Ch.11-1 Packet
advertisement

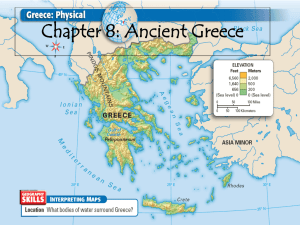
Name ______________________________________________________________ Hour _____________ Date _________________________ Chapter 11: Ancient Greece Lesson 1: The Geography of Greece - p.354 -359 Main Ideas Geography: Rugged mountains divided Greece into many regions. Geography: The sea linked the regions of Greece to each other and to foreign regions. Sea trade became common. Culture: Trade helped the early Greeks develop a sophisticated culture. Vocabulary Term Definition Other Representation (Icon, Picture, Example, Sentence, etc.) Application: What learning target does this term connect to? Why? peninsula Peloponnesus isthmus Phoenician alphabet 1 Geography Shapes Ancient Greek Life - p.355-356 1. The mainland of Greece sticks out into the ________________________________. It is a ___________________, a body of land that has water on three sides. A _________________ of water almost divides the Greek ______________________ into two. The southern tip forms a second _____________________ called the ___________________________________. A narrow strip of land called an _______________________ links the __________________________________ to the rest of Greece. 2. What landform covers much of Greece? What are some of the effects of this on daily life, trade, travel, development of cities? 3. Describe the climate in Greece. 4. Where was most farmland in Greece located? Why was this where they would farm? 5. Describe the life of a landowner in Greece. 6. How did Greeks get more farmland? 7. How did the Greeks make the best use of the land that they did have for farming? (Hint: See Geography box on p. 356.) 8. What resources did Greeks have? What resources did they lack? 2 Trade Helps Greece Prosper – p.357 9. Just as rivers influenced other ancient cultures, the __________ influenced Greece. Greece has a long ______________________, and most places in Greece are less than __________ miles from the coast. In fact, many cities were built directly on ______________________. 10. What seas made up the “highways of water” that linked most parts of Greece to each other? 11. Describe war ships and sailing ships in Greece. 12. What food from the seas was an important part of the Greek diet? Besides eating it, what else did they do with it? 13. What items did the Greek trade and trade for? Who did they trade with? The Earliest Greeks – p.358 - 359 14. What was the name of the first Greek civilization? Describe the government and culture. 15. What happened after the Mycenaean civilization fell? 3 16. What did the Greeks learn from the Phoenicians? 17. How does the Greek alphabet affect us today? 18. What did the Greeks learn from other peoples? Why It Matters Now: The Greek alphabet influenced the development of all Western alphabets, including the English alphabet. Geography Practice (Use map on next page) Answer the questions below using the map on the NEXT page of the packet. 1. By what geographic feature are most of the Mycenaean cities located? 2. Judging from the location of the cities, which sea did the Mycenaeans sail on most often? 3. Draw a line from Mycenae to each of the other major cities shown on the map. 4. How would you describe the location of Mycenae compared to the other major cities? 5. Notice that Mycenaean civilization includes some islands. How do you think their culture spread to those lands? 4 Geography Practice Mycenaean Greece, about 1300 B.C. In about 2000 B.C., a Greek-speaking people moved from the north onto the Greek peninsula. These people built towns that were protected by strong walls. The larger cities had palaces. Each one was ruled by a king. Each king commanded a force of warriors who made up the noble class of society. The strongest of these fortified cities was called Mycenae. It was located on the Peloponnesus, the southern peninsula of Greece. Because of this city, the civilization developed by these earliest Greeks is called Mycenaean. The Mycenaean Greeks were traders. Their society also had many fine artisans who would work with gold, silver, and bronze to make weapons and beautiful objects. Sometime around 1200 B.C., most of the Mycenaean cities were destroyed, perhaps by invaders. Civilization did not return to Greece for hundreds of years. 5 Reteaching Activity Find the name or term in the lettered column that best matches the description in the first numbered column. Then write the letter of your answer in the blank. 1. ________ A body of land that has water on three sides 2. ________ The southern top of Greece, which is connected to the rest of Greece by a narrow strip of land 3. ________ The large sea that is South of Greece 4. ________ The small sea that is East of Greece 5. ________ One of the surplus goods that Greece traded for products such as timber, animal hides, and nuts 6. ________ The most important city of the first Greek civilization 7. ________ A narrow strip of land that connects two larger masses of land 8. ________ A trading people who lived on the coast of the Eastern Mediterranean and who influenced early Greeks 9. ________ The set of symbols that the Greeks developed into their own system of writing. 10. ________ Metal objects invented in Anatolia about 650 B.C. for use in trade A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. Athens Peloponnesus olive oil Phoenicians coins peninsula Aegean isthmus Mycenae alphabet Mediterranean grain 6