Theories of Adaptations
advertisement

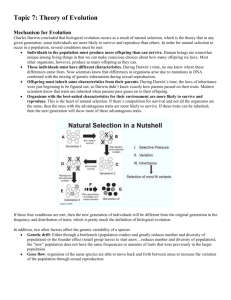
Adaptation Theories Lamarck vs. Darwin Lamarck “Acquired Characteristics” “Acquired Characteristics” – Desired changes that occurred during a parent’s lifetime were passed on to offspring o example: Parents that developed large muscles through exercise was thought to be passed on to offspring Organisms have changed over time Organisms changed because they wanted to survive Organisms can never become extinct The environment had something to do with why organisms changed Parents are able to pass on at least some of their traits to their offspring Organisms could decide to change something about their body and pass on that change to their offspring Organisms are still changing Darwin “Natural Selection” “Natural Selection” - The process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the same species Organisms have changed over time There was variation in population Certain traits helped organisms survive and reproduce better than other organisms without those traits The environment had something to do with why organisms changed Parents are able to pass on at least some of their on traits to their offspring Parents are only able to pass on traits that they were born with Organisms are still changing 4 Principles of Natural Selection 1. overproduction – producing more offspring than can survive 2. competition – offspring will compete for food another resources, such as territory and mates 3. variations – a difference between members of same species that may help it to survive 4. selection – over time, the environment “selects” organisms with helpful traits to be parents of the next generation Over a long period of time, natural selection can lead to the evolving of new species. Helpful variations remain and unfavorable ones disappear. Other vocabulary: adaptations: any structural or behavioral change that helps an organism survive in its particular environment gradualism: model describing evolution as a slow process by which one species changes into a new species through a continuing series of mutations and variations over time punctuated equilibrium: model describing the rapid evolution that occurs when mutation of a few genes results in a species suddenly changing into a new species species: group of organisms that share similar characteristics and can reproduce among themselves producing fertile offspring