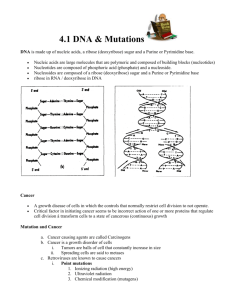
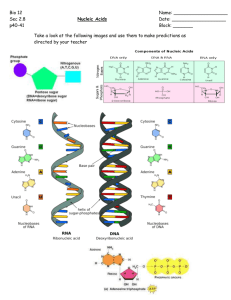
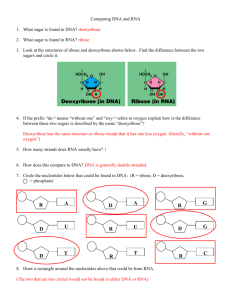
Nucleotides: consist of a base, sugar & phosphate
advertisement

Vocabulary for Today…. 1.Nucleotide 2.Nucleic Acid 3.DNA HEREDITARY INFORMATION CONTROLS LIFE PROCESSES Atoms of elements (C,H,O,P,N) Nucleotides -3 parts:a.phosphate b.sugar c.nitrogen base Nucleic Acids - 2 types: a.RNA b.DNA Gene- sequence of DNA nucleotides on a chromosome that code for one characteristic Chromosomes- long thread like group of genes found in the nucleus Nucleus Cell All these create HEREDITY (Chemical instructions passed from parents to the offspring at reproduction) NUCLEOTIDES General Structure: Nitrogen Base Sugar Phosphate STRUCTURE OF NUCLEOTIDES: A. Phosphate • Supplies “NRG” (energy) for: 1. Making Nucleic Acid (DNA & RNA) Molecules which create HEREDITY for the organism 2. Replication- making exact copies of Nucleic Acids 3. Protein Synthesis B. Nitrogen Bases: • • • • Adenine Guanine Thymine (DNA) or Uracil (RNA) Cytosine C. Sugars: 2 types • Deoxyribose – 5-Carbon Sugar (Pentose) – Has one less Oxygen than ribose • Ribose: – 5-Carbon Sugar (Pentose) – Has one more Oxygen than deoxyribose • Nucleotides are “Building Blocks” for the 2 types of Nucleic Acids A. Deoxyribonucleotides B. Ribonucleotides - Make DNA: DeoxyriboNucleic Acid - Types of Nitrogen Bases: - Make RNA: RiboNucleic Acid - Cytosine Guanine Adenine Thymine (C) (G) (A) (T) NB D P - 2 Chemical differences between DNA and RNA are: 1. DNA has Deoxyribose sugar 2. DNA Has Thymine - Cytosine Guanine Adenine Uracil (C) (G) (A) (U) NB 1. RNA has Ribose sugar 2. RNA Has Uracil R P Heredity is established by… …The number and sequence of the nucleotides. This is how we get our genetic diversity. Review! • What are the building blocks for nucleic acids? – Nucleotides! • What are the 2 types of Nucleic Acids? – DNA & RNA • What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? – Phosphate – 5-Carbon Sugar • (Deoxyribose or ribose) – Nitrogen Base