Instructional Programs for ELLs
advertisement
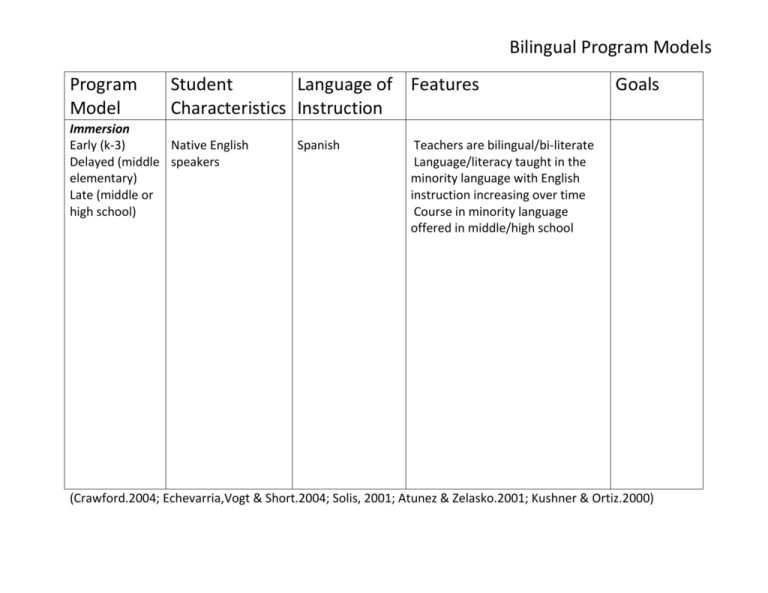
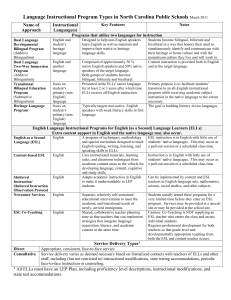
Bilingual Program Models Program Model Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Immersion Early (k-3) Native English Delayed (middle speakers elementary) Late (middle or high school) Spanish Goals Teachers are bilingual/bi-literate Language/literacy taught in the minority language with English instruction increasing over time Course in minority language offered in middle/high school (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Two-Way Dual Immersion Dual Language Two-way Immersion Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Goals Balanced, preferably 50% English speakers and 50% from the same target language group Bilingualism/biliteracy English speakers are taught another language Speakers of other languages are taught English Teachers are bilingual/bi-literate The two languages are given equal status in schools (e.g., materials Positive crossare available in both languages, cultural communications in both) interactions Course in minority language offered in middle/high school 90% minority language, 10% English in the early grades 50% minority language, 50% English as students get older (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Developmental Maintenance Late-exit Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Goals Most students are ELLs from the same language group Bilingualism/biliteracy Native Language English Teachers are bilingual/bi-literate Native Language development Acculturation Academic skills taught in the native language Structured ESL program Support for native language development continues even after the student is considered English proficient (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Transitional Early-exit Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Most students are ELLs from the same language group Native Language English Goals Teachers are bilingual/bi-literate English Language Majority of instruction in K-1 in the proficiency native language including native language development and Native language academic skill instruction development but only until Structured ESL program students can be transitioned to ELS instruction rapidly increases English with the goal of moving to Englishonly instruction as quickly as Exit to possible mainstream classes by 2nd or 3rd grade Assimilation (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Submersion Sink or swim Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Students are in English general education classrooms with a diverse range of students (e.g., native speakers of English, other ELLs, and those with varying degrees of proficiency in either or both languages) Goals Most teachers are monolingual; if English they are bilingual they provide proficiency some native language support (e.g., translation) Assimilation ELLs receive the same instruction as native English speakers There are no systematic attempts to teach ESL or to make instruction understandable to the ELLs (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model English as a second language (ESL) Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction All students are ELLs and typically represent multiple language groups English Goals Most teachers are monolingual; if English they are bilingual they provide proficiency some native language support (e.g., translation) Assimilation Full day self-contained classes or used in conjunction with other program models Focus depends on students’ oral proficiency and academic levels (e.g., conversational, academic, content-based, sheltered) (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Content based ESL Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Goals All students are ELLs and typically represent multiple language groups English proficiency associated with content/subject English Mainstream and ESL teachers are monolingual; if they are bilingual they provide some native language support (e.g., translation) Designed to develop academic Assimilation English and to prepare students for subject/content instruction Is submersion + content-based ESL if students are in mainstream classes with teachers who do not modify for ELLs (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000) Bilingual Program Models Program Model Sheltered English Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English Structured Immersion Student Language of Features Characteristics Instruction Students are from same language group in classes offered specifically for ESL students or ESL students are integrated into mainstream classes taught by teachers with ESL training Intended for students with developing English proficiency English Goals Mainstream and ESL teachers are Content monolingual; if they are bilingual knowledge and they provide some native language skills support (e.g., translation) Assimilation Teachers have content and ESL training Sheltered instruction strategies are used to make content understandable Students are provided access to content courses (e.g., science, social studies) and generally follow scope and sequence of mainstream class Is submersion + content-based ESL if students in mainstream classes with teachers who do not modify for ELLs (Crawford.2004; Echevarria,Vogt & Short.2004; Solis, 2001; Atunez & Zelasko.2001; Kushner & Ortiz.2000)