Write
advertisement
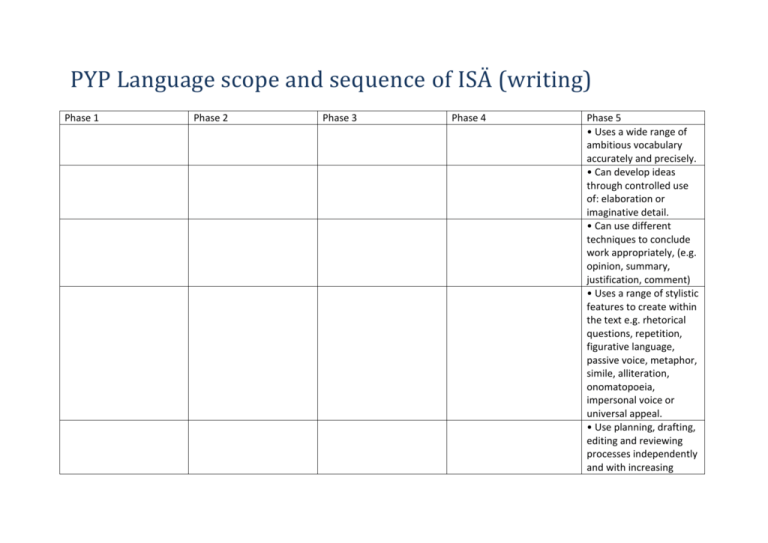
PYP Language scope and sequence of ISÄ (writing) Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 • Uses a wide range of ambitious vocabulary accurately and precisely. • Can develop ideas through controlled use of: elaboration or imaginative detail. • Can use different techniques to conclude work appropriately, (e.g. opinion, summary, justification, comment) • Uses a range of stylistic features to create within the text e.g. rhetorical questions, repetition, figurative language, passive voice, metaphor, simile, alliteration, onomatopoeia, impersonal voice or universal appeal. • Use planning, drafting, editing and reviewing processes independently and with increasing • Can extend sentences using a wider range of connectives to clarify relationships between points and ideas (e.g. when, because, if ,after, while, also as well) • Can use correct grammatical structures in sentences (nouns, verbs) • Organize ideas in a logical sequence for example, write simple narratives with a beginning, middle and end. • With teacher guidance, publish written work, in handwritten form or in digital format. • Use familiar aspects of written language with increasing confidence and accuracy, for example, spelling patterns, high frequency words, high interest words. Write engaging stories that have a recognizable and appropriate structure competence. • Identify and describe elements of a story – setting, plot, character, and theme. Have a fluent and legible style of handwriting and show competency in word processing Use standard spelling for most words and use appropriate resources to check spelling. • Can open and close writing in interesting, unusual or dramatic ways, when appropriate. • Edit and proofread their own and peers’ writing before completing a final copy. Use figurative language appropriately in writing (e.g. simile, metaphor, alliteration, idioms) • Write independently and with confidence, showing the development of their own voice and style . • Choose to publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format independently. Recognize and use the main parts of speech correctly (noun, verb, pronoun, adjective, adverb) Beginning to use some common spelling patterns. • Use increasingly accurate grammatical constructs Can make recognizable attempts at the spelling words not known, (most decodable without child’s help) Uses capital letters for beginning of sentences, names. • Use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example, Mind Maps®, storyboards Use appropriate punctuation and grammar (e.g. semicolons, colons, apostrophes, quotation marks) Edit and proofread their own and peers’ writing before completing a final copy. • Use feedback from teachers and other students to improve their writing. Use appropriate paragraphing. Revise writing to clarify ideas, provide examples, change sequence and to improve smooth flow of ideas. Use a variety of strategies for collecting and organizing ideas, details and information. Uses full stop when necessary. • Enjoy writing and value their own effort. • Can use adjectives and adverbs for description. • Participate in shared writing, observing the teacher’s writing and making suggestions. • Create illustrations to match their own written text. • Engage confidently with the process of writing. • Listen and respond to shared books (enlarged • Write an increasing number of frequently • Use a dictionary, a thesaurus and word banks Use a range of prewriting strategies. • Use a range of tools and techniques to produce written work that is attractively and effectively presented. • Locate, organize, synthesize and present written information obtained from a variety of valid sources. • Write using a range of text types in order to communicate effectively, for example, narrative, instructional, persuasive • Use written language as a means of reflecting on their own learning. • Adapt writing according to the audience and demonstrate the ability to engage and sustain the interest of the reader. • Vary sentence structure and length. texts), observing conventions of print, according to the language(s) of instruction • Show an awareness of sound–symbol relationships and begin to recognize the way that some familiar sounds can be recorded• Begin to discriminate Between letters/characters, numbers and symbols- • Illustrate their own writing and contribute to a class book or collection of published writing. Writes from left to right. used words or ideas independently. to extend their use of language. • Demonstrate an awareness of the conventions of written text, for example, sequence, spacing, directionality. • Write to communicate a message to a particular audience, for example, a news story, instructions, a fantasy story. • Proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvements. Use a range of models in writing: Narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository. • Demonstrate an increasing understanding of how grammar works. • Write about a range of topics for a variety of purposes, using literary forms and structures modeled by the teacher and/or encountered in reading. • Form letters/characters • Overtime, create conventionally and legibly, examples of different with an understanding as types of writing. to why this is important within a language community. Use knowledge of written code patterns to accurately spell highfrequency and familiar words. Write for a range of purposes, both creative and informative, using different types of structures and styles according to the purpose of the writing Show individuality and creativity in writing styles. • Use a dictionary, thesaurus, spellchecker confidently and effectively to check accuracy, broaden vocabulary and enrich their writing. • Use standard spelling for most words and use appropriate resources to check spelling • Participate in shared and • Write legibly and in a guided writing, observing consistent style. Plan, organize and complete writing • Use appropriate paragraphing to organize Leaves space between words the teacher’s model, asking questions and offering suggestions. • Illustrate their own writing and contribute to a class book or collection of published writing. Prints all letters lower case formations. • Discriminate between types of code, for example, letters, numbers, symbols, words/ characters. Prints all letters upper case formation with ascenders and decenders. • Connect written codes with the sounds of spoken language and reflect this understanding when recording ideas. projects of increasing length and complexity ideas • Can use interesting and varied word characters. Reread, edit and revise to improve their own writing, for example, content, language, organization.(Use appropriate writing process independently and confidently to communicate effectively and fluently.) • Can use the full range of punctuation, almost always accurately and precisely, including for sub- division, effect, listing, direct speech, parenthesis. • Is experimenting with a wide range of punctuation, although use may not be accurate (e.g. commas, inverted commas, exclamation marks and apostrophes. • Can use sentence punctuation accurately, full stops, capitals and question marks. Participate in an appropriate writing process( e.g. group discussions, brainstorming, webbing, planning, drafting, revising, editing) Write independently and with confidence, demonstrating a personal voice as a writer. • Can write neatly and accurately at speed, preferably in a joined style. • Can vary front for the effect or emphasis when appropriate(italic or capitalization)