Matter 2 Vocab
advertisement

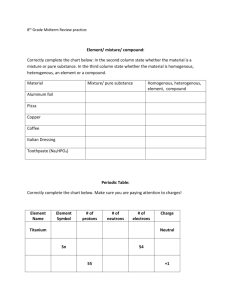
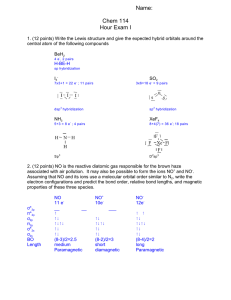
Eighth Grade Physical Science Matter Unit II Vocabulary (Chapters 20, 21) 1. Compound – substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined in definite proportions 2. Chemical formula – shorthand representation for a molecule of a compound, shows the kinds and numbers of elements in the compound 3. Molecule – the smallest particle of a compound 4. Ion – charged particle of a substance that has lost or gained electrons 5. Ionic bond – a strong electrical bond between ions, positive and negative, metal and nonmetal, left and right side of Periodic Table (ionic compounds have high melting points, crystalline structure, dissolve in water to form ions, solutions conduct electricity) 6. Covalent bond – weaker bond formed when electrons are shared, two negative oxidation numbers, two nonmetals, two elements on right side of table (covalent compounds have low melting points, usually do not have crystalline structure, do not ionize in water, do not conduct electricity) 7. Metallic bond – a strong bond that holds atoms of a metal together, formed by a common cloud of electrons surrounding the positive nuclei of the metals, account for the properties of metals 8. Oxidation number – shows the combining capacity of an element (or polyatomic ion), shows the number of electrons gained, lost, or shared (group one +1, group two +2, group three +3, group four 4, group five -3, group six -2, group seven -1, group eight none (full)) 9. Chemical reaction – when one or more substances changes into one or more new and different substances 10. Reactant – a substance that enters into a chemical reaction, on the left side of the equation 11. Product – substances that are formed by a chemical reaction, on the right side of the equation 12. Conservation of mass – matter cannot be created or destroyed only changed from one form to another, the reason equations must be balanced 13. Chemical equation – a shorthand representation of what happens in a reaction, shows the elements and compounds involved in a reaction and their numbers 14. Coefficient – a whole number multiplier used to show the number of elements or compounds in an equation 15. Exothermic reaction – a reaction in which heat is released 16. Endothermic reaction – a reaction in which heat is absorbed 17. Synthesis – a reaction in which two small particles combine to form one larger compound ( A + B → AB ) 18. Decomposition – a reaction in which a larger compound breaks down into smaller pieces ( AB → A + B ) 19. Single Replacement – a reaction in which a single element replaces an element in a compound ( A + XY → X + AY ) 20. Double Replacement – a reaction in which the two metal (A and B) ions switch places in two reacting compounds ( AX + BY → BX + AY ) 21. Catalyst – a substance that speeds up a reaction without being used up by the reaction, therefore not a reactant. EX. Enzymes in cellular reactions.