Ancient Greece: Geography, Minoans, Mycenaeans, City-States
advertisement

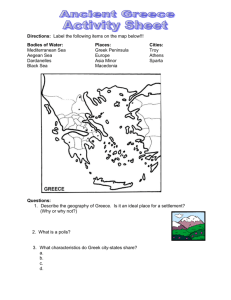
Chapter 8: Ancient Greece Main Idea 1: Geography helped shape early Greek civilizations. • Mountains cover much of Greece, so contact with other villages was difficult. • People created their own governments and ways of life. • People settled in the flat areas along the coast and in river valleys. • Because travel was so difficult inland (from isolation), Greeks turned to the seas on all sides. • They became skilled shipbuilders and sailors. • The sea became a source of food as well as a way of trading with other communities. • They also exchanged ideas with other cultures. What is the main peninsula in Greece called? Main Idea 2: Trading cultures developed in the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations. • • • • Minoans They spent much of their time at sea, trading in the Mediterranean. Ships carried goods such as wood, olive oil, and pottery all around the eastern Mediterranean. They became the victims of a huge volcano that erupted north of Crete (ruining its crops), which led to the fall of Minoan Civilization. They were not considered to be Greek, since they didn’t speak Greek. • • • • • • • Mycenaeans They were the first people to be considered Greek. They lived inland and built fortresses. They were more violent in their trade. They took over Crete and became the major traders in the eastern Mediterranean. They developed colonies in northern Greece and Italy, from which they shipped goods around the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Mycenaeans attacked the city of Troy and the civilization began to fall. At the same time, earthquakes destroyed many cities including Mycenae , leading Greece into what is known as the Dark Age. What is a ______ ? • a traditional or legendary story, usually concerning some being or hero or event, with or without a determinable basis of fact or a natural explanation, especially one that is concerned with deities or demigods and explains some practice, rite, or phenomenon of nature. • The Minotaur – Greek legend tells of a horrifying half-man, half-bull creature known as the Minotaur that lived in a maze beneath the palace of Knossos What is a _______ ? • a nonhistorical OR unverifiable story handed down by tradition from earlier times and popularly accepted as historical. • The Minoan civilization may have inspired stories about Atlantis, a legendary island kingdom that supposedly disappeared beneath waves caused by earthquakes. The Greek philosopher Plato wrote about Atlantis. He also may have gotten the story from ancient Egyptian records that report the Thera eruption. • Page 234-235 Check Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. On what geographic feature is Greece located? Why was travel difficult in Greece? Where was the Minoan civilization located? How was the decline of the Minoans and Mycenaeans similar? Why did the Mycenaeans put such importance on building powerful fortresses? Where was the Knossos Temple located? In what direction would the Mycenaeans have had to travel to reach the Minoan civilization? How might the Minoans’ civilization location provide them with protection? Main Idea 3: The Greeks created city-states for protection and security. • During the Dark Ages, the Greeks started joining together in small groups for protection. • These groups set up independent city-states. The Greek word for city-state is polis. • The creation of city-states marks the beginning of Greece’s classical age, an age marked by great achievements. Why was this time in Greece called the Dark Ages? Main Idea 3: The Greeks created city-states for protection and security. • A city-state was usually built around a strong fortress on top of a high hill called an acropolis. • The town around the acropolis was surrounded by walls for protection. People no longer had to fear raiders. • Life in the city focused on the marketplace, or agora. • The city-state became the foundation for Greek civilization and gave the Greeks an identity. Not everyone lived inside the city walls (like farmers), but at the time of war, women, children and the elderly would gather inside the city walls. Acropolis Check Questions • Log-in to Socrative Student • Type in the Room # • Only use your first and last name for question #1, no nicknames Check Questions • What is a classical age? • Why did Greeks decide to establish colonies? • How did city walls and acropolises benefit Greek city-states?