Past exam questions- Art and architecture of the Roman Empire
advertisement

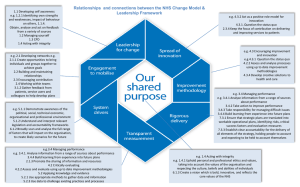
Past exam questions- Art and architecture of the Roman Empire The Arch of Titus not only honours a specific event, but links human and divine elements in the portrayal of Titus. Analyse how these human and divine elements have been integrated into this relief sculpture. In your answer, you must: • identify the human and divine characters present in this scene, and the historical event commemorated by this relief • analyse in detail in what ways the sculptor has linked human and divine elements in this scene, and why he might have chosen to do so. In both classical and modern times, the Colosseum has stood as one of the most distinctive buildings in Rome. Discuss the aesthetic appeal of the exterior of the building and the ways in which the design of the building as a whole served a propagandist purpose. In your answer, you must: • describe the exterior features of the building as it appeared in the first century ce • analyse in detail at least TWO ways in which the exterior had aesthetic appeal • analyse in detail the ways in which the design of the Colosseum glorified the city of Rome and the imperial family. Reproduction F(i) is a ground plan of Hadrian’s Island Villa (sometimes known as the Maritime Theatre). Reproduction F(ii) is a photograph of part of the remains of that structure. It has sometimes been observed that Hadrian’s Villa at Tivoli is like a microcosm of the Roman Empire, and that the Island Villa is a microcosm of Hadrian’s Villa as a whole. Discuss in what ways the Island Villa reflects the design, location, and purpose of Hadrian’s Villa at Tivoli as a whole. Patricians were the chief patrons of the veristic style of portraiture. Analyse in detail with supporting evidence: The messages that the sculptor is trying to convey about the social standing and the character of the patrician, and the ways in which he uses the veristic style of portraiture to deliver these messages The messages that the sculptor is trying to convey about the patrician’s relationship with his ancestors, and the methods he uses to deliver these messages The Pantheon is considered an architectural masterpiece, partly because of its beauty and partly because of its structural integrity. Analyse in detail with supporting evidence: The features that make the interior of this building aesthetically pleasing The features that make this building structurally sound The two mosaics shown in these reproductions were found in Hadrian’s Villa at Tivoli. Analyse in detail with supporting evidence: The ways in which these two mosaics contrast in their treatment of subject matter and theme The ways in which these two mosaics are stylistically similar The most important examples of the Constantian decoration on the Arch of Constantine are the reliefs that wrap around the middle of the arch, below the roundels. Analyse in detail with supporting evidence: The events commemorated by these Constantian reliefs The ways in which Constantine is glorifies in these reliefs, including specific reference to the two scenes shown in reproductions F (ii) and F (iii). “The origin of the Roman theatre can be traces directly back to a Greek model, although the Romans made several alterations to the traditional plan”. Analyse in detail and with supporting evidence: The ways in which the design of the Theatre at Lepcis Magna incorporates features of Greek and Roman innovation The ways in which the design and architectural features of this building reflect its function as an entertainment venue Bathing occupied a central position in the social life of the Romans, and provincial towns like Lepcis Magna had substantial bathing complexes which were show-pieces for the community and the empire as a whole. Analyse in detail with supporting evidence: The ways in which the layout and design of Hadrian’s Baths reflect their function as a bathing complex as well as a venue for exercising and socialising The ways in which Hadrian’s Baths at Lepcis Magna provide a vehicle for Roman propaganda