Basic Grammar Terminology
advertisement

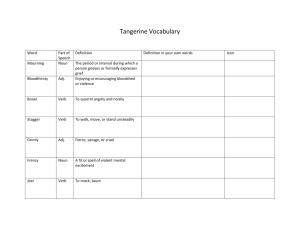
Basic Grammar Terminology parts of speech -- content words words that carry meaning nouns -- cat, pencil, transportation, enthusiasm, happiness, store, Olean, John action verbs – speak, walk, know, sing transitive verbs – take direct objects (She bought a present). intransitive verbs – do not require direct objects (She paints well). adjectives – modify nouns, -er and –est words (exs. quick, small, tallest) adverbs – modify verbs, adjectives and other adverbs, -ly words(exs. quickly, soon, very) parts of speech -- functional words words that perform functions linking verbs – forms of the verb to be (exs., is, are, were) conjunctions – join grammatical units (exs. and, but, or) prepositions –combine with a noun to form prepositional phrases(exs. about, around, at, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, near, of, off, on, through, to, toward, under, until, with) determiners -- articles (exs. the, a, an) and demonstrative pronouns (exs. these, that, those) pronouns -- personal pronouns (exs. he, she, it, they) auxiiary or helping verbs – help determine tense (exs. could have gone, will be sold) parts of the sentence clauses -- The fundamental structure in grammar is the clause. A clause is a subject and predicate. Clauses which can stand on their own are independent clauses. Clauses which need to be attached to something else are subordinate clauses. Because English class ended early yesterday, the teacher gave us a reading assignment. subordinate independent subject – noun along with its modifiers (English class, the teacher) predicate – verb along with its modifiers (ended early yesterday, should have studied) direct object – receives the action of the verb (you can find the direct object by naming the subject + the verb + asking the question“what?” = the teacher gave what? = an assignment) indirect object – the “secondary” receiver of the verb (us) complement – is linked to the subject with a linking verb predicate adjective (She was very generous). predicate noun (He was a great athlete). phrases: prepositional phrases – prepositions along with the noun with which they have a relationship (to the store, of unknown origin, from an old friend). A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition and its object. Prepositional phrases are modifiers, acting as adjectives or adverbs. (ex. She went to the store.) appositive – a noun which immediately follows the noun it modifies (ex. Science, my favorite subject, is the last class in the day.) verb phrase – sometimes used to refer to a predicate noun phrase – sometimes used to refer to a subject Other Useful Terminology linguistic grammar – a new way of studying grammar that focuses on describing how grammar is used rather than prescribing how grammar should be used syntax – word order verbals -- “verbs” which act as other parts of speech participle – “verb” used as an adjective (exs. waxed floors, acquainted with the subject matter, the student…) gerund – “verb” used as a noun (ex. Minimizing the screen will solve the problem.) infinitive – “to” form of a verb used as a noun, adjective or adverb (ex. To try is the important thing. Ready to go, we got into the car. antecedent – the object or person which a pronoun stands in for He loves pizza. He eats it everyday. (The antecedent of “it” is pizza). pronoun case – nominative (I, you, he, she, they, we) objective (me, her, him, them, us) parallelism – balance created by similar grammatical structures (Before her meeting she planned to finish her homework, complete her chores and call her friend). idiom – a word or phrase that is not literal, or does not conform to conventional rules but is accepted and understood by a large group of people (she means well, we agree on that point) passive and active voice – in active voice, the subject performs the action of the verb. In passive voice the subject does not perform the action of the verb. The homework was assigned last week (passive – the homework doesn’t “do” the assigning. The teacher assigned the homework last week (active – the teacher does the assigning). compound sentence – contains two or more independent clauses complex sentence – contains a subordinate clause