File

Themes of Classical Greece
Early Greeks – origins and influence of geography
Cultural and Scientific Advancements
Athens VS Sparta – different cultures within Greece
Conflicts
Legacy
Origins of
Classical Greek
Civilization
MAIN IDEA
The roots of Greek culture are based on the interactions of the Mycenaean, Minoan, and Dorian cultures.
WHY IT MATTERS NOW
The seeds of much of
Western cultural heritage were planted during this time period.
Influence of
Geography
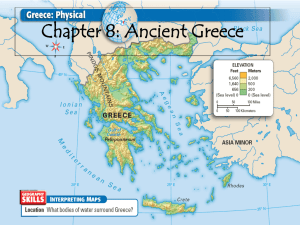
Looking at the map, how do you think geography played a role in the development of
Classical Greek
Civilization?
Geography
Mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Mediterranean Sea
2000 islands in the Ionian and
Aegean Seas
Greece was surrounded by water
Geography – Importance of the Sea
Dependant on the seas
Rarely had to travel more than 85 miles to get to the coast
Important travel and trade routes – enabled the Greeks to get much needed natural resources that they lacked (i.e. timber, metals, and farmland)
Enabled the Greeks to become the most skilled seafarers of the time
Geography – Difficulties of the Land
Greece is roughly 75% rugged mountains
Mountains acts as natural borders between regions within Greece - led to the development of small communities rather than a single government
Travel overland was difficult
Stony landscape – very little was suitable for farming
There were small fertile valleys for small scale farming, but the Greek landscape could never support a very large population – never reached more than a few million people
Landscape encouraged the Greeks to colonize elsewhere
Geography - Climate
Moderate climate (48 in the
Winter; 80 in the Summer) supported an outdoor lifestyle
Huge influence on culture – outdoor public events
Notes on Greek Geography
Surrounded by water – travel and trade
Rugged terrain – isolated villages and limited farming
Warm climate
Limitations forced Greeks to expand empire
Mycenaeans – The First Greeks
Indo-Europeans that migrated to Greece in
2000 BCE
Main city was in
Mycenae
Civilization flourished from 1600-1100 BCE
Dominated Greece through conquest – warring aristocracy
Mycenaean Culture
Written language
Elaborate burial rituals
Crops – grain, olives and grapes
Huge textile industry
Art – jewelry, frescoes, architecture, advanced weapons
Mycenaean Civilization Notes
From Mycenae, Southern
Greece
Dominated Greece 1600-
1100 BCE
Militant
Minoans – Other Early Greeks
Occupied the island of Crete and came into contact with the Mycenaeans around 1500
BCE
Influenced the Mycenaeans
Seaborne trade
Much more “civilized” than the Mycenaeans
Language, art, architecture, technology
Minoan Notes
Trade
Writing
Influenced Greek religion, art, politics and literature
Mycenaeans and Minoans - Notes
Set the groundwork for modern Western civilizations
And then came the Dorians…
After the collapse of the Mycenaean and Minoan civilizations, the Dorians moved in… they almost ruined a good thing.
Far less advanced
Economy and trade collapsed
Lost written language
No written records
Even though they weren’t too sharp, the Dorians played a huge role in the development of Greek culture
Loss of written language led to an oral tradition – epic poems
Most Greek myths/gods stem from epic poems
Dorians - Notes
Far less advanced
Lost written language, few records