rna nucleic
advertisement
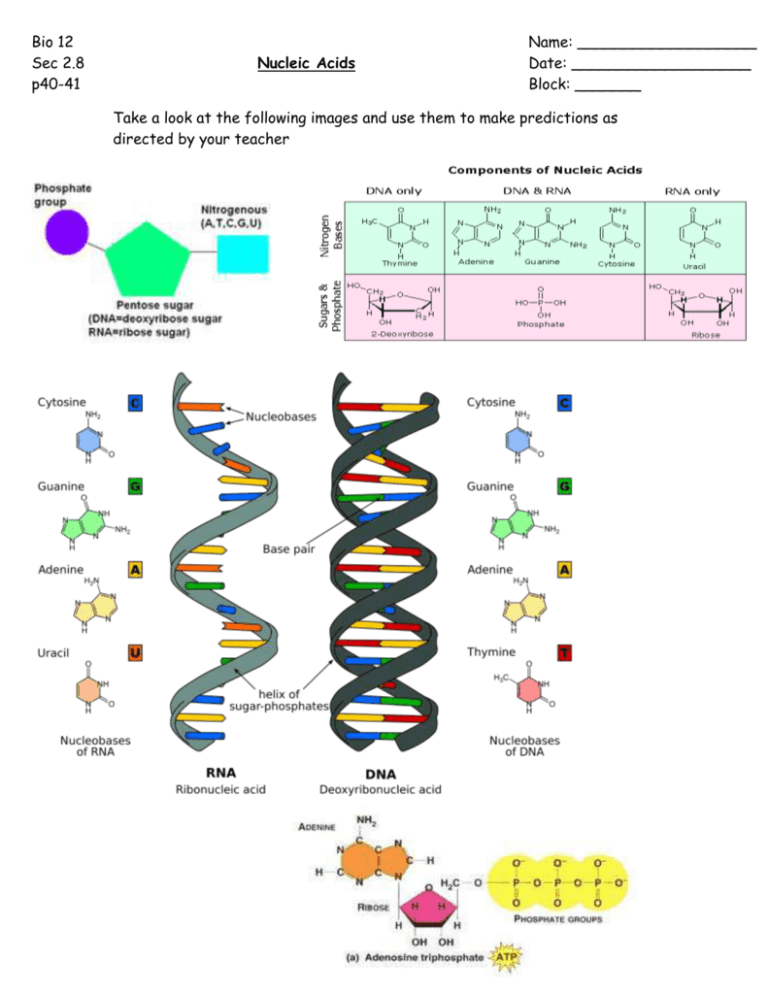
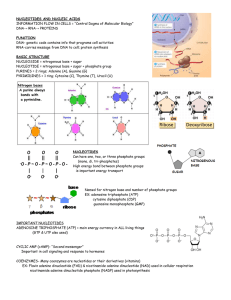
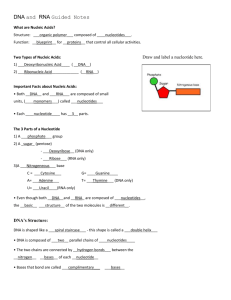
Bio 12 Sec 2.8 p40-41 Nucleic Acids Name: ___________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _______ Take a look at the following images and use them to make predictions as directed by your teacher Bio 12 Sec 2.8 p40-41 Nucleic Acids Name: ___________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _______ Make predictions about the answers to the questions below using the pictures that were provided on a separate sheet. Use point form. 1. Is a nucleic acid a polymer or a monomer? Explain. A nucleic acid is a polymer. It is a very big molecule made up of many smaller monomers (nucleotides) joined together. 2. What are the 3 “subunits” that make up a nucleotide? i) Sugar (pentose) ii) Nitrogenous Base iii) Phosphate Group Note: RNA nucleotides-sugar is ribose, bases can be U, G, C or A DNA nucleotides: sugar is deoxyribose, bases can be T, G, C, or A 3. a) What do Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil have in common? They are all nitrogenous bases & needed to form a nucleotide b) What differentiates Adenine and Guanine from the others? Adenine and Guanine have 2 rings in their structures 4. What do DNA and RNA have in common? DNA and RNA are both: -Nucleic Acids -made up of nucleotides joined together -polymers/macromolecules. -needed to make protein 5. What differences do you see between DNA and RNA? Sugars are different: DNA- deoxyribose vs RNA- ribose sugar Nitrogenous Bases are different - DNA: A,T, C, G RNA: Uracil not Thymine Functions differ: DNA- replication and protein synthesis RNA- protein synthesis Structural Differences: DNA- double strand RNA- single strand Location Differences DNA- in nucleus vs RNA moves to cytoplasm and ribosome 6. What does ATP stand for? How many phosphate groups are there? Adenosine Triphosphate 3 phosphate groups 7. What type of sugar is in ATP? A pentose sugar