermoregulation) What is the difference between an effector and a receptor? Identify the effector and receptor in thermoregulation. List the essential life processes that all cells require (Include: obtain food, convert energy, eliminate wastes, reproduce, grow and repair, transport substances) Describe the movement of materials into and out of cells (passive transport, osmosis, diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis Identify factors that influence the movement of substances across a membrane.(Include: size of molecule, concentration gradient, temperature, polarity of molecules) Be prepared to relate the theme ‘Homeostasis’ to any of the systems we have studied this year. THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM *TEST: Circulatory System *LAB: Circulation in a fish tail *LAB: Blood typing *LAB: Heart Dissection Major Concepts 9. LABEL the external and internal anatomy of the heart. 10.Explain the various functions of the circulatory system. 11.Be able to identify/describe the pericardium, myocardium, endocardium. 12.Be able to identify/describe the various valves in the heart (bicuspid, tricuspid, semilunar) 13.Describe the major differences between the anatomy and function of a vein, artery, capillary, arteriole and venule. 14.Why are veins able to carry blood back to the heart? 15.What aspect of the capillaries enables nutrients, oxygen, CO2 and wastes to diffuse? 16.Outline the pathway of blood through the heart. 17.Outline the pathway of blood through the following circulatory branches: pulmonary circulation, renal circulation, hepatic portal circulation. 18.Explain the difference between pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation and coronary circulation. 19.Explain the heart beat cycle (Diastole vs. Systole) 20.List several causes of high blood pressure 21.List the various components of the blood and describe their main function. 22.Explain the differences between veins, arteries and capillaries in terms of their elasticity, muscle layers, valves and what they transport. 23.State what antigens and antibodies are present in persons with type : A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, O- blood 24.Which blood type is the universal donor and why? 25.Which blood type is the universal recipient and why? 26.What is agglutination and what are the physiological consequences? 27.Why is the Rh factor and where is it suspected to have originated? 28.Why is it important to know the RH factor of a woman? Explain the risks of having the Rh factor in your second pregnancy. III. THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM *TEST – Respiration Major Concepts 29.LABEL the anatomy of the respiratory system including: lungs, nasal cavity, epiglottis, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, diaphragm, pharynx, larynx, trachea, uvula, ribs, intercostals, pulmonary capillaries 30.Explain the negative feedback cycle that causes a person to breathe. Start with Inspiration and end with expiration. Include the change, receptor, control center and effectors in both scenarios. 31.Describe the different types of lung volumes. Include: tidal volume, inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, vital capacity, residual volume, dead space. 32.Explain how oxygen and carbon dioxide move across the membrane in the alveoli. What things enable this process? 33.Describe the pressure changes in the lungs that help you breathe. 34.Explain how the carotid and aortic bodies help you control respiration. 35.A person climbs a mountain and finds it much more difficult to breathe. What types of changes are impacting their ability to breathe? IV. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM * TEST: The Immune System Major Concept 36.Explain the main differences between the first, second and third lines ofdefense. (Which lines are specific/non-specific, List some of the body’s chemical and physical barriers, which line of defense do inflammation and fever fall under? Which line of defense involves the specialized B and T cells) 37.What three main things does the body need to be able to do to defend itself? Define Self Recognition. What type of disease results when the self-recognition system fails? 38.What is the MHC? Why must the MHC be matched for organ/tissue transplants? 39.Define Microflora. Provide an example of one of your body’s natural micro flora, how is it beneficial to your immune system? 40.Explain the general function of the following cells in the second line of defense: Eosinophil’s, Basophils, and Neutrophils. 41.Which two cells of the second line of defense are the phagocytes? 42.Explain how phagocytosis works. 43.List the benefits of a fever. 44.What is the difference between naturally and artificially acquired immunity? Provided examples of both. 45.What is the difference between active and passive immunity? Provide examples of both. 46.What is lymph? Where is lymph located? What is the purpose of Lymph? What is the purpose of the lymph nodes? Why do the lymph nodes become swollen and hard when you are sick? What are the lymphatic vessels? 47.Where are the B and T cells produced? 48.What is the difference between the humoral and cell mediated immune responses? 49.Explain the humoral immune response from start to finish. Be sure to include the following in your explanation: Memory B cells, Plasma B cells, antigen, antibody, pathogen 50.Explain the cell mediated immune response from start to finish. Be sure to include the following in your explanation: Helper Tcell, Macrophage, Cytotoxic T cell, Suppressor Tcell, Antigen, Memory 51.Explain what an auto immune disease is. List three examples of autoimmune diseases. V. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM *Test: Digestion& Nutrition *LAB: Frog Dissection Major Concepts 52.Be able to label the following on a diagram: tongue, salivary glands, epiglottis, esophagus, pharynx, sphincters (esophageal & pyloric), stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum), large intestine (ascending, transverse, descending), rectum, anus, appendix, liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. 