1-Changes in Earth
advertisement

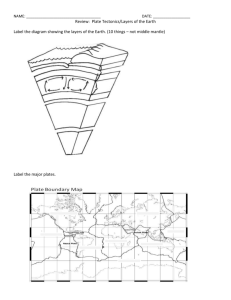
Unit D: Cycles in Earth and in space Chapter 1: Movement of Earth’s crust The Earth’s layers: 1-Crust 2-Mantle 3-Outer core 4-Inner core Earth’s plates: -Earth’s crust and uppermost mantle are divided into sections, called plates. -Plates are blocks of crust and upper mantle rock that fit together like puzzle pieces. -The theory that the Earth’s plates are always moving is called plate tectonics. 1-Earthquakes An Earthquake is a vibration in Earth’s crust, caused by the release of energy at a fault A fault is a break in the crust where rock moves. The point inside Earth where an Earthquake begins is called the focus. The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake is the epicenter. Seismograph readings can be used to calculate an earthquake’s strength. The Richter scale estimates the amount of energy released by an earthquake. 2-Volcanoes A Volcanoes is a mountain formed by lava and ash. Magma is liquid rock inside a volcano. Lava is liquid rock (magma) that flows out of a volcano. Match the clue to the simple machine. a break in Earth’s crust molten rock that flows out of a vent and arrives at Earth’s surface the point on Earth’s surface that is directly above where an earthquake’s energy is released molten rock under Earth’s surface A. lava B. fault C. magma D. epicenter Complete the following: (fault-volcano-magma-Earthquake) 1-Molten rock beneath Earth’s surface is _______. 2-A movement of the ground, caused by the sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust, is an _______. 3-A break in Earth’s crust is called a _______. 4-A mountain made of lava and ash is a _______. Choose the best answer 1-The theory that the plates of Earth are always moving is called: a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 2-The point inside Earth where an earthquake begins is a-epicenter b-focus c-Fault d-plate tectonics 3-A break in the Earth’s crust where rocks can move is called a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 4-The point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake is a-epicenter b-focus c-Fault d-plate tectonics 5-which of these is being released as rocks in a fault slide past one another? a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 6-Which instrument is used to detect an earthquake a-barometer b-hygrometer c-seismograph d-thermograph 7-which of these is being released as rocks in a fault slide past one another? a-earthquake b-Volcano c-Fault d-plate tectonics 8-During an earthquake which of these will suffer the most damage? a-epicenter b-focus c-Fault d-plate tectonics Use this space to complete the graphic organizer. Label the layers of Earth 1-………………………………………………………….. 2-…………………………………………………………. 3-…………………………………………………………. 4-…………………………………………………………. Complete each sentence with the correct term from the box. (Earthquake-focus-epicenter) 1-The people in the town felt the trembling of the . 2-The buildings at the of the earthquake suffered the worst damage. 3-The is the point where the earthquake begins. Answer the following: Using the data in the chart, identify the largest earthquake. Which earthquake of 1999 had the greatest magnitude? ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Use this space to complete the graphic organizer.