The Journey of DNA 11-30–12-4
advertisement
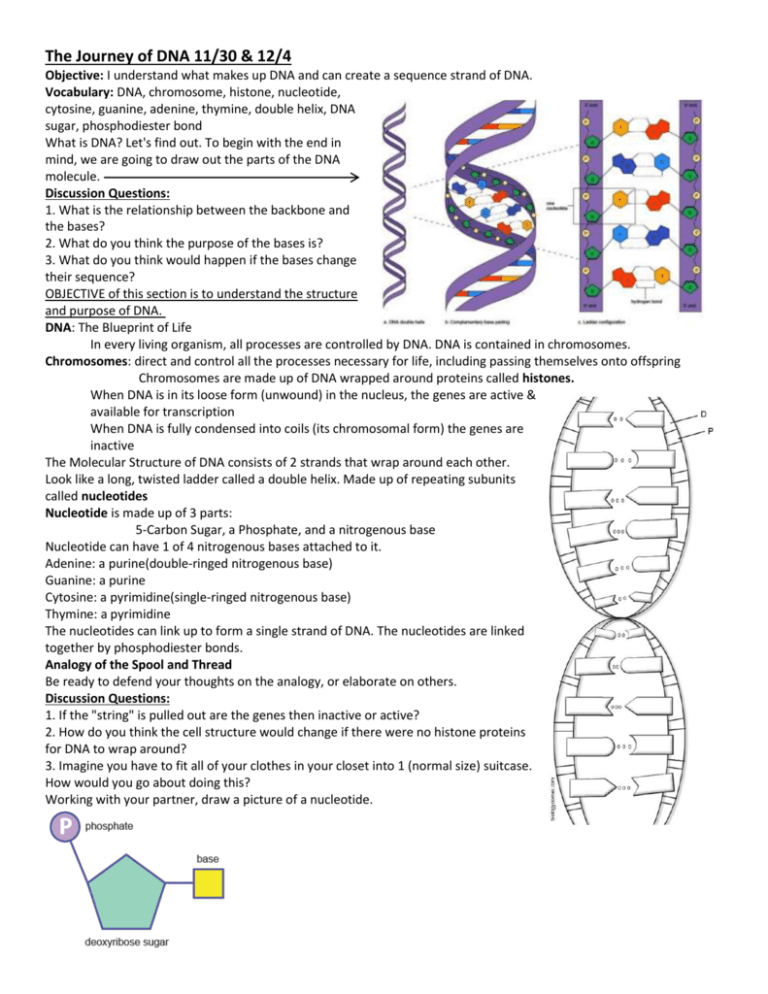
The Journey of DNA 11/30 & 12/4 Objective: I understand what makes up DNA and can create a sequence strand of DNA. Vocabulary: DNA, chromosome, histone, nucleotide, cytosine, guanine, adenine, thymine, double helix, DNA sugar, phosphodiester bond What is DNA? Let's find out. To begin with the end in mind, we are going to draw out the parts of the DNA molecule. Discussion Questions: 1. What is the relationship between the backbone and the bases? 2. What do you think the purpose of the bases is? 3. What do you think would happen if the bases change their sequence? OBJECTIVE of this section is to understand the structure and purpose of DNA. DNA: The Blueprint of Life In every living organism, all processes are controlled by DNA. DNA is contained in chromosomes. Chromosomes: direct and control all the processes necessary for life, including passing themselves onto offspring Chromosomes are made up of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones. When DNA is in its loose form (unwound) in the nucleus, the genes are active & available for transcription When DNA is fully condensed into coils (its chromosomal form) the genes are inactive The Molecular Structure of DNA consists of 2 strands that wrap around each other. Look like a long, twisted ladder called a double helix. Made up of repeating subunits called nucleotides Nucleotide is made up of 3 parts: 5-Carbon Sugar, a Phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Nucleotide can have 1 of 4 nitrogenous bases attached to it. Adenine: a purine(double-ringed nitrogenous base) Guanine: a purine Cytosine: a pyrimidine(single-ringed nitrogenous base) Thymine: a pyrimidine The nucleotides can link up to form a single strand of DNA. The nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester bonds. Analogy of the Spool and Thread Be ready to defend your thoughts on the analogy, or elaborate on others. Discussion Questions: 1. If the "string" is pulled out are the genes then inactive or active? 2. How do you think the cell structure would change if there were no histone proteins for DNA to wrap around? 3. Imagine you have to fit all of your clothes in your closet into 1 (normal size) suitcase. How would you go about doing this? Working with your partner, draw a picture of a nucleotide. Check for understanding 1. What are the 3 parts of the DNA molecule? a. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine d. Thymine and Cytosine 5. DNA is contained in b. Ribose, Adenine, Phosphate a. Histones c. Phosphate, Ribose, Base b. Chromosomes d. Base, Phosphate, Cytosine 2. What are the 2 pairs of bases in DNA? a. Adenine - Cytosine, Guanine Thymine b. Adenine - Thymine, Cytosine Guanine c. Adenine - Guanine, Cytosine Thymine d. Thymine - Cytosine, Guanine Adenine 3. Which bases are purines? a. Adenine and Guanine b. Adenine and Cytosine c. Adenine and Thymine d. Thymine and Cytosine 4. Which bases are pyrimidines? c. Nucleotides d. Spool 6. Chromosomes are made up of a. Histones and DNA b. DNA and nucleotides c. DNA and bases d. Histones and bases 7. What sugar is found in DNA? a. Adenosine b. Adenine c. Ribose d. Sucrose 8. What bonds are between bases in DNA holding the 2 strands together? a. Phosphodiester Bonds a. Adenine and Guanine b. Hydrogen Bonds b. Adenine and Cytosine c. Ionic Bonds c. Adenine and Thymine d. Covalent Bonds








