Quantitative vs. Qualitative Data Comparison
advertisement
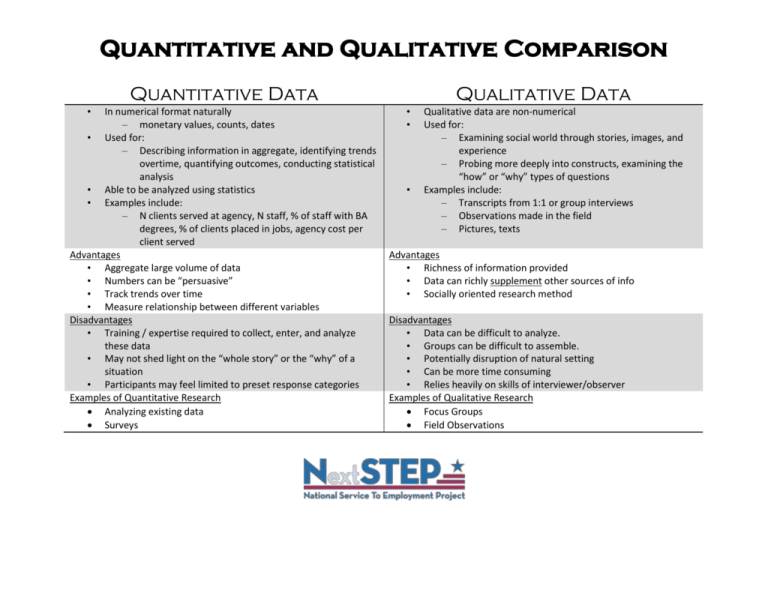
Quantitative and Qualitative Comparison Quantitative Data • In numerical format naturally – monetary values, counts, dates • Used for: – Describing information in aggregate, identifying trends overtime, quantifying outcomes, conducting statistical analysis • Able to be analyzed using statistics • Examples include: – N clients served at agency, N staff, % of staff with BA degrees, % of clients placed in jobs, agency cost per client served Advantages • Aggregate large volume of data • Numbers can be “persuasive” • Track trends over time • Measure relationship between different variables Disadvantages • Training / expertise required to collect, enter, and analyze these data • May not shed light on the “whole story” or the “why” of a situation • Participants may feel limited to preset response categories Examples of Quantitative Research Analyzing existing data Surveys Qualitative Data • • • Qualitative data are non-numerical Used for: – Examining social world through stories, images, and experience – Probing more deeply into constructs, examining the “how” or “why” types of questions Examples include: – Transcripts from 1:1 or group interviews – Observations made in the field – Pictures, texts Advantages • Richness of information provided • Data can richly supplement other sources of info • Socially oriented research method Disadvantages • Data can be difficult to analyze. • Groups can be difficult to assemble. • Potentially disruption of natural setting • Can be more time consuming • Relies heavily on skills of interviewer/observer Examples of Qualitative Research Focus Groups Field Observations











