Osmosis & Diffusion: Gummy Bear Experiment Explained
advertisement
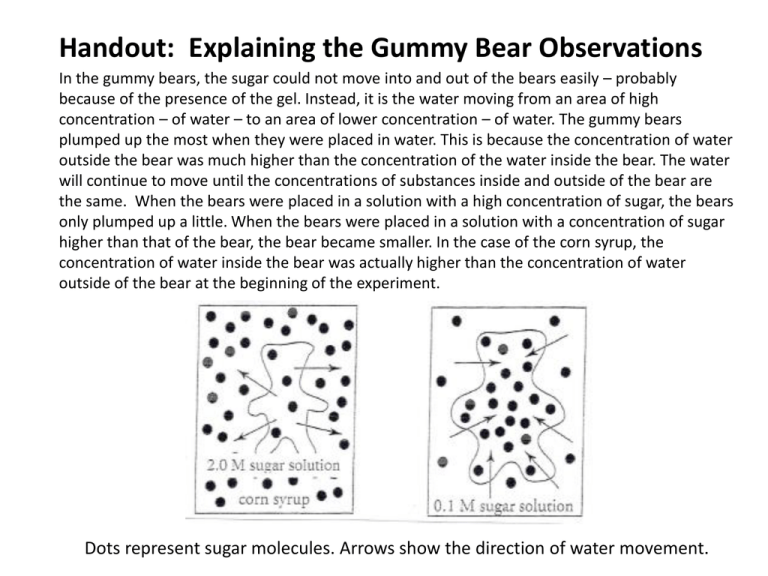
Handout: Explaining the Gummy Bear Observations In the gummy bears, the sugar could not move into and out of the bears easily – probably because of the presence of the gel. Instead, it is the water moving from an area of high concentration – of water – to an area of lower concentration – of water. The gummy bears plumped up the most when they were placed in water. This is because the concentration of water outside the bear was much higher than the concentration of the water inside the bear. The water will continue to move until the concentrations of substances inside and outside of the bear are the same. When the bears were placed in a solution with a high concentration of sugar, the bears only plumped up a little. When the bears were placed in a solution with a concentration of sugar higher than that of the bear, the bear became smaller. In the case of the corn syrup, the concentration of water inside the bear was actually higher than the concentration of water outside of the bear at the beginning of the experiment. Dots represent sugar molecules. Arrows show the direction of water movement. Handout: Osmosis / Diffusion • Osmosis is the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water potential (low solute concentration) to an area of low water potential (high solute concentration). • Osmosis is a passive process, like diffusion which describes the spread of particles through random motion from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. • Net movement of solvent is from the less-concentrated (hypotonic) to the more-concentrated (hypertonic) solution, which tends to reduce the difference in concentrations. • The osmotic pressure is defined to be the pressure required to maintain an equilibrium, with no net movement of solvent. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity.