ICP Background: Inductively Coupled Plasma is used to detect trace
advertisement

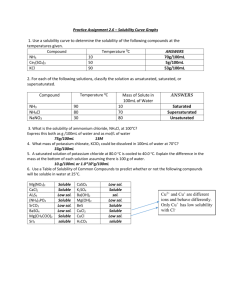
ICP Background: Inductively Coupled Plasma is used to detect trace metals in samples by using argon plasma. Wavelengths are created for each element. Purpose: Run zinc and copper through ICP using 10ppm, 20ppm, 30ppm, 40ppm, and 50ppm. Create calibration curves. Run samples of water. Method: -Prepare the five standards from 10 to 50ppm with a mixture of both copper and zinc in a 100 mL volumetric flask -Turn on the cooling system behind the ICP and allow to run for 15 minutes -Turn on Argon gas in gas room and on the benchtop -After 15 minutes turn on ICP on the computer screen -Pull the tubing so that blue and white tabs are in place and then tighten the tubing by locking the rollers in place -Open the ICP expert program -Select worksheet, new; name new file and select save -Select edit method tab -Click and drag elements that are being tested to the box below -Select the standards tab and enter standard concentrations -Exit screen and select yes to save -Click plasma on -Once flame is lit allow to warm up for 15 minutes -Put tubing in distilled water (blank) while waiting -Select sequence editor and select number of samples not including a blank -Check the ‘begin with calibration’ box and ensure the ‘include blank in calibration’ box is checked -Select the analysis tab -ensure all standards and samples are highlighted yellow and if not, click on the tube number to highlight them -Click green arrow to begin running samples -Follow on screen instructions -Be sure to rinse tubing in between each sample -Print results Data/Calculations: Standards made from stock solutions: 1000ppm stock 10ppm: (10ppm)(100mL) = (1000ppm)(1mL stock) 20ppm: (20ppm)(100mL) = (1000ppm)(2mL stock) 30ppm: (30ppm)(100mL) = (1000ppm)(3mL stock) 40ppm: (40ppm)(100mL) = (1000ppm)(4mL stock) 50ppm: (50ppm)(100mL) = (1000ppm)(5mL stock) Sample blank 1 2 3 4 5 sink bathroom fountain Cu Intensity 318.5 94619 204725 227579 396914 489760 717.54 462.85 1049.2 Zn Intensity 478.18 125606 264516 288172 492665 578092 693.25 660 1163.4 Results: We received acceptable results for this instrument. As the concentration increased the Intensities of both copper and zinc increased as well. Conclusion: Our experiment was very successful and we received very good results which helped us to understand how to use the instrument. In our unknown samples we were able to detect very low traces of both copper and zinc. AA Background: Atomic absorption is used to measure different metals in samples. Atoms in their gaseous state are used to analyze absorptions when exposed to light. Purpose: Create standards of both Zinc and Copper, from 10 to 50 ppm, and run on AA. Create calibration curves for each element using the data of the known concentrations. Method: -Prepare standards of both copper and zinc , 10ppm, 20ppm, 30ppm, 40ppm, 50ppm, and dilute with 100mL of distilled water -Turn on power switch on front of instrument -Turn on acetylene and compressed air in gas room and on benchtop -Turn on exhaust fan on the column, if not already on -Check to make sure all lamps of the AA are pushed in by lifting the AA lid -Open WinLab32 software -Click lamps and turn on by highlighting the row and clicking the on/off button to turn green -Allow lamp to warm up for ten minutes -To create a method, click Wrkspc icon -Select ‘Man.flm’ -Click File drop down menu and select ‘New’ then ‘Method’ -Select element from drop down menu, check ‘Recommended values’ and select ‘Ok’ -Select ‘Spectrometer’ tab in method editor and check for correct element -Select ‘Calibration’ tab and enter blank and standard information -Click ‘Equations and Units’ tab and select equation for calibration curve and plug in concentration units -Click ‘SamInfo’ icon and enter relevant information into sample information editor window and then close window -To ignite the flame, select flame control window and check the ‘safety interlocks’ box -When a green check is seen, click ‘On’ to ignite the flame -Select manual analysis control window and place probe in black solution and click ‘analyze blank’ -Place probe in first standard and click ‘analyze standard’ and repeat for all standards -Place probe in sample and click ‘analyze sample’ and repeat for all samples -Once completed aspirate DI water for several minutes to rinse system -To shut down, click ‘lamps’ icon and turn them all off by clicking ‘on/off’ -Select flame control window and click ‘bleed gases’ -When finished, check valves in gas room to make sure they are under 15psi and then they can be turned off -Turn off gases on benchtop Data: Stock = 1000ppm 10 ppm: (10ppm)( 100ml)= (1000ppm)(1ml stock) 20 ppm: (20ppm)( 100ml)= (1000ppm)(2ml stock) 30 ppm: (30ppm)( 100ml)= (1000ppm)(3ml stock) 40 ppm: (40ppm)(100ml)= (1000ppm)(4ml stock) 50 ppm: (50ppm)( 100ml)= (1000ppm)(5ml stock) Copper blank 10 20 30 40 0 0.4082 0.7111 1.1077 1.3764 50 1.5492 Zinc blank 10 20 30 40 50 0 1.1726 1.5774 1.6247 1.6427 1.6727 Results: The results for the calibration curve of copper came out very well. But the Zinc calibration was not as good. The data point for 10ppm was much lower than expected. Conclusion: The experiment was very successful and I learned how to use the AA. Although our results were not perfect we still learned how to use the instrument. To better this experiment we would run the zinc samples again.