DNA Workshop : Worksheet KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

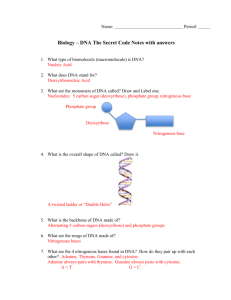
DNA Workshop : Worksheet KEY BASIC BACKGROUND – From reading and notes 1. DNA is a “macromolecule” or polymer, made up of many repeating monomers. Each monomer or building block is called a nucleotide. What three basic units make up a single nucleotide? Phosphate Group Sugar (Deoxyribose) Nitrogenous Base 2. All nucleotides are the same except for the type of base they attach to. There are four different nitrogenous (DNA) bases; name the four different nitrogenous bases: a) Adenine c) Cytosine b) Guanine d) Thymine 3. Which bases have double rings? Adenine &Guanine 4. What name is collectively given to any base that has two rings? PURINE 5. Bases complimentary pair up with other bases, but a given base can only bond up with its perfect match. Give the name of the bases that always match the base given below. a) Adenine : THYMINE b) Cytosine : GUANINE 6. What type of bond forms between two complimentary bases? HYDROGEN First Website : 1. What is the proper name of the spiral shape that DNA takes? DOUBLE HELIX 2. If you took a typical piece of DNA from a Eukaryotic Cell (animal, plant etc.) and it you built a model of it to the same scale as the image on the screen, how far would it stretch? Image Size would be 1600 km Actual Size : 5 cm 3. Give the correct term for the procedure where DNA copies itself. REPLICATION Second Website : 1. How many H- Bonds form between : A–T : TWO C – G : THREE * Click on the “Structure Of Molecule” to see the structure of DNA. 2. What is the size of the distance between turns of the Helix? * Hint: there are a thousand nanometers (nm) in a single micrometer (um), and a thousand (um) in one mm. 3.4 nm 0.0034 um 0.0000034 mm Part 2 : Gel Electrophoresis: Third Website 1. What do restriction enzymes do? They cut DNA at specific sequencing sites. 2. What size of DNA fragments tends to move most easily through the agarose? Small Charged 3. What type of charge do the fragments of DNA have? Slightly Negative 4. Why do scientists cover the gel with a nylon membrane? To have something they can handle and manipulate. 5. What special property of the probes allows scientists to detect where the DNA fragments are located? The probes are Radio-actively Labeled 6. Who committed this crime? HONEY Part 3 : Replication/Transcription/Translation http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/# 1. Give one example of a cell using DNA to make a proteins or new cells. Cells building enzymes, hair, fingernails, blood proteins, muscle repair, and growth. 2. Where in the cell do replication and transcription take place? In the NUCLEUS 3. Where in the cell does translation take place? In the cytoplasm at Ribosomes 4. After translation has taken place, list the names of the three amino acids that this strand of DNA coded for. (In their correct order) METHIONINE GLYCINE SERINE