Standard 5 Core 40 (DNA) ECA Review
advertisement

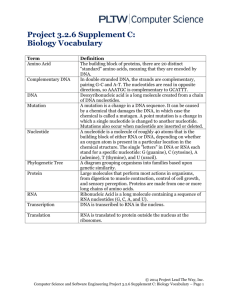
Standard 5 Core 40 (DNA) ECA Review Standard 5: Molecular Basis of Heredity B.5.1 Describe the relationship between chromosomes and DNA along with their basic structure and function. B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in the regions of DNA molecules called genes. B.5.3 Describe the process by which DNA directs the production of protein within a cell. B.5.4 Explain how the unique shape and activity of each protein is determined by the sequence of its amino acids B.5.5 Understand that proteins are responsible for the observable traits of an organism and for most of the functions within an organism. B.5.6 Recognize that traits can be structural, physiological or behavioral and can include readily observable characteristics at the organismal level or less recognizable features at the molecular and cellular level. Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which series is arranged in order from largest to smallest in size? a. Chromosome, nucleus, cell, DNA, nucleotide b. Cell, nucleus, chromosome, DNA, nucleotide c. Nucleotide, chromosome, cell, DNA, nucleus d. Cell, nucleotide, nucleus, DNA, chromosome 2. Adenine and guanine are: a. Double-ringed purines c. Double-ringed pyrimidines b. Single-ringed purines d. single-ringed pyrimidines 3. Which statement is true? a. Hydrogen bonding of cytosine to guanine is an example of complementary base pairing b. Adenine always pairs up with guanine in DNA, and cytosine always teams up with thymine c. Each of the four nucleotides in a DNA molecule has the same nitrogen-containing base. d. When adenine base pairs with thymine, they are linked by three hydrogen bonds. 4. How are genes and proteins related? a. Gene codes for a protein c. its replication b. Proteins contains amino acids that code for genes d. protein is a part of a gene 5. DNA polymerase a. Is an enzyme c. adds new nucleotides to a strand b. Unzips the DNA molecule d. all of the above 6. How many different types of RNA molecules are needed to make protein? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 7. Termination of protein translation is due to a. lack of amino acids c. lack of messenger RNA b. AUG/start codon d. stop/UAA codon 8. The best adjective to describe DNA replication is a. Democratic c. nondisruptive b. Conservative d. semiconservative 9. There are how many different kinds of amino acids in proteins? a. 2 b. 20 c. 200 d. 2000 10. The RNA molecule is made up of how many strands? a. 2 b. 3 c. 1 d. 5 11. One strand of DNA could be as long as a football field if it were stretched out lengthwise. One of the factors allowing DNA to fit inside the nucleus of a cell is its ability to: a. Break apart into separate genes c. coil tightly around associated proteins b. Extend to form very long, thin molecules d. denature form the effect of enzymes 12. In the bonding of nitrogenous bases, a. adenine is paired with cytosine. b. adenine is paired with guanine. 13. The DNA molecule could be compared to a a. hair pin. b. ladder c. key 14. Which of the following statements is true? a. b. c. d. e. c. cytosine is paired with thymine. d. guanine is paired with cytosine. d. globular mass e. flat plate The hydrogen bonding of cytosine to guanine is an example of complementary base pairing. Adenine always pairs up with guanine in DNA, and cytosine always teams up with thymine. Each of the four nucleotides in a DNA molecule has the same nitrogen-containing base. When adenine base pairs with thymine, they are linked by three hydrogen bonds. In the DNA of all species, the amount of purines never equals the amount of pyrimidines. 15. This is a 3-base sequence of mRNA that codes for a single amino acid a. Anticodon c. gene b. Protein d. codon 16. What is the form of RNA that carries the code from the DNA to the site where the protein is assembled a. Messenger RNA c. ribosomal RNA b. Nuclear RNA d. structural RNA 17. One-half of DNA molecules is CGATCCTA what would the complementary DNA read? a. GCTAGGAT c. LOLBRBIDK b. GUTUCUA d. TAGCTTTCG 18. A gene mutation a. Is a change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA b. May be caused by environmental agents c. May arise spontaneously d. All of these 19. The flow of information from DNA to protein a. is reversible. d. was discovered by Gregor Mendel b. involves transcription only. e. uses forms of RNA in the process. c. explains evolution. 20. The nitrogenous base found in DNA but not in RNA is a. adenine. b.cytosine c. guanine d. uracil e. thymine 21. Transcription a. involves both strands of DNA as templates. b. uses the enzyme DNA polymerase. c. results in a double-stranded end product. d. produces three different types of RNA molecules. e. all of these Short Answer: 22. A point mutation does NOT change the amino acid sequence of a protein is known as a silent mutation. Explain why a silent mutation might not affect the protein of which it codes. 23. Explain why a mutation in a lung cell would NOT be passed on to offspring. 24. Starting with the mRNA leaving the nucleus, list and describe four major steps involved in protein synthesis. 25. Use the chart to answer the following questions. Below is an RNA sequence consisting of three amino acids and a stop codon. Above each amino acid and the stop codon is the list of bases that code for that amino acid. a. What will be the fourth codon in the new sequence? b. What amino acid will be coded for by the fourth codon in the new sequence? c. What name is given to this type of mutation?