Chapter 21 Community Ecology
advertisement

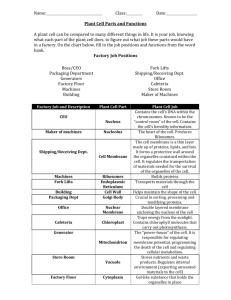
Name ____________________ Hour ______ Date _________ Biology A Chapter 4: Structure and Function of the Cell 4-1 Introduction of the Cell A __________ is the smallest unit of __________ that can carry on all of the __________ of life. Discovery of the Cell - Every _______________ thing-from the tiniest bacterium floating in a drop of __________ to the largest whale-is made of one or more __________ cells. - In 1665, scientist Robert __________ used a _______________ to examine a thin slice of __________. o Described it as consisting of “a great many little _____________.” o These “little __________” reminded him of the small rooms in which __________ lived, so he called them __________. - What __________ had observed were actually the remains of __________ plant __________. - The first person to observe _______________ cells was a Dutch microscope maker, Anton van _______________. Cell Theory - About 150 years passed before scientists began to organize the observations begun by _______________ and van _______________ into a unified _______________ known as the cell _______________. o The _______________ theory has _______________ parts: 1. All ___________ things are composed on one or more _________. 2. Cells are the basic units of _______________ and _______________ in an _______________. 3. Cells come only from the _______________ of _______________ cells. - In 1838, the _______________ Matthias Schleiden concluded that all _______________ are _______________ of cells. - _______________, Theodor Schawann came to the same conclusion about _______________. - In 1855, Rudolf Virchow, a _______________ who had been studying how disease affects living things, reasoned that ___________ come only from other ___________. Cell Diversity - Even cells within the same _______________ may show enormous diversity in _______________, _______________ and internal _______________. - Your body, contains at least _______ different __________ types. Size - A few types of cells are _______________ enough to be seen by the _______________ eye. 1 - Most cells are _______________ only with a _______________. - Cells are limited in _______________ by the ratio between their outer _______________ area and their _______________. o For a cuboidal cell, volume _______________ with the cube of the side _______________, but surface area increases with the square of the side _______________. o If a cell keeps the same _______________ as it grows, its _______________ will increase more rapidly than its _______________ area. o _______________, oxygen, and other _______________ a cell requires must enter through its _______________. As a cell grows larger, at some point its surface area becomes too small to allow these materials to enter the cell quickly enough to meet the cell’s needs. Shape - Cells come in a variety of _______________. - This diversity of _______________ reflects a diversity of _______________. Internal Organization - Cells contain a variety of _______________ structures called _______________. o An _______________ is a cell component that performs specific _______________ for the cell. o The entire cell is surrounded by a thin _______________, called the ________ _______________. o The large _______________ near the _______________ of the cell is the _______________. It contains the majority of the cell’s _______________ _______________ and directs most of the _______________ of the cell. - Organisms whose cells contain a _______________ -bound _______________ and other _______________ are called _______________. - Bacterium has a cell _______________, but none of the _______________ inside a bacterium are surrounded by a _______________. o A bacterium has no membrane-bound nucleus like that of a _______________ cell. o _______________ organisms that lack a membrane-bound _______________ and other organelles are called _______________. 4-2 Part of the Eukaryotic Cell The structures that make up a __________ cell are determined by the specific __________ carried out by the cell. Eukayotic cells generally have three main components: a ____________, a __________, and other ____________. Cell Membrane - All cells must take in __________ and other ___________, and they must also dispose of the _________ they produce. o Both nutrients and wastes must pass through the ____________. 2 o The cell membrane controls the ease with which substances pass _____ and _____of the cell-some substances easily cross the membrane, while others cannot cross at all. For this reason, the cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable. The ___________ of the cell membrane depends on the functions the cell performs. Membrane Lipids - One of the major types of lipids in the cell membrane is _____________. o Both sides of the cell membrane are surrounded by _______) molecules. o These water molecules cause the phospholipids of the cell membrane to form _____ layers- a lipid ________. - Eukaryotic membranes also contain steroids. Membrane Proteins - Peripheral proteins are located on both the __________ surface and the ___________ surface of the cell membrane. o ______ bonds link peripheral proteins to membrane lipids or to other proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer. o Proteins that are ________ in the bilayer are called integral proteins. o Because the cell membrane is __________ ________, cells much have mechanisms for _____________ molecules through the lipid bilayer. Membrane proteins play an important role in this process. Some __________ proteins form channels or pores through which certain substance can pass. Other proteins bind to a substance on one side of the membrane and carry it to the other side. Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane - Scientists use the fluid mosaic model to describe the _____ _________. o According to this model, the lipid bilayer behaves more like a ______ than a solid. Organelles - Between the ____ __________ and the _________ lies the ___________, which contains the various organelles of the cell. - The organelles are bathed in a gelatin-like aqueous fluid called the __________. Mitochondria - Mitochondria are the sites of chemical reactions that transfer energy from organic compounds to ATP. o ATP is the molecule that most cells use as their main energy currency. o The ATP ultimately drives most of the chemical reactions that occur in the cell. - Mitochondria are usually more numerous in cells that have a high energy requirement. o The inner membrane has many long ______ known as _________. The cristae greatly enlarge the _______ _______ of the inner membrane, providing more space for the _________ reactions. Ribosomes 3 - The most numerous organelles in many cells are the ribosomes. - Ribosomes are _____ surrounded by a membrane. - Each ribosome is an assemblage of two organic compounds- proteins and RNA. o Ribosomes play important roles in the _________ of _________. Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), is a system of membranous tubules and sacs. o The ER functions primarily as an __________ __________, a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another. o The amount of ER inside a cell fluctuates, depending on the cell’s activity. - A cell contains two types of ER. o ________ endoplasmic reticulum is prominent in cells that make large amounts of __________ to be exported from the cell or inserted into the cell membrane. o _________ endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of steroids in gland cells, the regulation of calcium levels in muscle cells, and the breakdown of toxic substances by liver cells. Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi Apparatus is the __________, ____________, and _________ organelle of the cell. o The Golgi apparatus is a system of ____________. o The Golgi apparatus _________ _________ for export by the cell. Lysosomes - Lysosomes are small, spherical organelles that enclose _______ enzymes within single membranes. - These enzymes can _______ proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, DNA and RNA. o They may also digest old __________ as well as viruses and bacteria that have been ingested by a cell. - Lysosomes are common in the cells of _________, ______, and ______, but they are rare in plant cells. Cytoskeleton - Your body depends on your skeleton to maintain its ______ and _____, so a cell needs a structure to maintain its shape and size. o In many cells, that structure is the cytoskeleton, a network of long _______ strands located in the _________. Not surrounded by membranes. - The cytoskeleton participates in the ____________ of _________ within the cytosol. - Two major components of the cytoskeleton are microfilaments and microtubules. o Microfilaments rethreads made of a protein called actin. - When a cell is about to divide, bundles of microtubules come together and extend across the cell. These bundles, known as spindle fibers are thick enough to be visible with a light microscope. Cilia and Flagella - Cilia and flagella are __________ organelles that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in ____________. 4 o When these organelles are short and present in large numbers on a cell, they are called _______. The movements of the cilia _______ these tiny organisms through the _______ as they search for _______ or escape from predators. - When the hairlike organelles are long and less numerous on a cell, they are called __________. Nucleus - The nucleus maintains its _________ with the help of a ________ skeleton known as the nuclear matrix. - The nucleus is surrounded by a ________ __________ called the ________ ___________. o Inside the nuclear envelope are fine strands of ___________, a combination of DNA and protein. When a cell is about to ________, the chromatin strands ____ up and become _________ packed, forming ____________. - The nucleus stores hereditary information in its _____. The _________ is also the site where _______ is copied from _______. o ______ directs the synthesis of __________. - Nuclear pores are small holes in the nuclear envelope. - Most nuclei also contain at least one spherical area called the __________. o The nucleolus is the site where ___________ are _____________ and partially assembled before they pass through the nuclear pores to the cytosol. Plant Cells - Most of the organelles and other parts of the cell just described are common to all eukaryotic cells. However, plant cells may have three additional kinds of structurescell walls, vacuoles and plastids. Cell wall - Plants cells are covered by a rigid _____ _______ that lies ________ the cell membrane. - The __________ of cell walls helps ________ and ________ the plant. - Cell walls contain long chains of ____________. Vacuoles - _____________ are a second common characteristic of plant cells. - These fluid-filled organelles store __________ and metabolic wastes. - Some vacuoles may occupy ____ percent of a plant cell’s volume. Plastids - _________ are organelles that, like mitochondria and the nucleus, are surrounded by two membranes and contain ______. - Some plastids store starch or fats, while others contain compounds called ___________, which ________ visible light. o The most familiar type of plastid is the ____________. o Each chloroplast encloses a system of flattened membranous sacs called ____________. 5 o Chloroplasts are the organelles in a plant cell in which the energy of _________ is converted into __________ energy in organic compounds. 4-3 Multicellular Organization In a ______________ organism, ________ cell carries out all of the ______________ of life. Because of cell _______________, the cells of multicellular organisms _______________ on other cells in the organism for their _______________. Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems - In most _____________ organisms, cells are organized into ______________, or groups of cells that carry out a ______________ function. o In animals, _______________ tissue consists of sheets of closely packed cells that form _______________ coverings, such as the outermost living _______________ of the skin. o Several types of _______________ that interact to perform a _______________ function form an _______________. The _______________ is one example of an _______________. - An organ _______________ is made up of a _______________ of organs that work _______________ to perform a set of _______________ tasks. o Ex. The mouth, esophagus, _______________, intestines, and several other organs make up the _______________ system. - The different _______________ systems in a multicellular organism interact to carry out the _______________ of life. - Plants also have _______________ and _______________, although they are arranged somewhat _______________ from those in _______________. o The four plant organs are _______________, _______________, _______________ and _______________. Evolution of Multicellular Organization - _______________ evidence suggests that the earliest cells on Earth were simple _______________ similar to some present-day _______________. o As they _____________ and their numbers ____________, however, they began to compete for limited environmental _____________. o Because of the increasing ______________, cells with adaptations _____________. Some of these cells were eukaryotic. Colonia Organizations - Some of the early _______________ eukaryotes may have begun to live in temporary groups, or _______________, with other cells of the same _______________. 6 - Some of the cells in these _______________ may have _______________ in performing certain _______________, such as converting _______________. o Biologists refer to such _______________ of cells as _______________ organisms. o A colonial organism is a collection of _______________ identical cells that _______________ together in a closely _______________ group. An example of a _______________ organism that _______________ today is the green alga _______________. Many biologists believe that animals, _______________, and fungi probably _______________ from different varieties of _______________ organisms hundreds of millions of years ago. 7