Notes Part 5 water, limits to growth student
advertisement

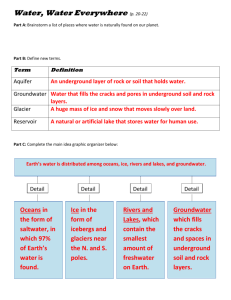
Topic 3 Human Population , Carrying Capacity and Resource Use Notes Ch. 3 – Part 5 3.5 Water Resources pp.146 – 152 Use textbook and internet research to answer the following questions. Use Answer sheet. 1. The amount of water present in the hydrosphere as freshwater is approximately A. 3 %. B. 6 %. C. 10 %. D. 20 %. 2. The percentage of the earth’s surface covered by oceans is about A. 90 %. B. 70 %. C. 50 %. D. 45 %. 3. Which of the following contains the greatest proportion of the world’s fresh water? A. Organisms B. The atmosphere C. Ice-caps and glaciers D. Streams, rivers and lakes 1 4. Which of the following is most likely to lead to an overall increase in the Earth’s freshwater storages? A. Removal of forests B. Melting of polar ice caps C. Increase in evaporation rates from the oceans causing increase in precipitation over the continents D. Discovery of new underground aquifers 5. What proportion (by volume) of the Earth’s water is fresh? A. 0.026 % B. 0.26 % C. 2.6 % D. 26 % 6. P = precipitation (rain, snow) falling on the surface of the lake I = inflow from streams E = evaporation from the surface of the lake Lake R = run-off in a stream flowing out of the lake S = loss by downward movement into the rocks Assuming there is neither a rise nor a fall in the level of the lake, and there are no other inputs or outputs, what is the value of R? A. P+I–E–S B. I+P+E+S C. (S + E) × (I + P) D. I+P+E–S 2 7. Which of the following contains the greatest proportion of the world’s freshwater? A. Ice caps and glaciers B. Rivers C. Lakes D. Groundwater 8. Which row correctly shows the storages of the water in order of decreasing size? LARGEST SMALLEST A. Oceans Groundwater Glaciers and ice caps Lakes, rivers and atmosphere B. Oceans Lakes, rivers and atmosphere Glaciers and ice caps Groundwater C. Lakes, rivers and atmosphere Oceans Groundwater Glaciers and ice caps D Oceans Glaciers and ice caps Groundwater Lakes, rivers and atmosphere 9. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Less than 0.1 % (by volume) of the Earth’s water is freshwater. B. The hydrological cycle is independent of solar energy. C. The main reservoir of the Earth’s freshwater is in ice caps and glaciers. D. Only abiotic storages are involved in the hydrological cycle. 3 10. The pie charts below show the usage of water in the United States and China. United States Industry 49 % China Agriculture 41 % Domestic 6% Industry 7% Domestic 10 % Agriculture 87 % Since 1950 the global rate of water withdrawal from surface and groundwater sources has increased almost fivefold and per capita use has tripled. [Source: Worldwatch Institute and World Resources Institute, 2000] (a) Discuss two reasons for differences in water usage between the United States and China. (b) Describe, with examples, three ways in which human population growth affects the world’s fresh water resources. 11. The diagram below shows storages (in percentage of total water) and flows in the global water cycle. The rates of flow are given in 1015 kg yr–1. 4 CLOUDS 0.001 % Condensation 400 ATMOSPHERIC WATER VAPOUR 0.001 % Precipitation 100 Evaporation 64 SURFACE WATER 0.001 % ICE 2% GROUND WATER 1 % (a) (b) (c) Precipitation 300 Evaporation 336 Run-off/groundwater flow OCEAN 97 % (i) What is the source of energy which drives the water cycle? . (ii) In which of the processes given in the diagram does this energy enter the cycle? (i) What percentage of all precipitation falls directly into the oceans? (ii) What percentage of all evaporated water comes from the oceans? (i) Assuming the cycle is in steady state, what mass of water flows into the oceans through run-off and groundwater flow per year? (ii) Explain why this figure might increase in the future, as a result of burning fossil fuels. (d) Name a storage of water in the biosphere that is not shown in the diagram, and explain how water is transferred in and out of this storage. (e) (i) State briefly one way in which one of the other flows in the diagram might change if evaporation rates were to increase. (ii) Describe how two changes in the flows shown on the diagram could lead to a fall in global temperatures and reduce global warming. (iii) Name the type of feedback involved in this reduction in global warming. (f) Identify each of the different processes referred to on the diagram as either transfer or transformation processes. 12. The diagram below shows some of the material flows which affect food production and fresh water resources. 5 atmosphere food production systems rivers available fresh water resources soil aquifers (a) Distinguish between the terms sustainability and sustainable yield. (b) Describe and explain two ways food production systems can be managed sustainably. (c) Describe and explain two ways fresh water resources can be managed sustainably. 