Earthquake and Volcano review
advertisement

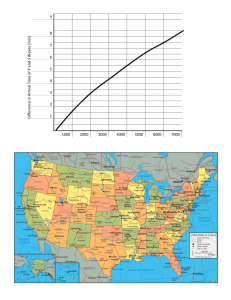
Name: ________________________________ Date: ________________________ Earthquake & Volcano Review Vocabulary Review: 1. _____ Epicenter 2. _____ Focus 3. _____Volcano 4. _____Vulcan 5. _____Volcanologist 6. _____Seismologist 7. _____Fault 8. _____Hot spot 9. _____Ring of fire 10. _____Elastic Limit 11. _____Magnitude 12. _____Richter scale 13. _____Viscosity 14. _____Theory of Plate Tectonics a. Person who studies earthquakes b. Theory that states the earth is broken up into plates and those plates MOVE! c. Area around the pacific plate that has a high level of seismic activity. d. Strength of an earthquake e. The point on the surface of the earth directly above the focus. f. Roman god of Fire. Lives under Mount Etna g. Resistance to flow h. Person who studies volcanoes i. Landform that develops on the surface of the earth where magma and gases erupt through a vent. j. An area in the mantle where magma is created and continuously rises to the surface. k. Scale used to rate the magnitude of an earthquake l. The breaking point m. Large fracture or break in the earth’s crust where movement occurs. n. The starting point or origin of an earth quake. Inside the earth. 1. Identify and describe the three types of faults. 2. What causes mountain building? 3. Which statement is NOT TRUE about seismic waves? a. surface waves that seem to roll across the ground are the most destructive earthquake waves b. the push-pull movement of P waves transmits energy through solids, liquids, and gases c. P waves can travel about 1.7 times faster than S waves d. S waves travel rapidly through liquids and gases 4. Identify and describe the three types of volcanoes (eruption type, size, shape) 5. Volcano shapes are determined in part by the particles produced in eruptions. The Hawaiian Islands a. are shaped by the accumulation of fluid basaltic lavas b. develop after large lava fragments harden in the air c. are produced from the cooling and hardening of pyroclastic fragments, like cinders 6. What are some of the risks earthquakes have for humans? 7. Why is a. b. c. the composite cone the most potentially dangerous type of volcano? when they erupt, they eject a small amount of pyroclastic material they generate the most explosive eruptions with the greatest amount of pyroclastic material they only erupt once so when they erupt, they release a large amount of material 8. What type of plate interaction produce both volcanoes? 9. Define Fault and provide an example. 10. What is a huge tidal wave created by earthquakes under the ocean floor? Use the information and diagram below to answer questions 11 & 12. A seismogram shows all three types of seismic waves that occur as the result of an earthquake. The first wave to arrive is the P wave, followed by the S waves. The last waves recorded are the surface waves. 11. Which type of wave produces the strongest reading on the seismogram? 12. Describe the sequence (how fast and when they arrive) and travel patterns (what they move through) of seismic Waves. 13. Determine the S-P interval for the seismogram above. 14. Earthquake vibrations are produced when rocks reach their ____________________________. 15. Many active volcanoes form around the edge of the Pacific Plate forming the _________________________. Use the information from the diagrams and passage to answer questions 15-18. A travel-time graph is used to determine the distance to the epicenter of an earthquake. The difference in the arrival times of the first P wave and the first S wave at Seismograph station A is 3 minutes. So the epicenter is roughly 1500 kilometers away. The epicenter is located using the distance obtained from the three seismic stations. The location where the three circles intersect is the epicenter. 15. According to the chart, your knowledge and the illustrations, what kind of data is needed to find the epicenter of an earthquake? 16. The epicenter of the earthquake is closest to which city? How do you know? 17. How many locations for an epicenter would be possible if only two seismic stations took measurements? 18. What time interval should occur between the P waves and S waves from an earthquake with an epicenter 4000 km away? Match up the pictures with the correct letters. 19.______ 20._____ 21._______ a. strike-slip fault b. reverse fault c. normal fault --------------------------------------------------------------------------22._____ 23.______ 24.______ a. cinder cone b. composite volcano c. shield volcano --------------------------------------------------------------------------25.______ 26. ______ 27. _______ a. P-wave b. L-Wave c. S-wave Explain what is happening to the pacific plate. Why is this happening? Explain the changes that occur to the earth’s surface as a result of plate tectonics, earthquakes and volcanoes. (Full sentences)