53.Describe the process of mechanical digestion that takes place at various sites along the digestive tract. (Include: Chewing in the mouth, peristalsis along the tract, muscle contractions in the stomach, emulsification by bile in the small intestine) 54.Identify sites of chemical digestion along the digestive tract as well as the type of nutrient being digested. 55.Explain the role of enzymes in the chemical digestion of nutrients and identify factors that influence their action (Examples: amylase, trypsin, pepsin etc.) 56.Describe the processes of absorption that take place at various sites along the digestive tract. (Uptake of nutrients by villi in the small intestine, uptake of water in large intestine etc.) 57.List ALL of the digestive enzymes discussed in class along with their function in the digestive process and where they are secreted. 58.Describe the role of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas in digestion. 59.Explain the process of emulsification in digestion. 60.What are amino acids and what role do they play in the body? 61.State the difference between an essential amino acid, non-essential amino acid and conditional amino acid. 62.How many essential amino acids does your body require and what food sources contain a complete complement of these essential amino acids? 63.What would occur if a person did not consume enough essential amino acids? Which two vegetable sources contain all 9 a.a? 64.List the difference between a monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide. Provide examples of each. 65.A person consumes too many monosaccharide’s, what type of polysaccharide will be created to store the extra energy? If left unused for a long period of time what will it turn into? 66.Are polysaccharides digestible by humans? What benefit do they give to digestion? 67.State the major difference between a monoglyceride, diglyceride and triglyceride? 68.What is adipose tissue? What positive role does adipose tissue play in the body *list 6+ functions of adipose tissue. 69.Summarize the major impact of the following disorders: a. Obesity b. Type 2 diabetes c. Vit A deficiency d. Vit B12 deficiency e. Vit C deficiency f. Vit D deficiency g. Iron deficiency h. Calcium deficiency i. Kwashiorkor VI. THE URINARY SYSTEM 70.Be able to label a diagram of the human urinary system (kidneys, renal cortex, renal medulla, renal pelvis, renal arteries and veins, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra) 71.Explain the process of filtration, re-absorption and secretion in the nephron (know which molecules are absorbed and secreted where) 72.Explain the role of antidiuretic hormone ADH. List two chemicals that inhibit ADH. VII. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM *LAB: Fetal Pig Dissection Major Concepts 73.Explain the difference between the central and peripheral nervous system. 74.Explain the difference between the somatic and autonomic systems. 75.Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. What major bodily responses occur in each system? 76.Why is the sympathetic nervous system called your ‘fight or flight’ response? 77.Why is the parasympathetic nervous system called your ‘rest and digest response’? 78.Which part of the nervous system would be affected by marijuana? 79.Be able to LABEL the major regions of the brain outlined in your notes. 80.State the function of the various regions of the brain outlined in your notes (table). 81.What is the role of the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid? 82.What is the purpose of the blood brain barrier? Which dangerous substances can directly cross the blood brain barrier? 83.Explain the role and function of a neuron including how signals are transmitted along an axon. 84.Label the structure of a neuron, include: cell body, dendrites, axon, Schwann cell, myelin sheath, node of Ranvier, branching ends. 85.Be able to recognize from a diagram multipolar, bipolar or unipolar neurons. 86.List the major function of sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. Be able to label them on a diagram. 87.How does the sodium potassium pump allow the membrane to maintain a resting membrane potential of -70mV? 88.What role does myelin play in transmitting an electrical signal? 89.What is salutatory conduction? Why is it beneficial? 90.What is the neurons: o Resting membrane potential? o Threshold potential? 91.At what potential difference does the neuron become: o Polarized o Depolarized o Hyperpolarized 92.How is an electrical impulse sent across a synaptic cleft? Include: synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters, post synaptic membrane 93.What is the major function of the following neurotransmitters: dopamine, Serotonin, Endorphins, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine. Major Concept Questions: Please prepare long answer responses to the following questions (3/4 page foolscap, diagrams encouraged) Respiration Explain the process of breathing. In your explanation be sure to discuss the role of the diaphragm and pressure changes. How would your respiratory system have to adjust in order to maintain homeostasis in higher altitude climates where there is lower atmospheric pressure? Include a diagram with your answer. Circulation Explain what the Rhesus factor is and how it affects individuals who are Rh- during pregnancy. Be specific in your answer explaining the complete antibody response (during the first and subsequent pregnancies). Are there any treatment options for mothers who are Rh-? Include a diagram with you answer. Immune System A potential pathogen has invaded your body. Explain how the first, second and third lines of defence work to destroy the pathogen. Be sure to use the appropriate terminology for each type of white blood cell. Digestion Explain the process of digestion from start to finish including the various secretions, where they are secreted and what nutrients the secretions break down. Include a diagram with your response. Urinary system Explain the process of filtration and absorption in the nephron. Be sure to include in your explanation how water and salt are drawn out of the nephron and the effects of ant diuretic hormone on re-absorption. Include a diagram to help explain your answer. Be sure to label all aspects of your diagram. Please be prepared to label the following diagrams ***It would be a good idea to also look over diagrams and photos of the heart, frog and pig dissections.