Chemical Reactions Review Worksheet
advertisement

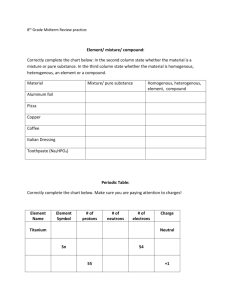
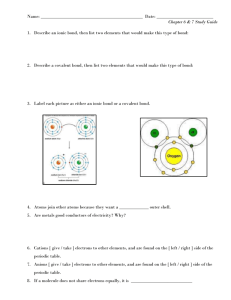
Chemical Reactions 1 Review Balance the following equations: 1. 2 C6H6 + 15O2 6H2O +12 CO2 2. 4 NaI + __ Pb(SO4)2 __ PbI4 + 2 Na2SO4 3. 4 NH3 + 5O2 4 NO + 6 H2O 4. Identify the reactant(s) and product (s) of the reaction below. AlBr3 + 3K 3KBr +Al 5. Where does the Potassium Bromide (KBr) come from in the reaction above? The reactants AlBr3 + 3K Ionic Bonds – Draw the Lewis structures for each atom, then show the transfer of electrons and charge for each ion. Write the chemical formula for each compound. 6. Magnesium (Mg – group 2) + Oxygen (O – group 16) See your bonding quiz for answer Covalent Bonds – Draw the Lewis structures for each atom, and then draw circles to show the electrons that are shared. Draw the structure with a straight line representing a single bond. Write the chemical formula for each compound. 7. Hydrogen (H – group 1) + Chlorine (Cl – group 17) See your bonding quiz for answer 8. What is the difference between a compound and an element? An element is made up of one atom and a compound is made up of more than one atom/element 9. What is an ionic bond? A bond that is formed when electrons are transferred between atoms 10. What is a covalent bond? A bond that is formed when pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms 11. Do noble gases form compounds? No 12. How do you correctly write a chemical symbol? A capital letter by itself or a capital letter followed by a lowercase letter 13. Does H & Cl form an ionic or covalent bond? Covalent 14. Does Magnesium and bromine form an ionic or covalent bond? Ionic 15. Which bonds are broken and which bonds are formed during the reaction in #4? Identify which substances are compounds and which are elements. AlBr3 is broken and 3KBr forms a new bond. AlBr3 and KBr are compounds, K and Al are elements. 16. Why are you able to change the coefficients of reactants or products, but not subscripts? You change the element/compound into a new substance if you change the subscript. The coefficient only changes the number or atoms in the element/compound. 17. Compare the writing and balancing of a chemical equation to the principle of conservation of mass. When you balance an equation the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. The conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction matter is not created or destroyed. All atoms present at the start of the reaction are present at the end of the reaction. 18. Count the atoms of each element in the following compounds: Co 2(SO4)3, Na3PO4 and 2Mg(OH)2. Co-2, S-3, and O-12 Na-3, P-1 and O-4 Mg-2, O-4 and H-4 Indicate whether the following are examples of synthesis, decomposition, combustion, single replacement, or double replacement. 19. Pb + FeSO4 PbSO4 + Fe Single 20. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 Decomposition 21. P4 + 3 O2 2 P2O3 Synthesis