Practice Quiz on Lipids: Answer Key
advertisement

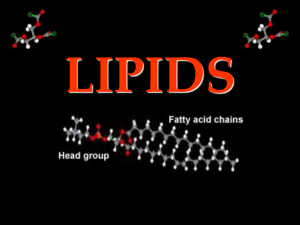
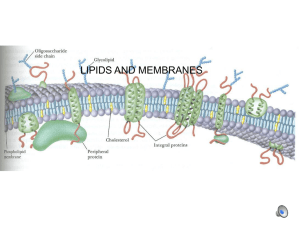
Lipids and Elements of Life: Formative Assessment Name: _______________________________________Per: _______ Date: _______________Total: / 20 Learning Goals A. Understand the elements that make up a living cell and how their properties impact life. LG-A: 1-2-3-4 B. LG-B: 1-2-3-4 Understand the structure and function of different types of lipids. Score 2: 1. (LG B ) Which of the following is an example of a type of triglyceride? a. Unsaturated fat c. Monounsaturated fat b. Saturated fat d. All of the above 2. (LG B ) Which type of lipid makes up the majority of the cell membrane? 3. a. phospholipids c. steroids b. waxes d. triglycerides (LG B ) What is the function of a triglyceride (fat)? a. Stores and transfers genetic information c. Control the rate of reactions b. Long term energy storage d. Help to fight disease 4. (LG B ) Phospholipids have a: a. hydrophobic head and hydrophilic tail 5. (LG B ) Which is NOT a function of lipids? a. protective coatings such as in the cell membrane of cells b. quick energy source b. hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail c. long-term energy source d. insulation 6. (LG A ) Which of the following is NOT one of the main elements found in living organisms? a. Hydrogen c. Neon b. Phosphorous d. Nitrogen 7. (LG A and B ) Long chains of these elements make up fatty acids in lipids: a. Carbon & Hydrogen c. Oxygen & Nitrogen b. Nitrogen & Sulfur d. Phosphorous & Sulfur 8. (LG B ) Sex hormones, cholesterol, and vitamins are all examples of a. triglycerides c. waxes b. steroids d. phospholipids Page 1 Lipids and Elements of Life: Formative Assessment 9. (LG B ) Fats that have double bonds between carbon atoms in their fatty acid chains and are liquid at room temperature are called a. Saturated fats c. Unsaturated fats b. Trans-fats d. Phospholipids 10. (LG B ) Which of the following describes the basic structure of a triglyceride? a. 3 glycerol molecules attached to a fatty acid chain b. 3 fatty acid chains attached to a phosphate head c. 3 fused carbon rings attached to a fatty acid chain d. 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule 11. (LG-A) Organic macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are all based on carbon. a. List the other 5 elements that make up these organic molecules. CHNOPS – Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Sulfur ____/ 2 Score 3: b. Why is Carbon such a useful element in making macromolecules? Explain by referencing carbon’s unique bonding properties (hint: valence electrons). ___/ 4 Carbon makes bonds easily. Carbon has four valence electrons. This makes it useful in forming large molecules with other elements. 12. (LG-B) Draw a phospholipid and label its parts. Next to your picture, explain how phospholipids interact with water. Explain using the following terms (polar, non-polar, hydrophilic, hydrophobic). _ / 4 Phosphate Head – Polar and Hydrophilic Fatty Acid Tails – Non-polar and Hydrophobic Page 2