Hurricane Note Help
advertisement

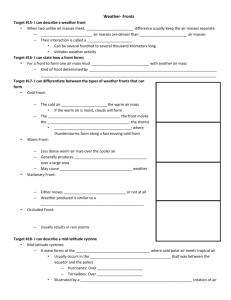
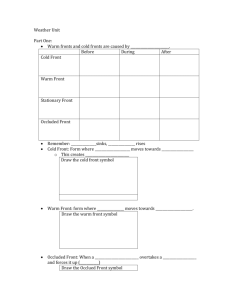
Hurricanes and Storm Surges And Air Circulation (Winds) Air pressure and winds Air is a fluid Warmer air is less dense Air moves from dense to less dense conditions Ex.: Land-sea breezes Global air circulation Equator receives most insulation Hot air rises, heads towards poles Air becomes heavy and sinks at 30°N and S Plus the Coriolis effect Coriolis effect - is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating frame of Reference. Main Points Warmer air “holds” more water Low pressure=warm air=precipitation High pressure=cold air=dry air What is a hurricane? A large rotating storm with strong winds blowing at speeds of 74 miles per hour or more, around a relatively calm center called the eye. It blows counter clock-wise in the Northern Hemisphere, and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. The whole storm system may be 5-6 miles high, 300-600 miles wide, and move forward like as immense spinning top Travels at speeds of about 12 mph What causes a hurricane? Correct amount of warmth & water vapor to supply energy Convection activity & vertical wind motion to bring in air from sea level and move it up through the system Must be given the right amount of spin or twist, provided by the rotating earth What is the eye of the hurricane? Innermost portion of the storm Light breezes or almost windless calm Clear skies, while winds and clouds continue raging around it On average, eyes are 14-20 miles across Within the eye: Lowest pressure Highest temperatures Lowest relative humidity Eye not always in the center. Why do hurricanes form over warm oceans? They draw their power from warm, extremely humid air found only over warm oceans. The key to their energy source is the latent heat that is released when water vapor condenses into cloud droplets and rain. Grow best in a deep layer of humid air that supplies plenty of moisture. Grow where air converges and begins to push upwards. If the air is unstable, it will continue rising after the initial shove. When winds at all levels are blowing at the same speed in the same direction, the disturbance will grow. Grow above high pressure areas high above the ocean, which help pump away the rising air, allowing more air to flow into the storm and rise. What is storm surge? Piling up of water as it is pushed along by the storm When the storm nears land, the ocean bottom blocks the water from flowing away, and the dome of water builds up to come ashore as the storm surge This dome of water can be as high as 18 feet deep as a storm hits land. What is the difference between a hurricane and a typhoon? Nothing except geography. Tropical storms occur in several of the world's oceans, and except for their names, they are essentially the same type of storm. In the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Eastern Pacific Ocean, they are called hurricanes. In the Western Pacific Ocean, they are called typhoons. In the Indian Ocean, the Bay of Bengal, and Australia, these types of storms are called cyclones.