6 3.6 Limits to Growth – Carrying Capacity pp.152 – 159 Carrying capacity – the maximum number of organisms that an area or ecosystem can sustainably support over a long period of time. KEY WORDS : Resources, technology, economic growth It is difficult to determine and apply the concept of carrying capacity to local human populations because the range of resources, technology and import-export trade is much greater than for any other species. Technological and economic developments will definitely allow humans to adapt to a decrease in resources and can increase the carrying capacity. Human carrying capacity is determined by the rate of energy and material consumption, the level of pollution and the extent of human interference in global life support systems. While reuse and recycling reduce these impacts, they can also increase human carrying capacity. Human carrying capacity does not depend as much on birth rates, death rates, population densities as in other species. Overpopulation occurs when there are too many people relative to the resources and technology locally available to maintain an adequate standard of living. Bangladesh, Somalia, parts of Brazil and India are overpopulated as they have insufficient food and materials. They suffer from natural disasters such as drought, famine and are characterized by low incomes, poverty, poor living conditions and high levels of emigration. A stable population can be reached by economic growth, high standard of living and higher education. Women in these types of countries usually marry at a later age, have lower birth rates and a decrease in the death rate. Under population occurs when there are far more resources in an area ( e.g food production, energy and minerals) than can be used by people living there. Canada could theoretically double its population and still maintain its standard of living, Countries like Canada and Australia can export their surplus food , energy and mineral resources. It is possible that the standard of living would increase through increased production if population were to increase. 7 8 Questions – Use answer sheet. Look for key words discussed above. Explain your choice on answer sheet. 13. Why is it difficult to calculate carrying capacities for human populations? A. Human populations have increased greatly over the last 50 years. B. Resources can be imported and exported and the level of technology can influence carrying capacity. C. Human populations can move more rapidly than the populations of other organisms. D. Pollution has damaged certain environments and reduced the carrying capacity. 14. Which of the following does not influence human carrying capacity? A. Birth rate B. Resource consumption rate C. Resource exploitation rate D. Level of medical technology 15. It is difficult to estimate accurately the global carrying capacity for the human population because B- key word technology A. population densities vary from country to country. B. technological developments may lead to changes in rates of resource consumption. C. birth and death rates in different countries vary greatly. D. humans produce more waste products than any other species. 9 16. The carrying capacity of a country depends mostly on A. the rate of increase of its population. B. the amount of insolation it receives. C. the quantity of its mineral resources. D. its state of economic and technological development. 17. Overpopulation occurs when A. the population level allows resources to be used sustainably, giving a good standard of living to all. B. there are too few people in an area to use the resources. C. resources are being used at a rate that allows them to be replaced for further harvesting. D. the available resources cannot support the number of people in the area at a reasonable standard of living. 18. Which combination of characteristics is most likely to be associated with a stable or falling human population? I. Increase in the proportion of women receiving higher education II. Increase in average income III. Decrease in the average age of marriage IV. Increase in birth rate V. Decrease in death rate VI. Increase in the average age of marriage A. I, II and III B. I, II and VI C. I, II, III and IV D. III, IV and V 10 19. These statements describe changes taking place in the populations of two different countries: • Country X begins to import a resource from another country. • Country Y increases its birth rate through a population policy. Which of the following predict the most likely effects these changes will have on the carrying capacity of each country? Increase in carrying capacity Decrease in carrying capacity No change in carrying capacity A. X Y — B. X — Y C. Y — X D. — X, Y — 11