DNA/RNA - High School Science Help
advertisement

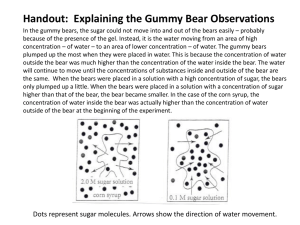
DNA/RNA Figure 13–10 1. What process is illustrated in the diagram above? 2. Identify Structure C in diagram above. 3. Which labeled structure is a codon? 4. What is the relationship between codons and anticodons? Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow. Black Bear Sightings are on the Rise Black bears are the largest mammals native to Maryland. Adults typically weigh between 150 and 400 pounds. Their color can range from black to brown to cinnamon. They have a tan muzzle and may have some white on their chest. Black bears have a short, bobbed tail and small, rounded ears. They live mostly in thick forested areas in Maryland. Black bears are shy, solitary animals. They require a lot of space for their home range. Adult black bears can have a home range of about 15 to 25 square miles. When the land was being settled, the black bear’s habitat was cleared for farms and villages. Because settlers misunderstood bears and felt threatened by them, bears were killed in large numbers. As a result, black bears were soon found only in small numbers and only in the westernmost part of the state. In 1956 there were only about 12 black bears in the whole state. When the black bear population was studied in 2000, as many as 437 bears were estimated to live in Maryland. Black bears eat a lot of different foods. They will eat whatever is easy to get. Their favorite natural foods include plants, berries, fruits, acorns, insects, roots, and DNA/RNA grasses. They may also eat reptiles, amphibians, fish, and dead animals. If available, black bears will eat non-natural foods associated with humans, such as garbage, bird seed, pet food, and agricultural crops like corn. Black bears will only come near a home if there is something to attract them, such as food. Once a bear finds available food, it will likely return again and again. Both black bears and humans feel threatened when confronted with one another. When threatened, bears often display unusual behaviors, such as hitting the ground with its paws, charging only to stop several feet from the threat, or standing upright on its hind legs. Since humans usually perceive these behaviors as being aggressive, black bears are once again being viewed as a problem. 5. What is the ecological role of the black bear? 6. Recent increases in bear-human interactions in the westernmost part of Maryland are causing serious problems. Identify the most likely cause for the increased interactions. 7. What does structure 2 in the diagram represent? 8. In what part of the cell is structure 1 produced? 9. The process shown in the diagram occurs in what cellular structure? DNA/RNA Figure 13–9 10. From which labeled structure in 13.9 is structure D made? Identify that labeled structure. 11. Identify structure F in Figure 13.9. What does it specify? 12. What is structure E in Figure 13.9? What does it specify? Figure 12–12 13. In Figure 12.12, what do the A, T, C, and G stand for? 14. In Figure 12.12, what percentage of thymine would you expect in yeast? Show your work. 15. Approximately what percentage of adenine would you expect to find in herring in Figure 12.12? Show your work. 16. If the level of thymine in humans were 34% instead of 29.4, would you expect the levels of guanine and cytosine to rise or fall, compared to the values in the table in Figure 12.12? DNA/RNA 17. Sequence the following terms from largest to smallest. Chromosome, nucleotide, DNA, gene A B C 18. If the nucleotide shown belongs to a RNA molecule, the structure labeled C could be any nitrogenous base except for what? 19. If the nucleotide show belongs to a DNA molecule, the structure labeled B would be what?